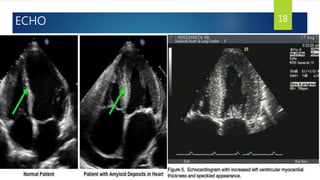
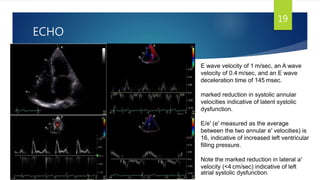
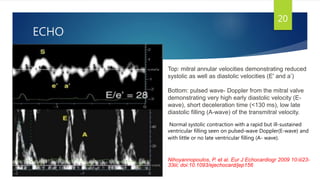
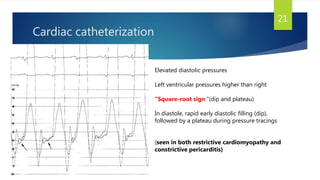
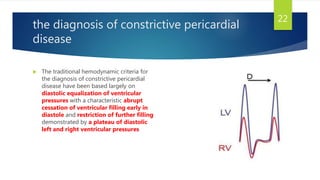
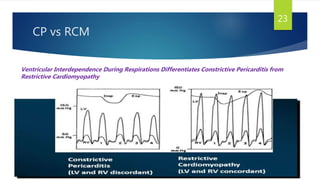
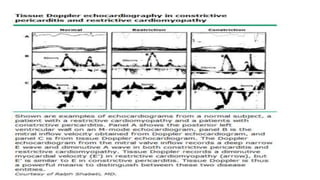
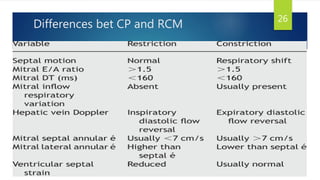
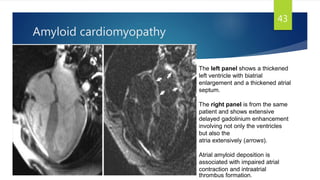
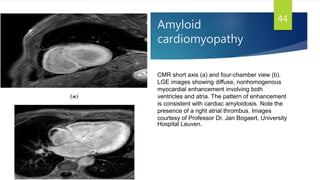
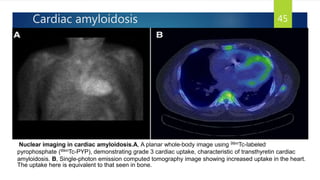
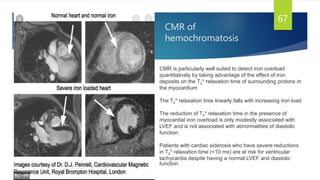
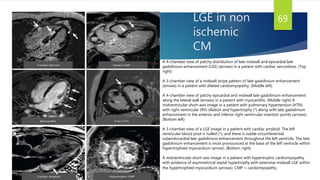
This document provides information on restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM), including its definition, classification, etiology, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Some key points:
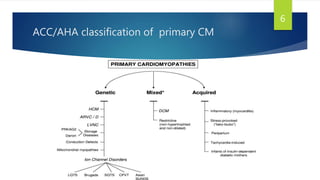
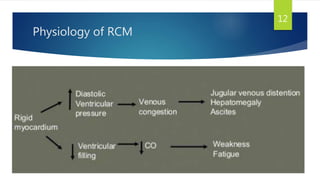
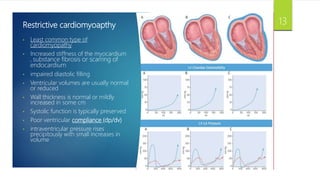
- RCM is characterized by diastolic dysfunction with a stiffened myocardium that impairs ventricular filling. It is usually not associated with ventricular dilation or hypertrophy.
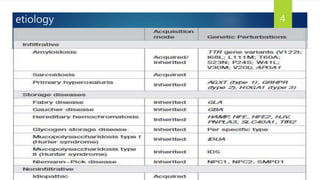
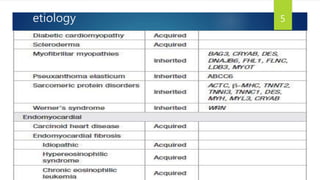
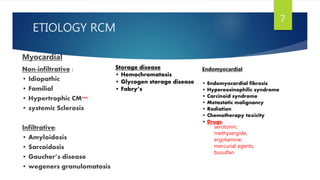
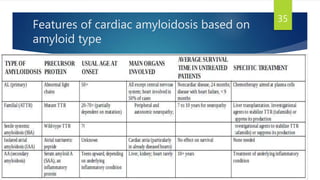
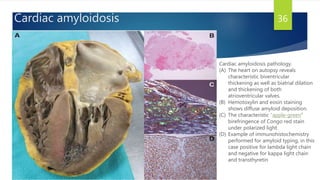
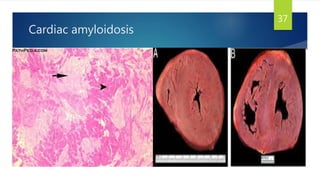
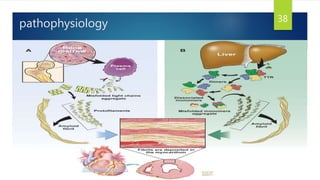
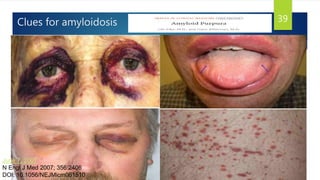
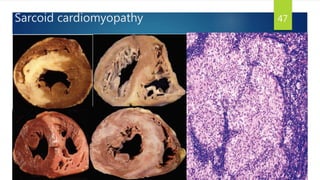
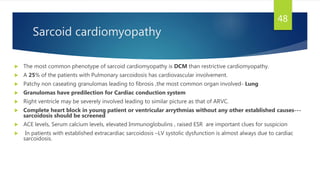
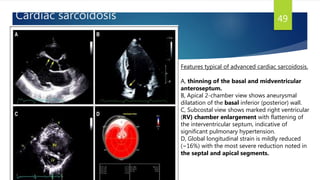
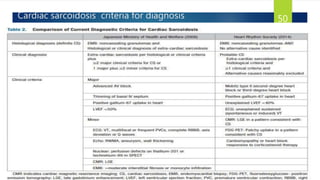
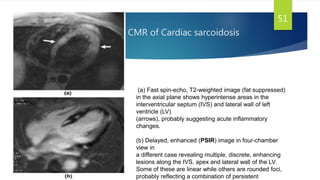
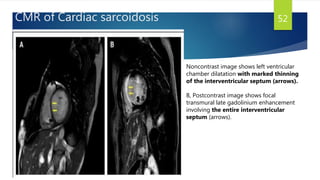
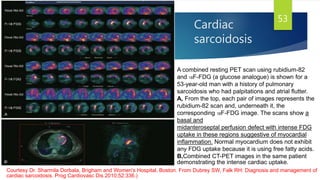
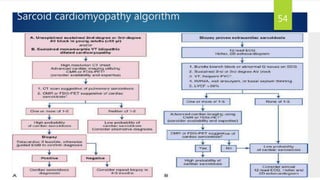
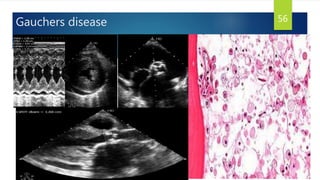
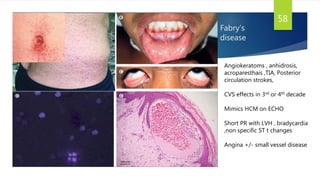
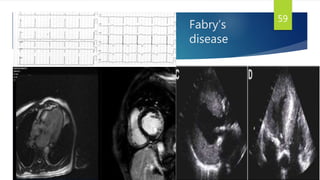
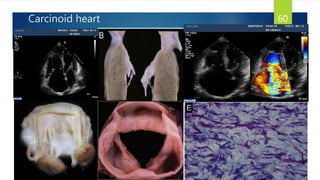
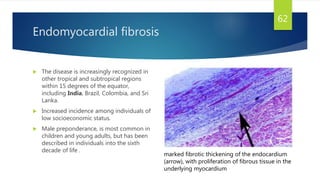
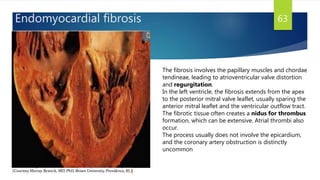
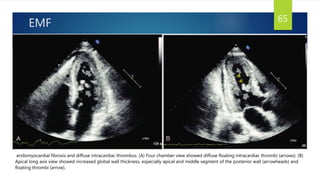
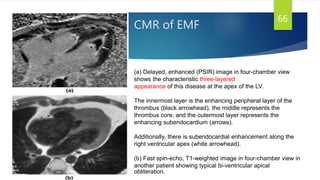
- Causes include infiltrative diseases of the myocardium (e.g. amyloidosis, sarcoidosis), endomyocardial fibrosis, and genetic/familial factors.
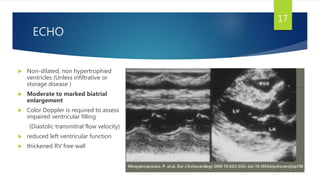
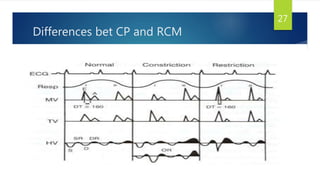
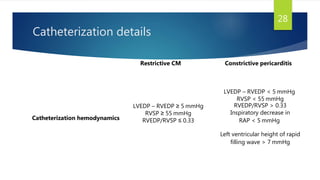
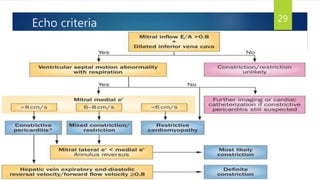
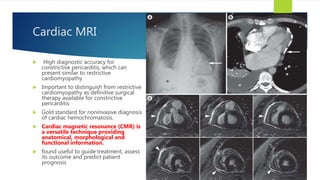
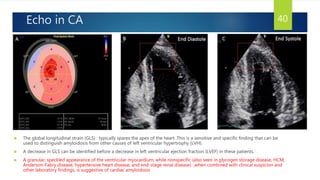
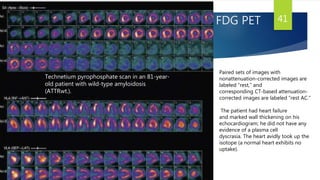
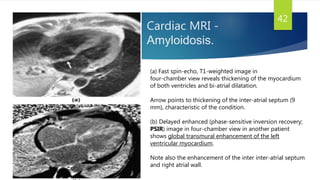
- Symptoms are related to reduced cardiac output and include dyspnea, fatigue, arrhythmias. Diagnosis involves echocardiogram, cardiac catheterization and MRI to evaluate