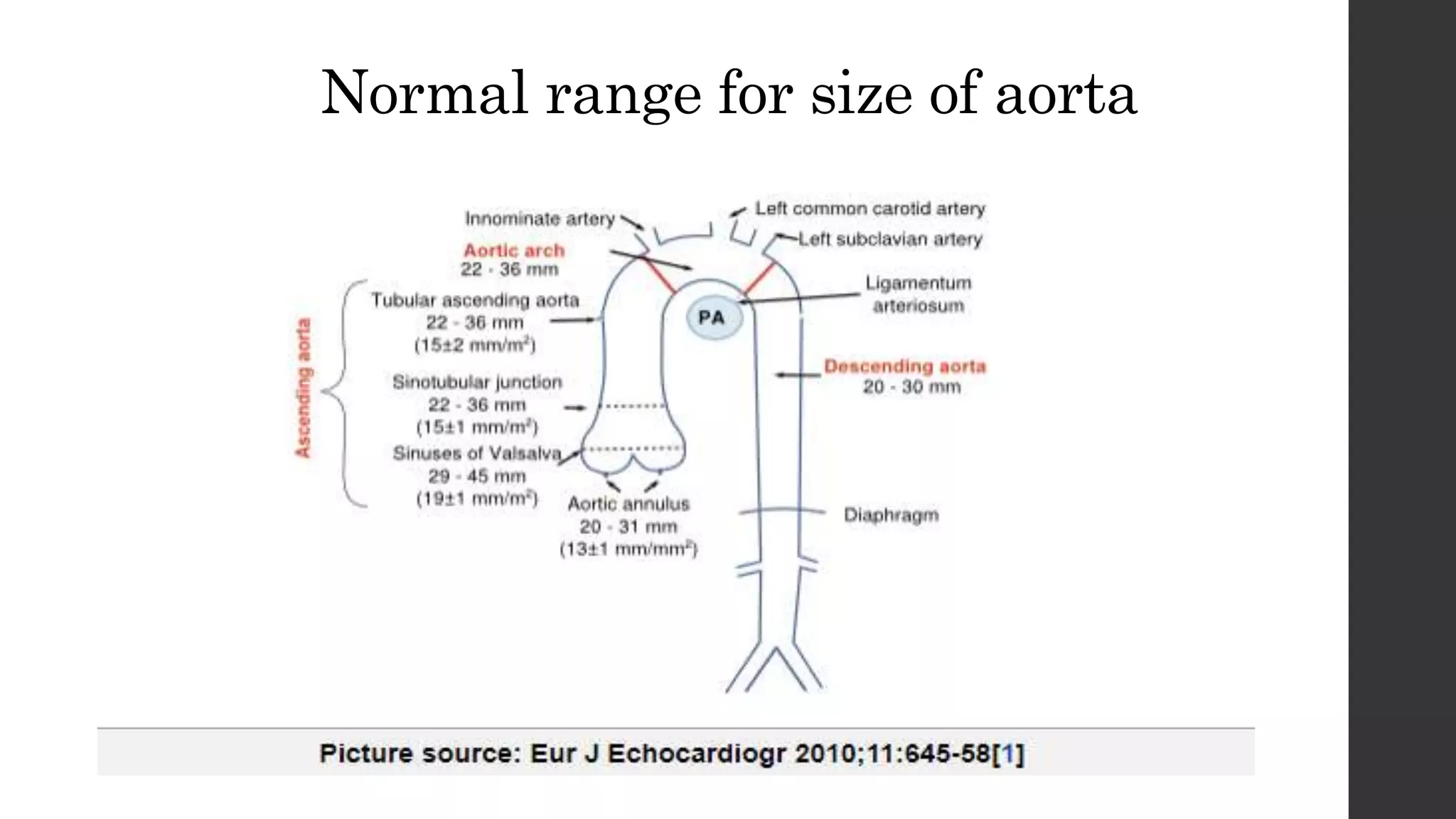
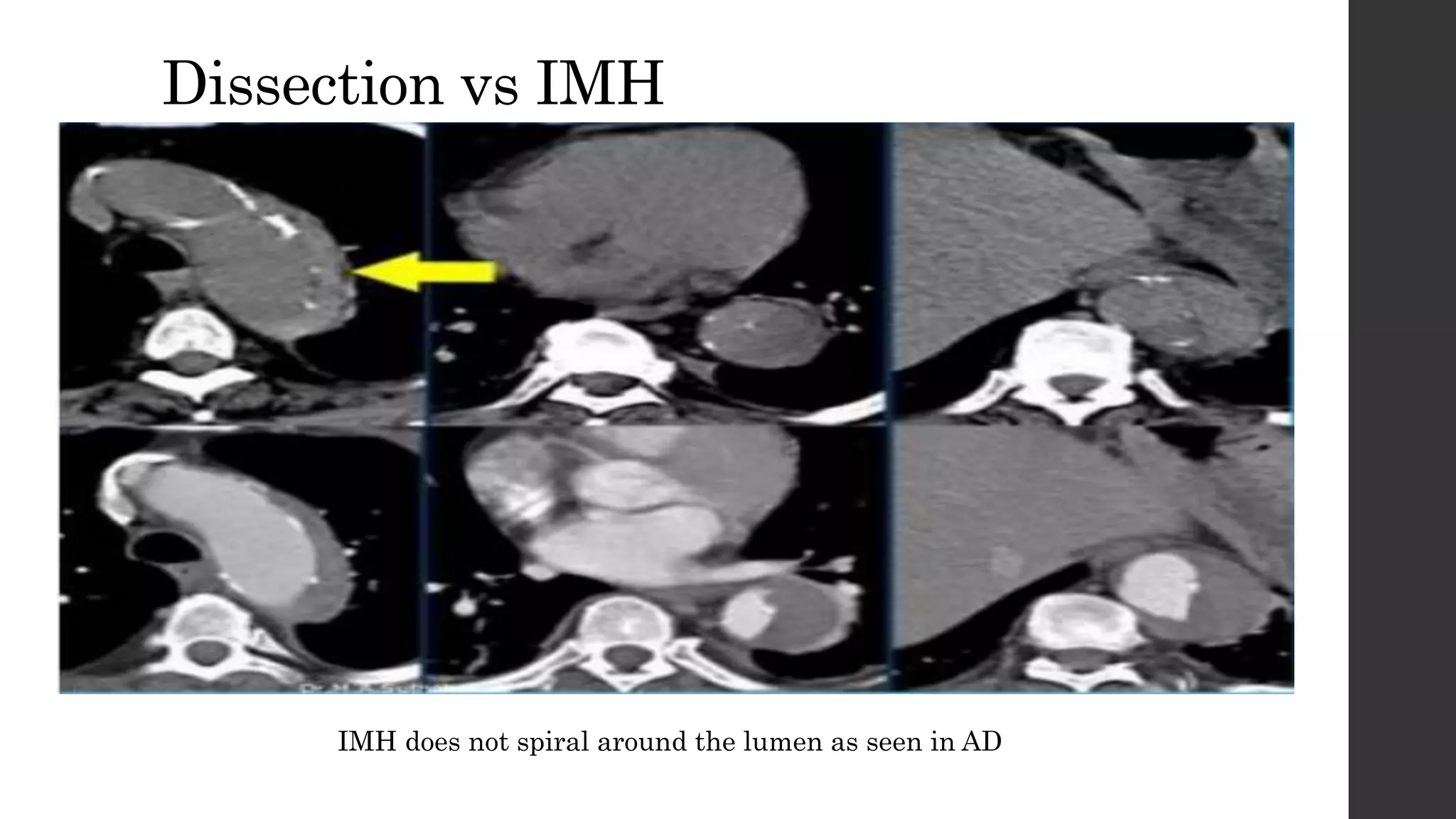
This document discusses acute aortic syndrome (AAS), which includes acute aortic dissection, intramural hematoma, and penetrating atherosclerotic ulcer. AAS is caused by disruption of the aortic wall layers from tears or ulcers, allowing blood to track within the layers. The most common type is aortic dissection, where blood passes through a tear separating the vessel layers. Presenting symptoms typically include sudden severe chest or back pain. Diagnosis involves imaging like CECT, MRI, or TEE to identify abnormalities. Prognosis depends on factors like involvement of the ascending aorta and complications. Classification systems differentiate type A dissections involving the ascending aorta from type B.