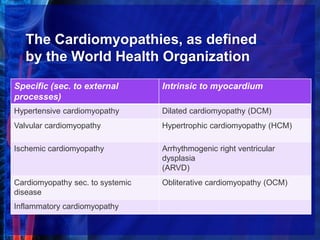
Cardiomyopathies are structural and functional abnormalities of the heart muscle that are not explained by coronary artery disease or abnormal loading. The main types are dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Dilated cardiomyopathy is characterized by enlarged heart chambers and poor contraction. Causes include viruses, toxins, inherited factors, and metabolic issues. Treatment focuses on managing heart failure symptoms. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy causes thickened heart muscle and outflow tract obstruction. Restrictive cardiomyopathy results in stiff heart muscles and high filling pressures. Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy replaces the right ventricle with scar tissue.