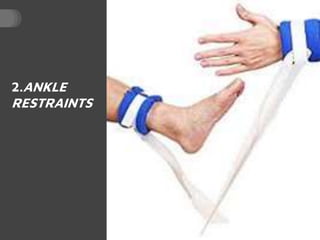
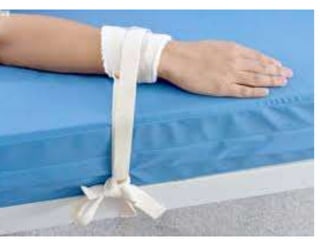
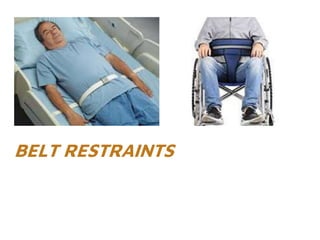
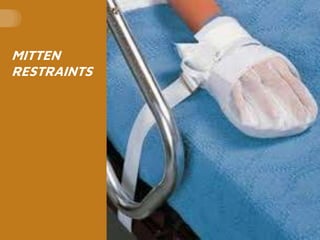
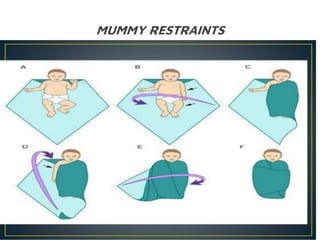
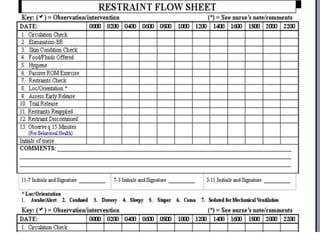
The document provides guidelines on the use of physical and chemical restraints in patients, detailing types such as belt, extremity, and elbow restraints, as well as medications used for sedation. It emphasizes the importance of patient safety, informed consent, and the need for regular assessment and reassessment to prevent complications. Additionally, it outlines the potential complications arising from restraint use, including pressure ulcers and changes in mental status.