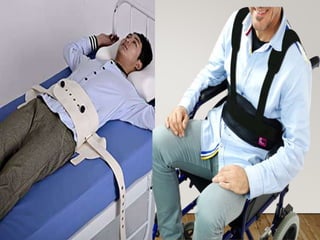
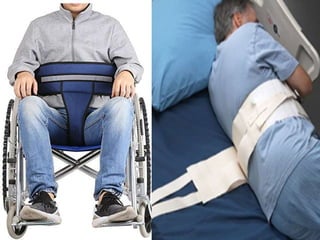
This document discusses restraints used in healthcare settings. It defines restraints as intentional restrictions of voluntary movement or behavior. Restraints are used to ensure safety during exams/procedures, protect from injury, and maintain prescribed positions. They include physical, environmental, and chemical methods. The document outlines principles of restraint use, types of restraints, risks, guidelines, and the nurse's role in monitoring patients and ensuring comfort, safety, and proper documentation when restraints are employed.