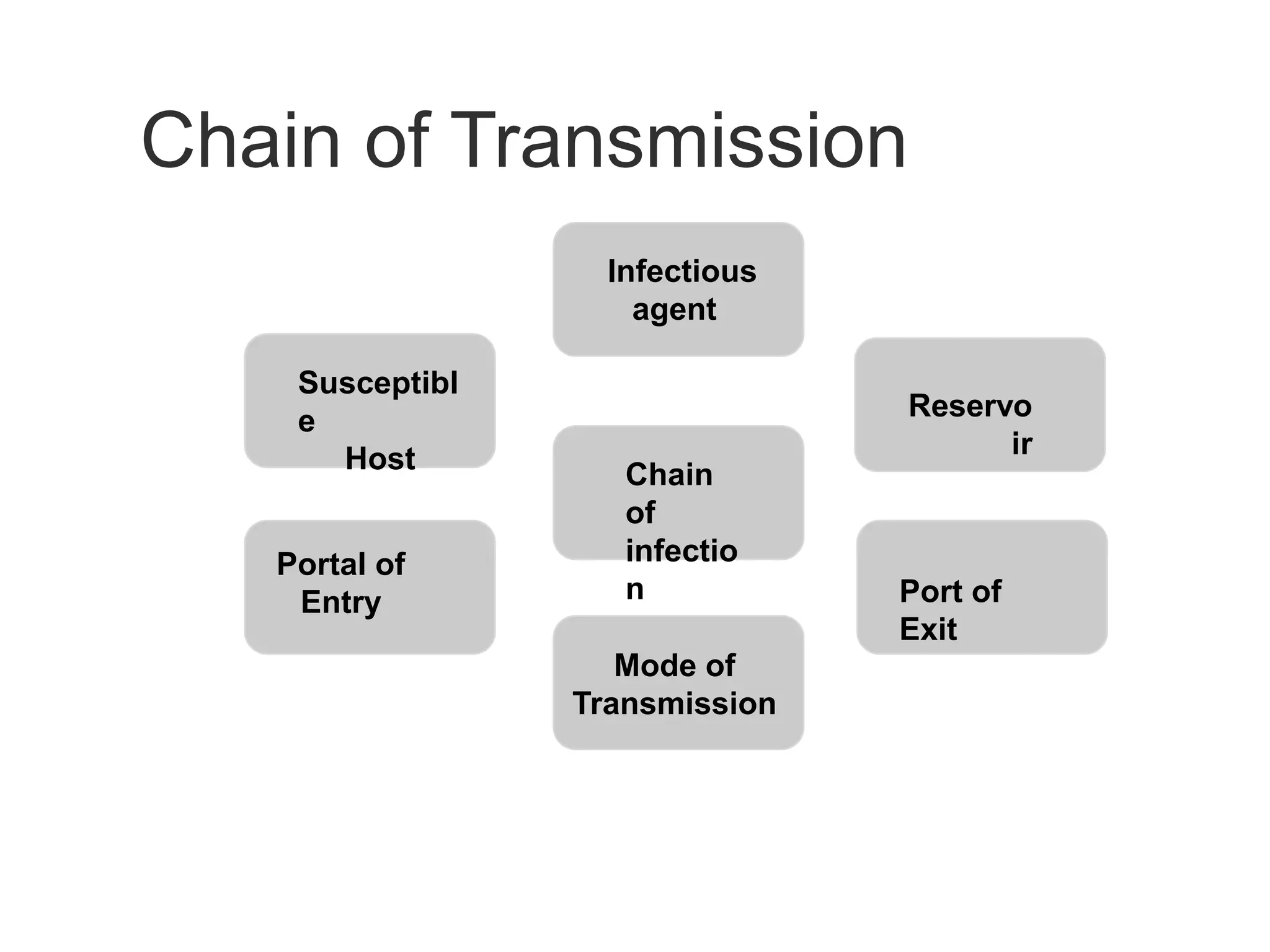
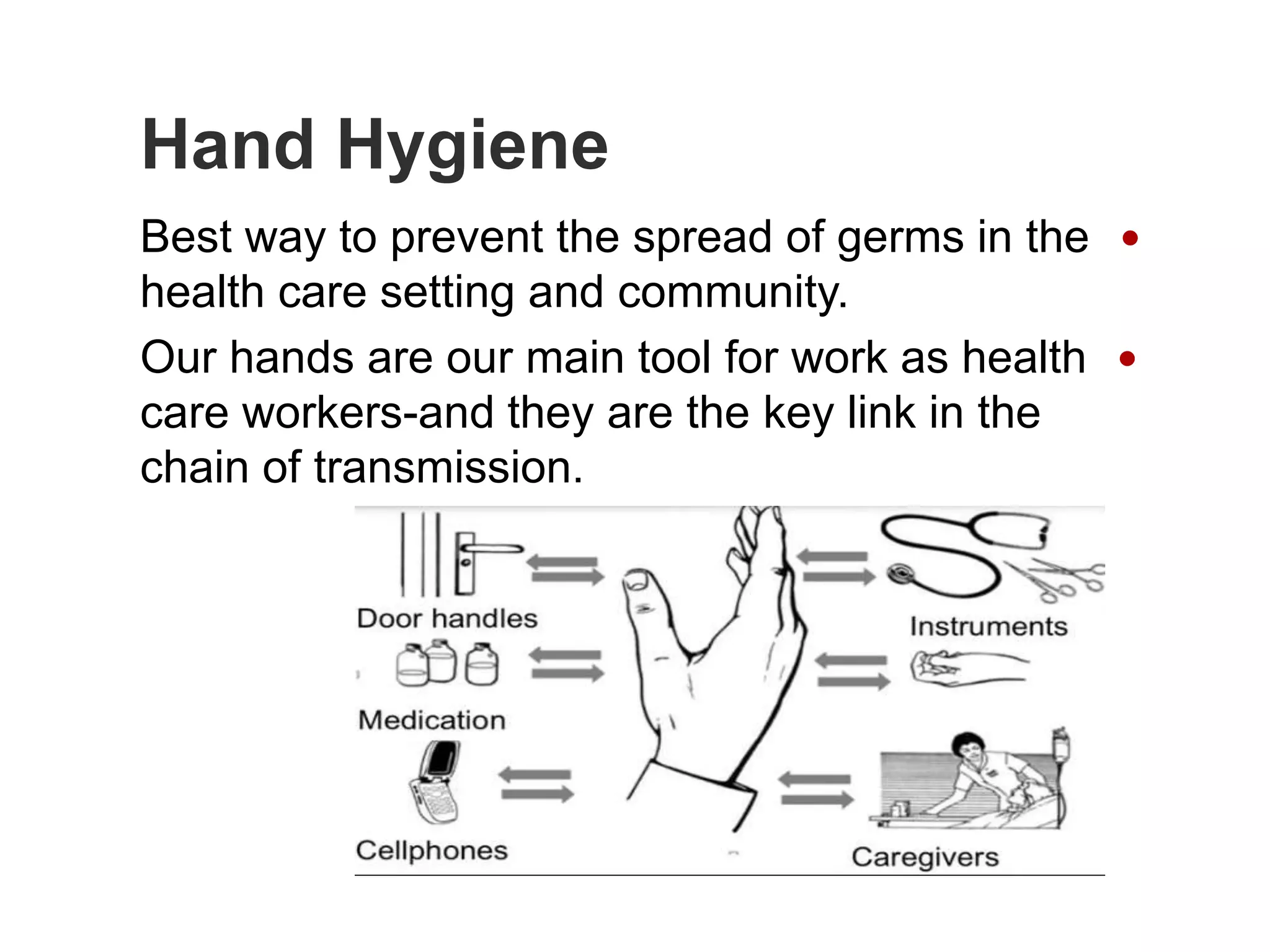
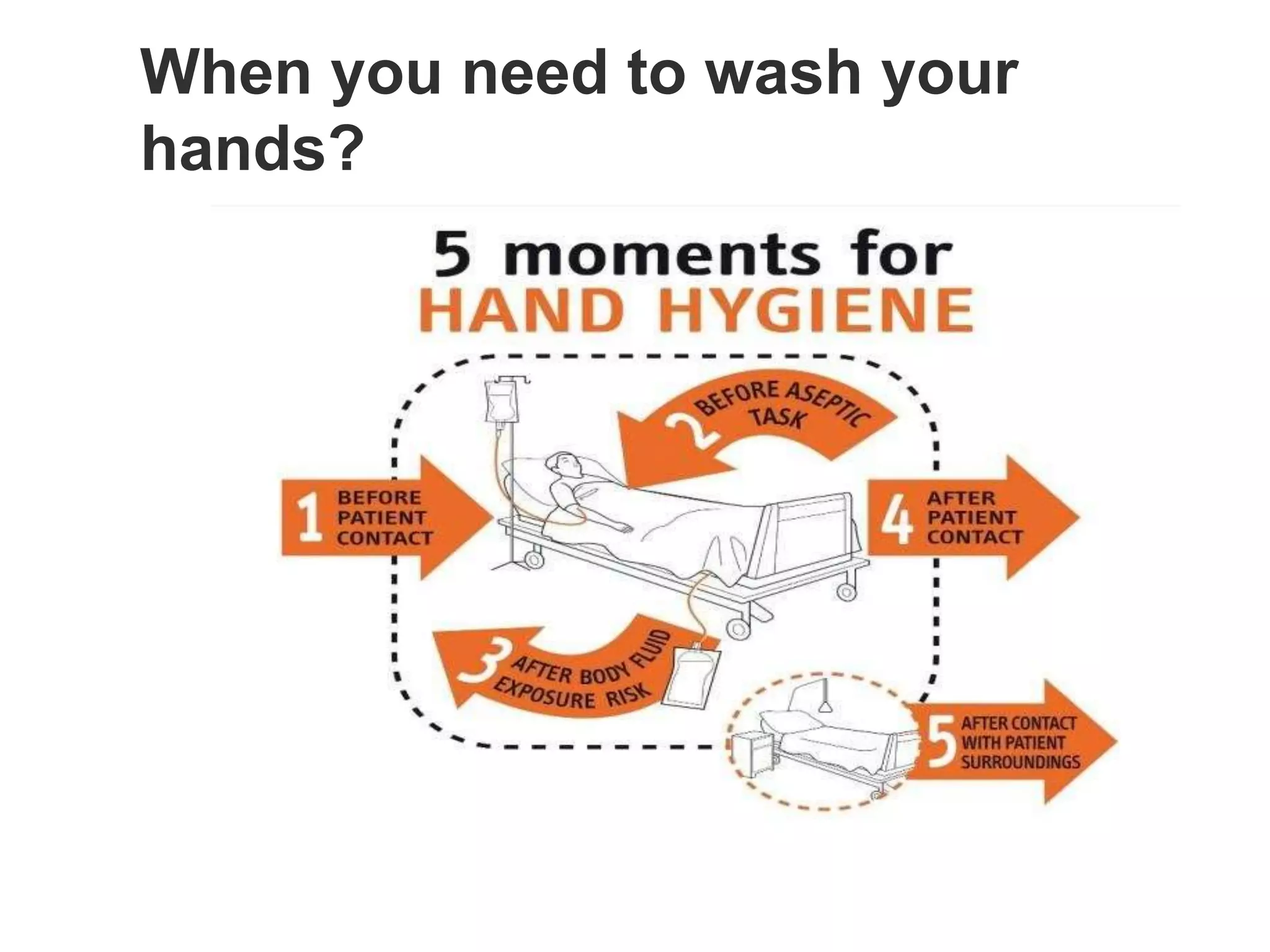
The document provides guidance on infection prevention and control (IPC) strategies for COVID-19 recommended by the WHO. It outlines standard IPC precautions that should be applied to all patients, including hand hygiene, respiratory etiquette, and appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE) based on risk assessment. The WHO recommends IPC strategies for health care settings to prevent or limit COVID-19 transmission, including applying standard precautions, early recognition and source control, implementing additional precautions for suspected cases, and administrative controls.