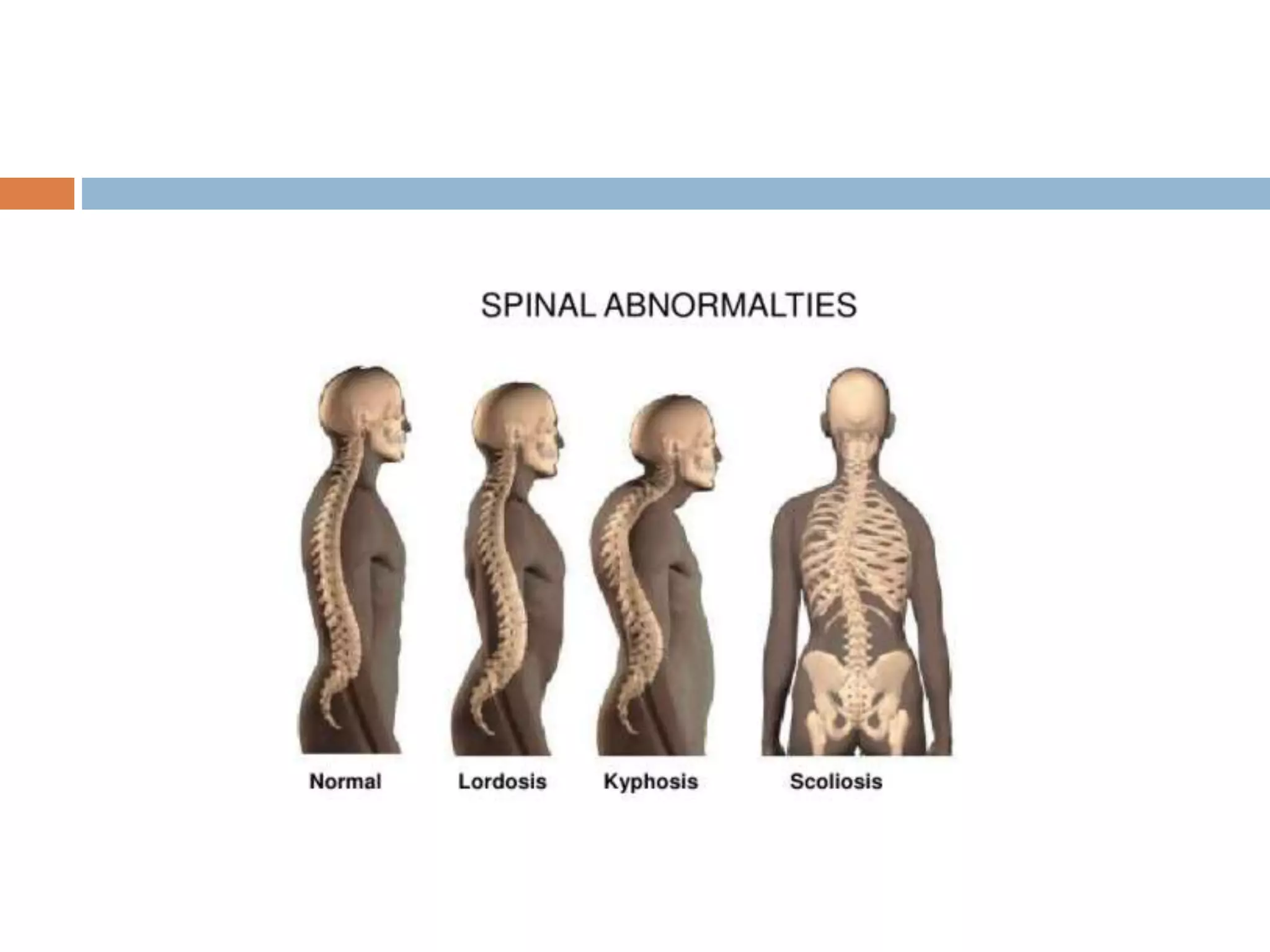
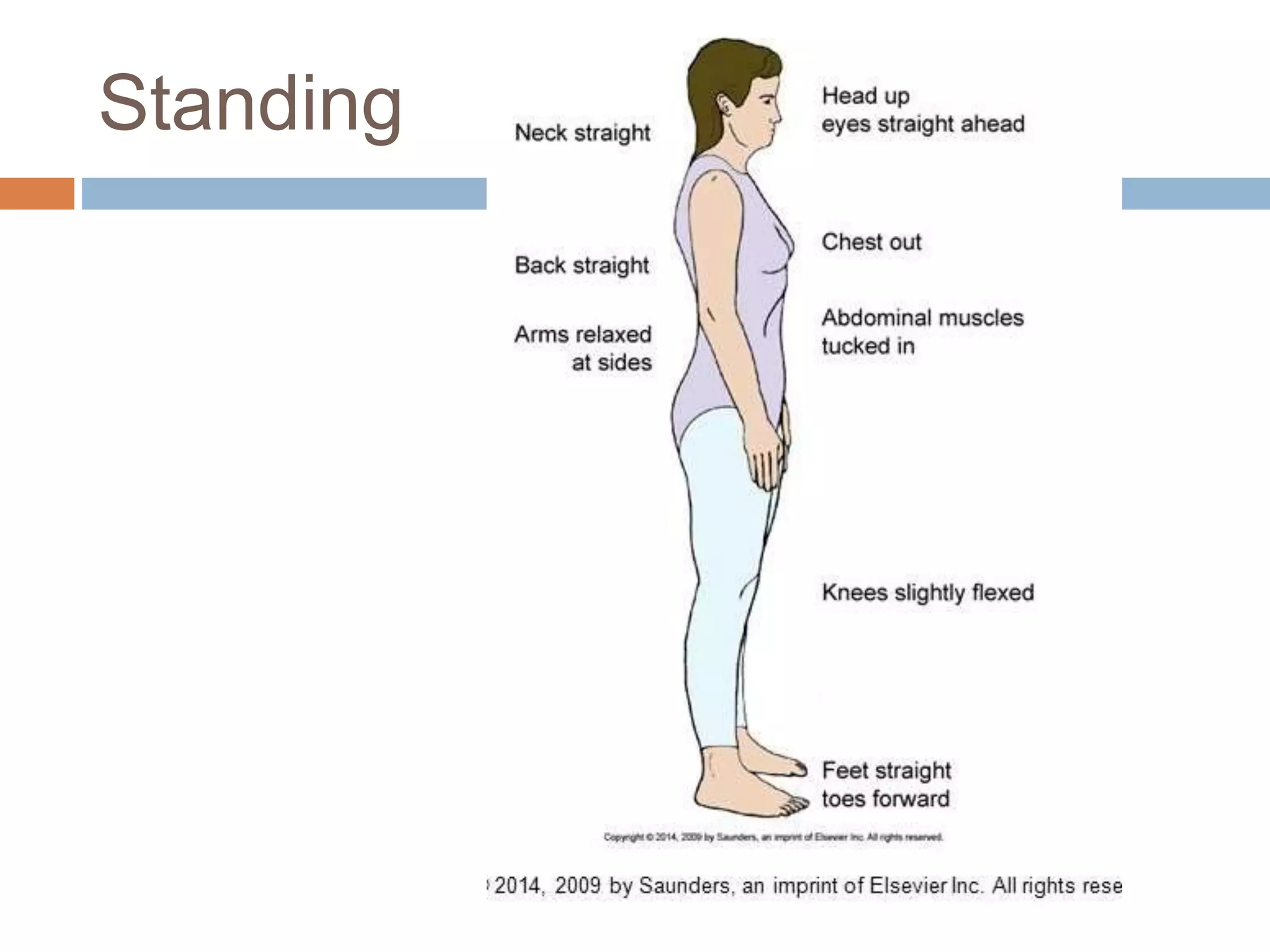
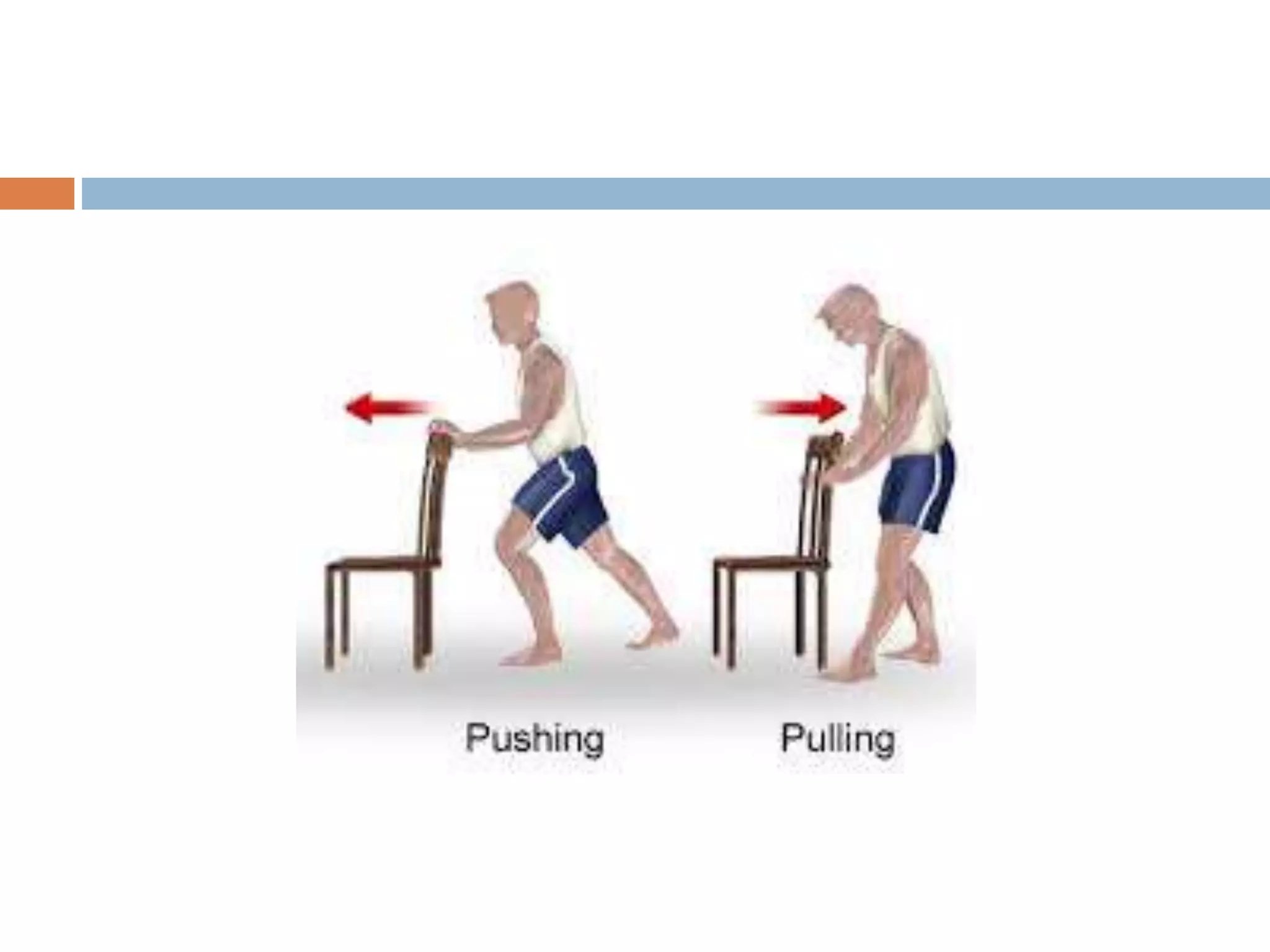
This document discusses mobility, body alignment, and body mechanics. It defines mobility as body movement requiring coordination between musculoskeletal and nervous systems. Body alignment refers to proper joint, ligament, and muscle positioning when standing, sitting, or lying down. Body mechanics is the safe use of the body through correct posture, balance, and movement to safely lift and move objects and people. Maintaining proper body alignment and mechanics is important for physiological function, injury prevention, and nursing care safety.