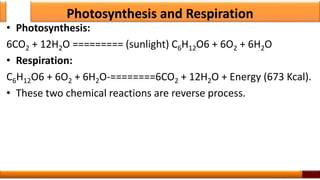
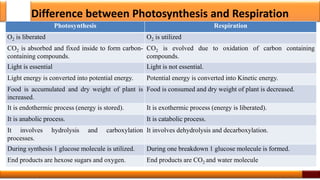
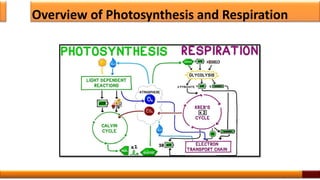
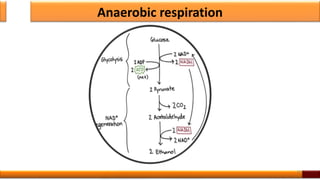
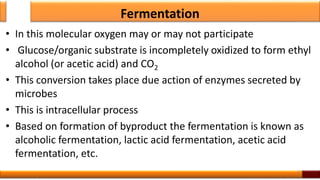
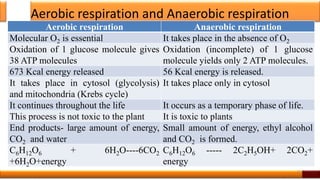
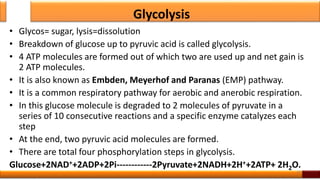
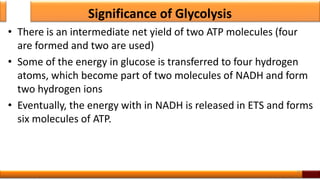
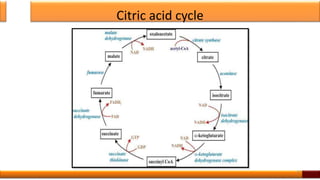
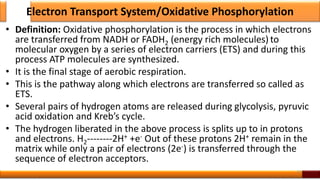
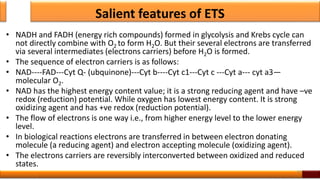
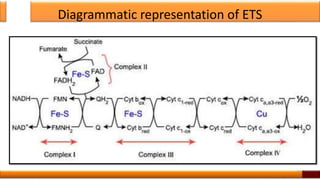
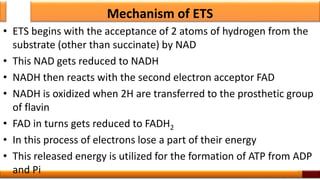
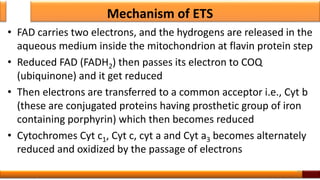
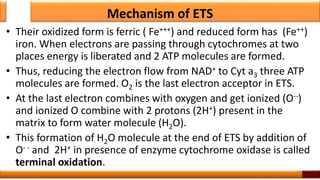
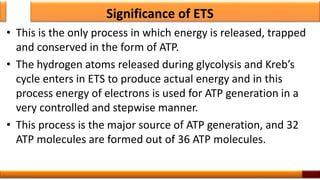
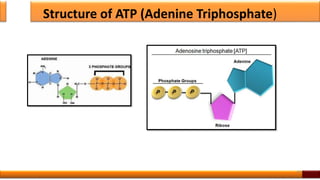
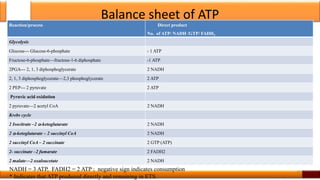
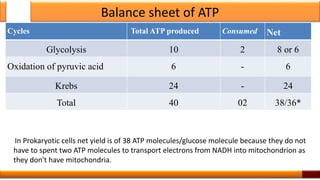
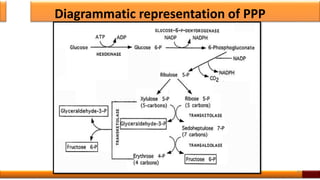
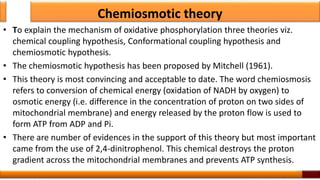
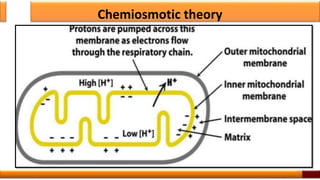
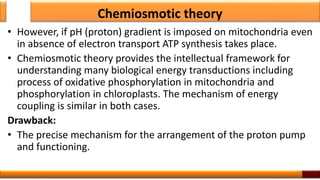
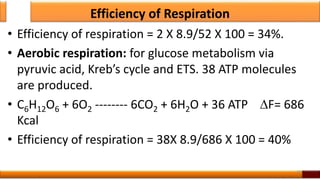
Respiration is the process by which glucose is oxidized to produce energy. It occurs via three main stages - glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate and produces a small amount of ATP. The citric acid cycle further oxidizes pyruvate and generates more ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation uses the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to power ATP synthase to produce the majority of ATP. Respiration is essential for producing the energy currency ATP that cells need to carry out life functions.