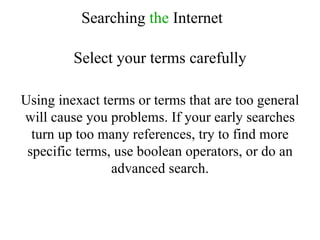
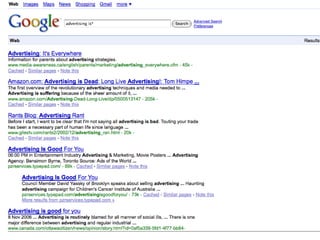
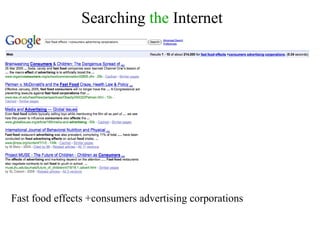
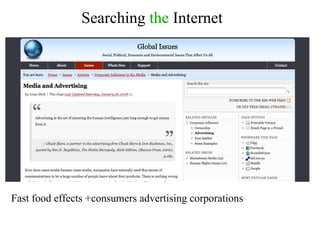
This document provides information on researching topics online, including searching the internet, evaluating sources, and taking notes. It discusses search engines, boolean operators, and directories for finding information. Meta-search engines and invisible web resources are described that can provide access to scholarly articles and databases. Guidelines are given for selecting search terms, evaluating sources, and properly citing quotes in notes.