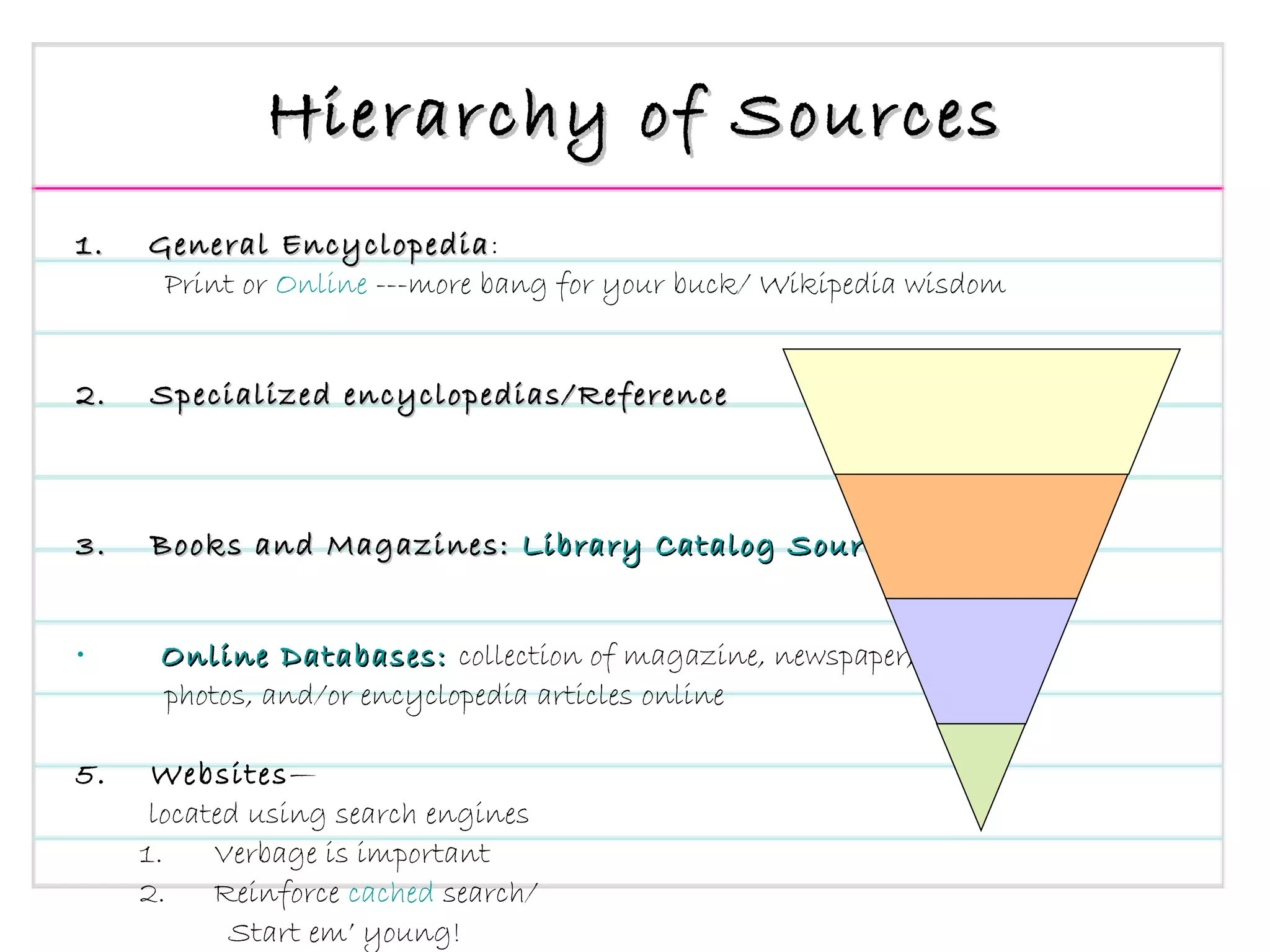
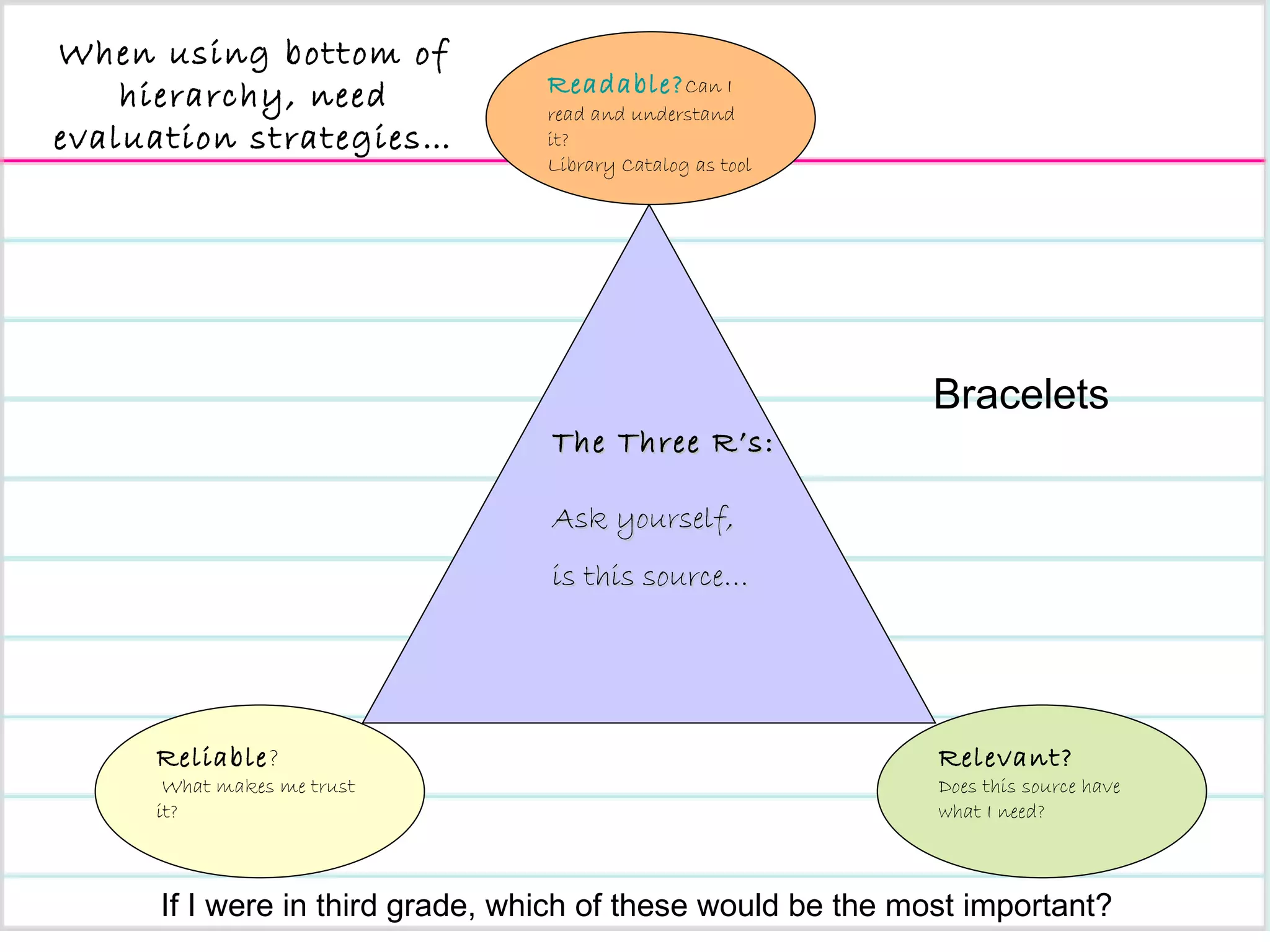
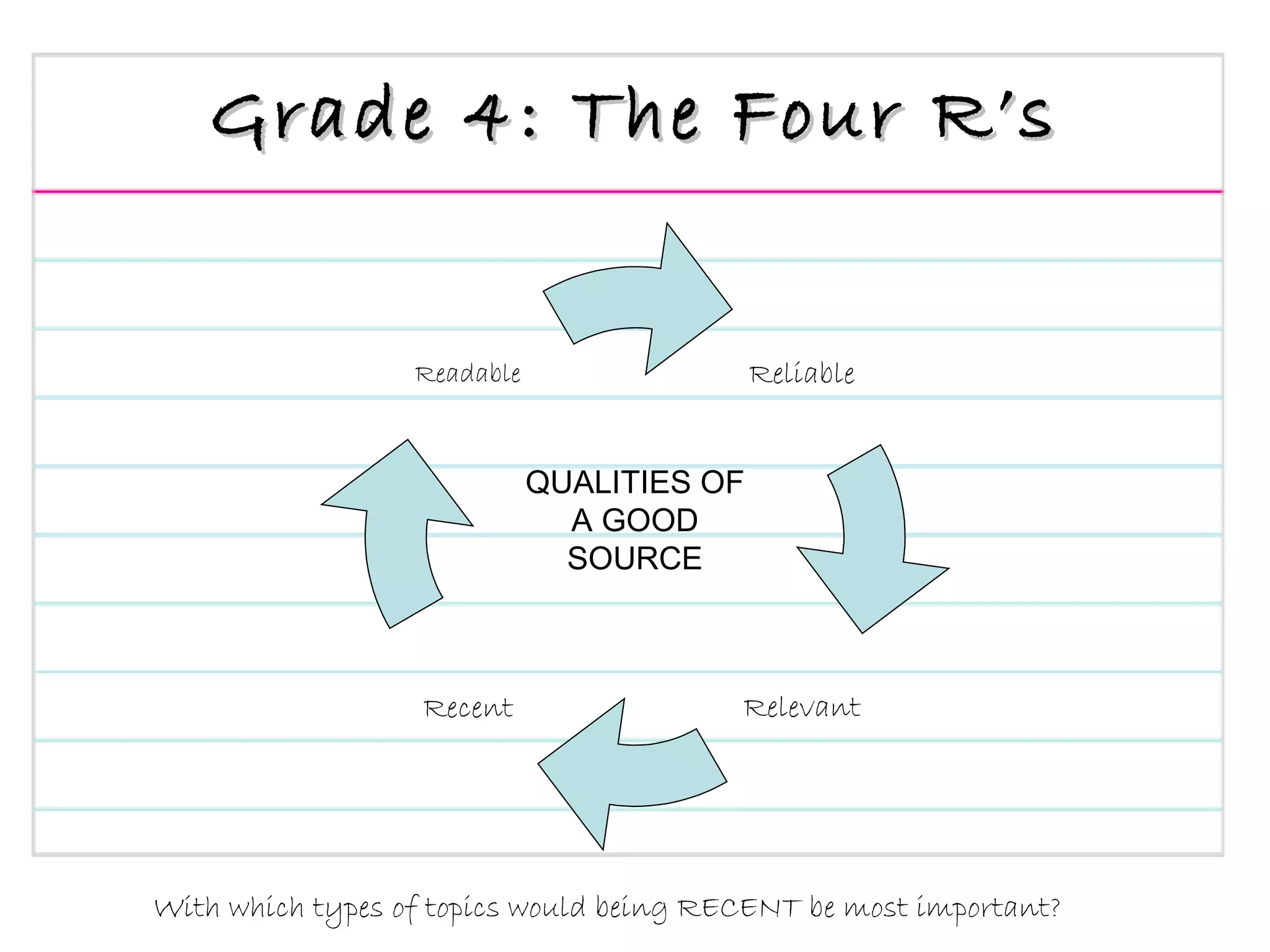
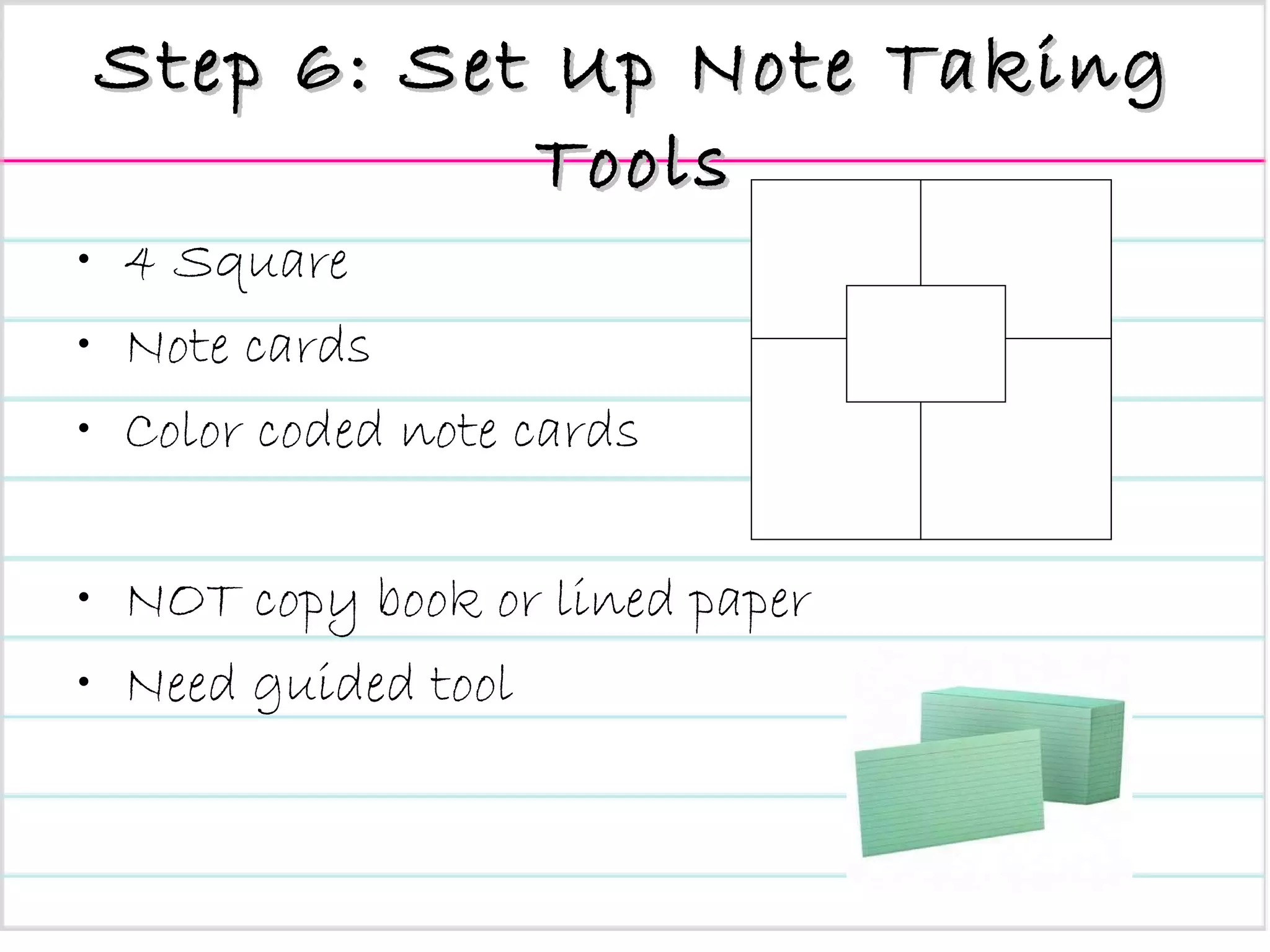
The document provides an overview of a presentation on teaching research and informational writing in elementary classrooms. It outlines a 10-step "CB Research Model" and discusses practical ideas and tools for teaching each step, including choosing topics, developing research questions, evaluating sources, taking notes, and organizing information.