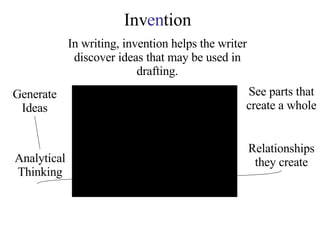
The document discusses the process of invention in writing, which involves using different thinking strategies to systematically develop and analyze ideas prior to drafting. It outlines several invention strategies including definitional, comparative, causal, and exemplification thinking. Examples are provided for each strategy using the topic of vegetarianism. The goal of invention is to generate as much material as possible in a messy drafting process before writing the first draft.


![Email: [email_address] www.slideshare.net/msbirkbeck](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/invention-1222226838362644-8/85/Invention-3-320.jpg)

















![Defin it ional Thi nk ing Think of a category that somehow restricts your word; you may use the phrase kind of to help create a restricting category; the category word or phrase follows is or are . 4. Use one of these words ( who , that , when , if , by , because , or caused by ) to add ideas [in a clause or phrase(s)] that further restrict and define the category word or phrase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/invention-1222226838362644-8/85/Invention-23-320.jpg)



![Defin it ional Thi nk ing 4. Use one of these words ( who , that , when , if , by , because , or caused by ) to add ideas [in a clause or phrase(s)] that further restrict and define the category word or phrase.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/invention-1222226838362644-8/85/Invention-27-320.jpg)




















