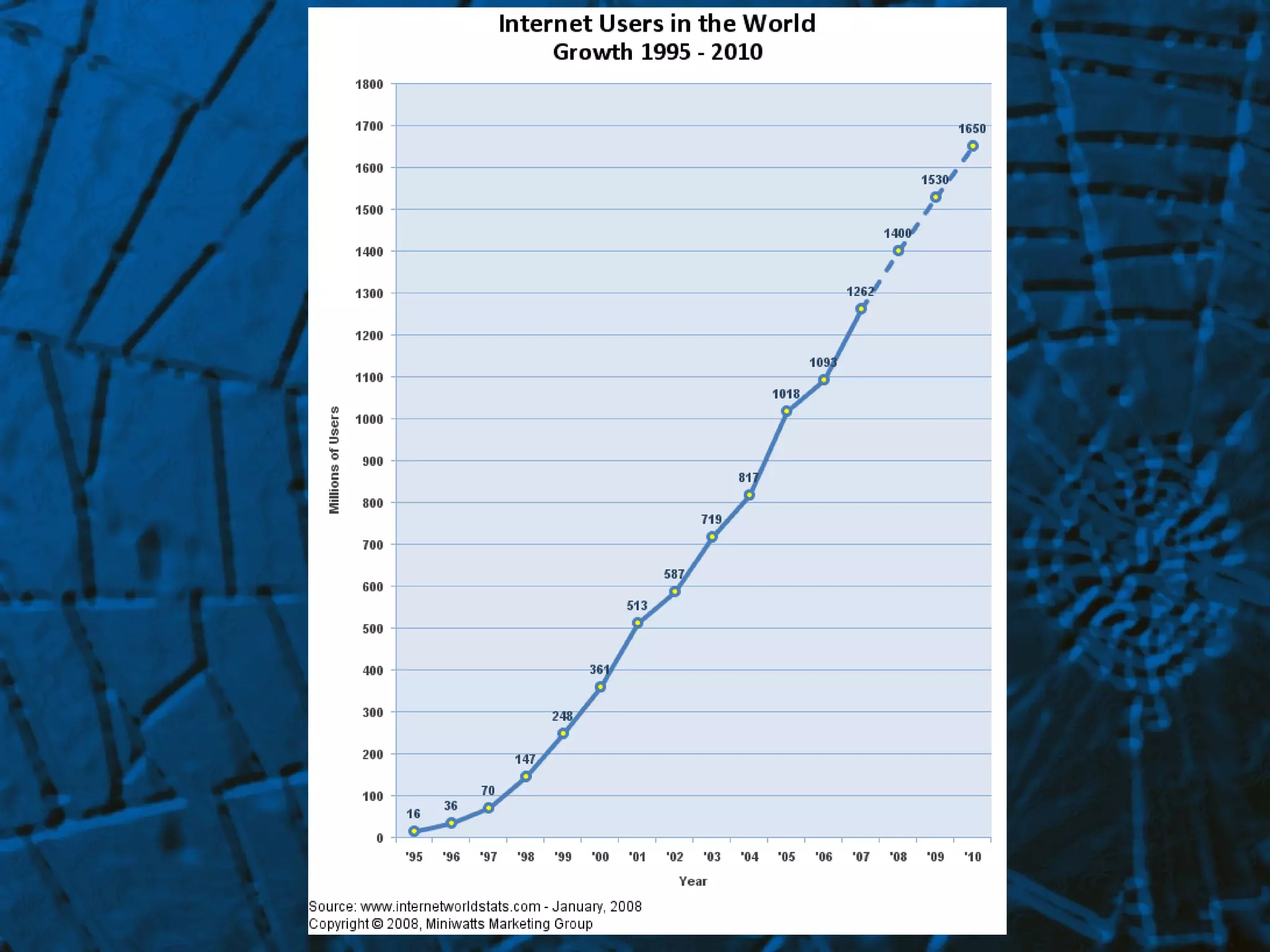
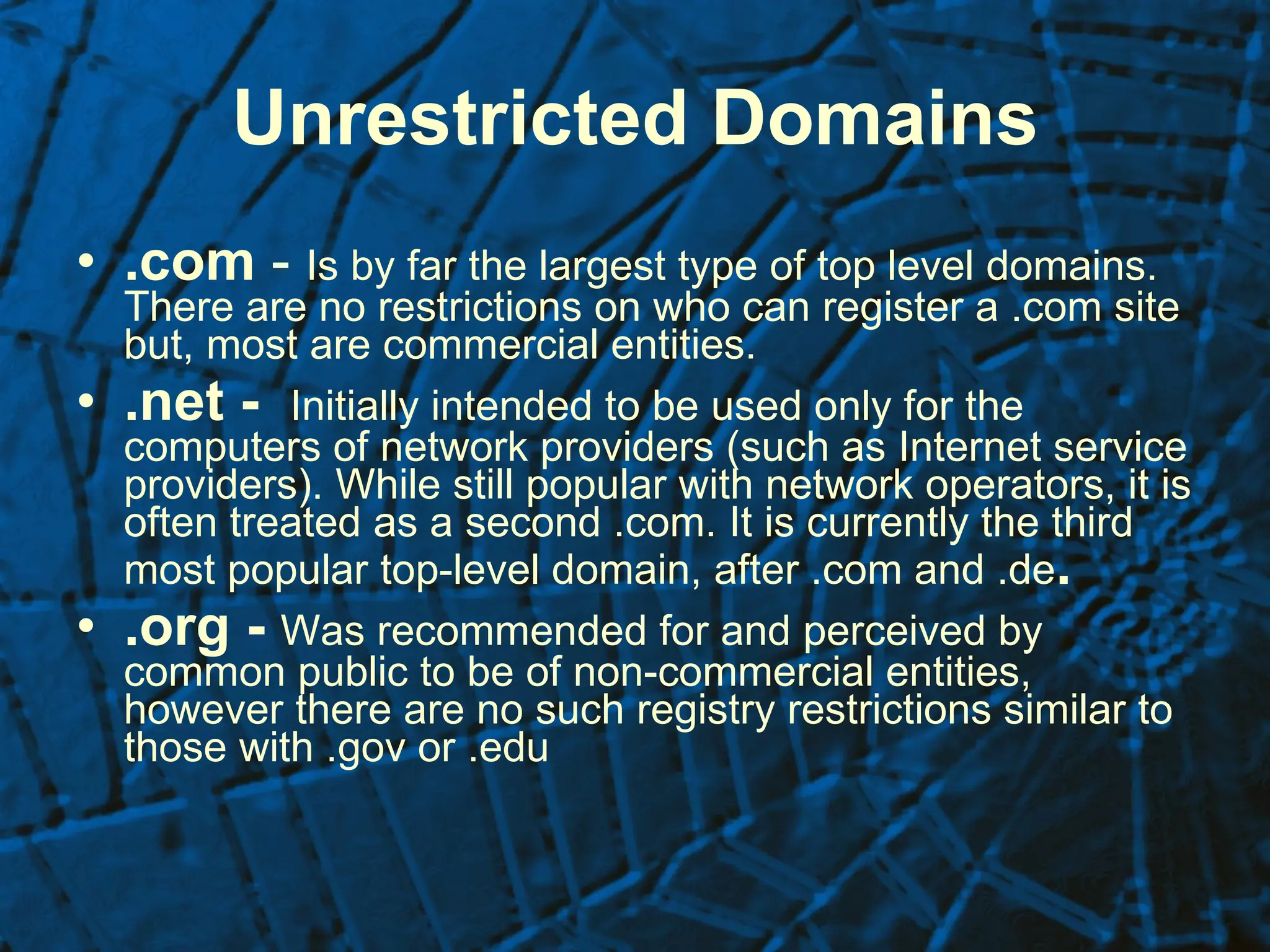
The document provides an overview of the history of the internet from its origins in the 1960s as a way for computers to share information for research purposes to its growth and popularization in the 1980s and 1990s. It discusses the development of key technologies and protocols like email, domains, and search engines. It also provides tips for evaluating online medical information and lists some reputable health-related websites and resources.