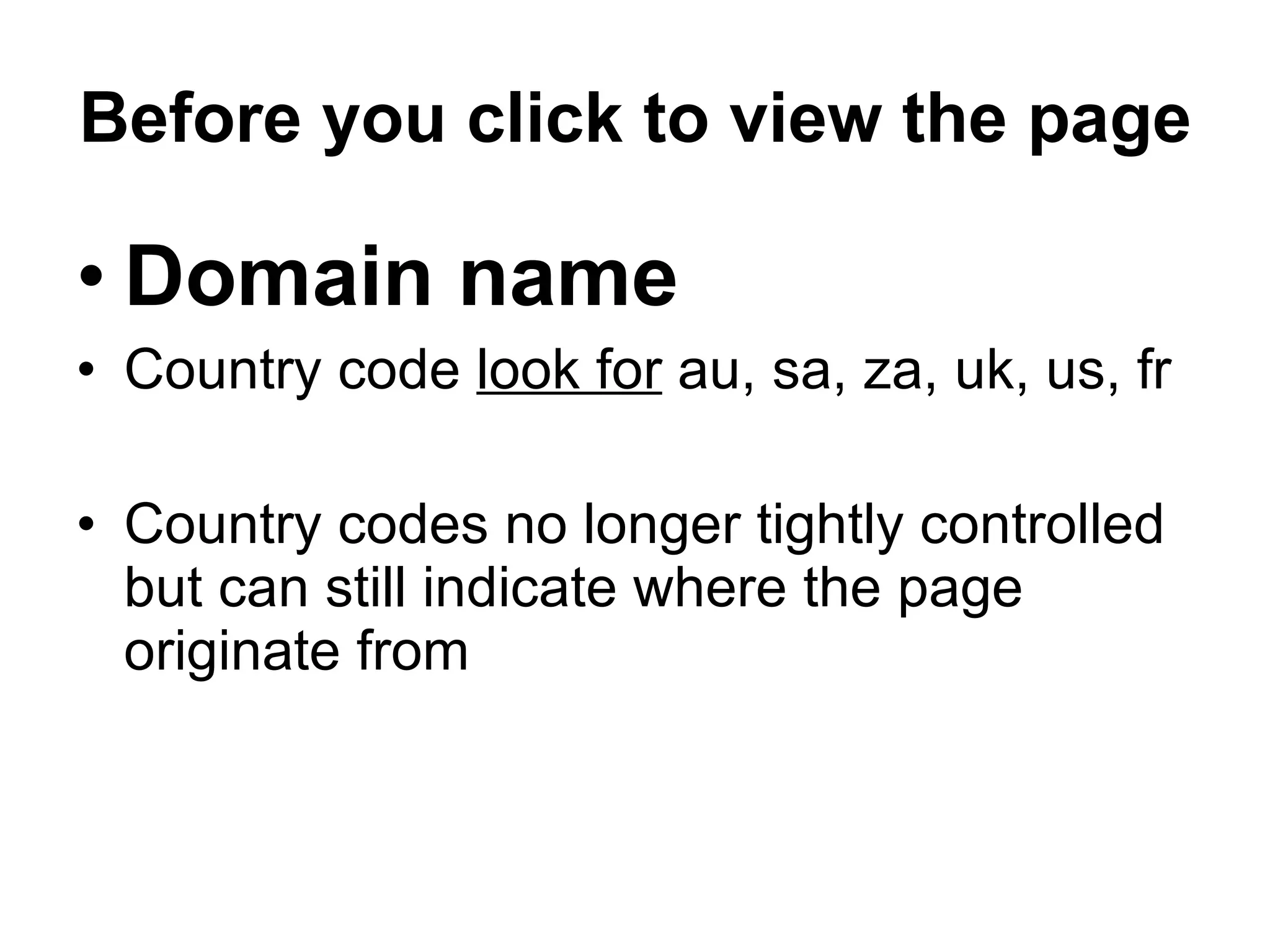
The document provides an overview of how to effectively search the internet. It discusses what the internet is, how it works, and the history and terminology associated with searching online. It then gives guidelines for developing successful search strategies, such as being specific, using keywords and phrases, trying different search engines and refining searches based on results. It emphasizes evaluating websites for credibility by examining aspects like the domain, author, date updated and external links.