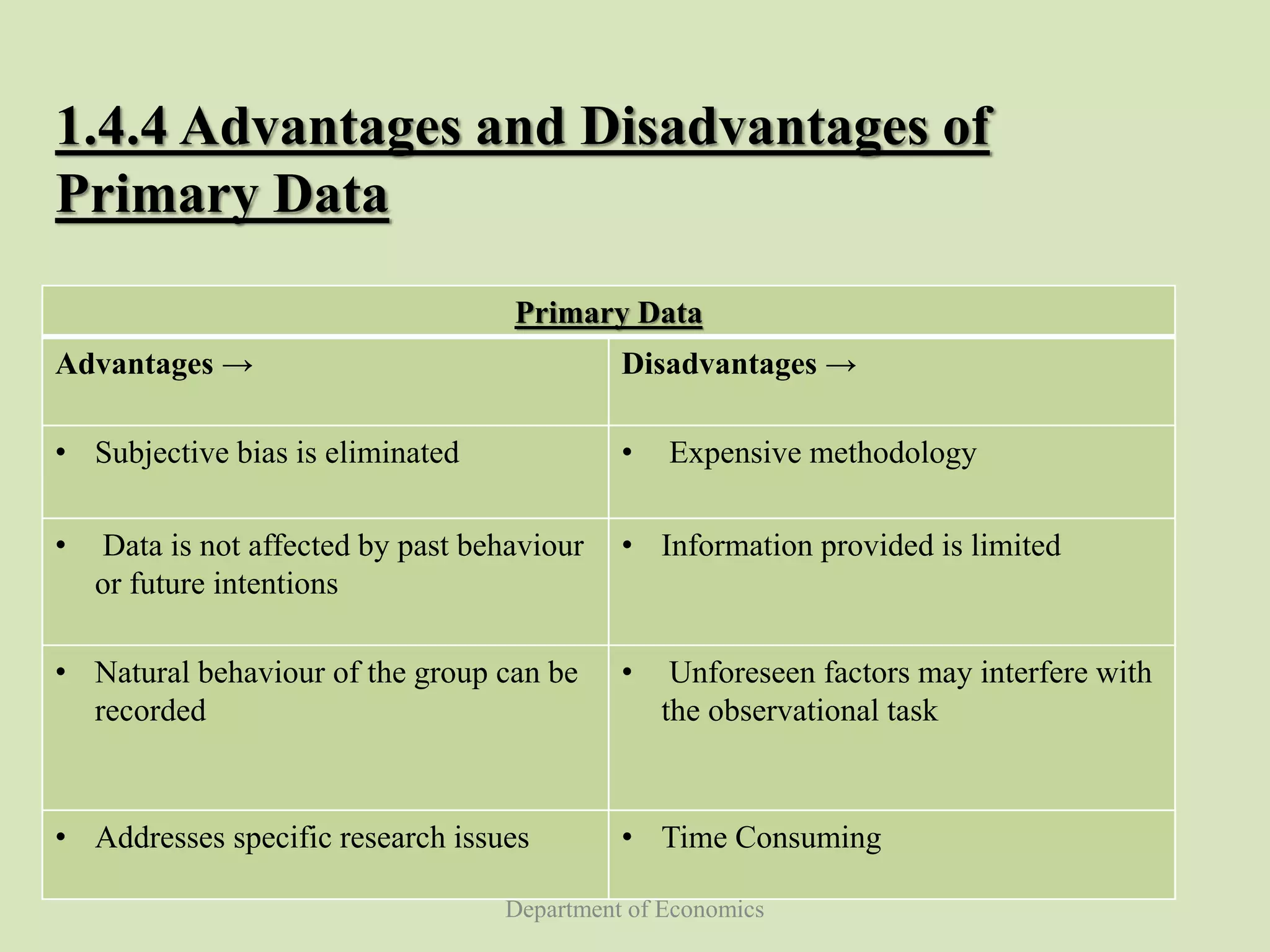
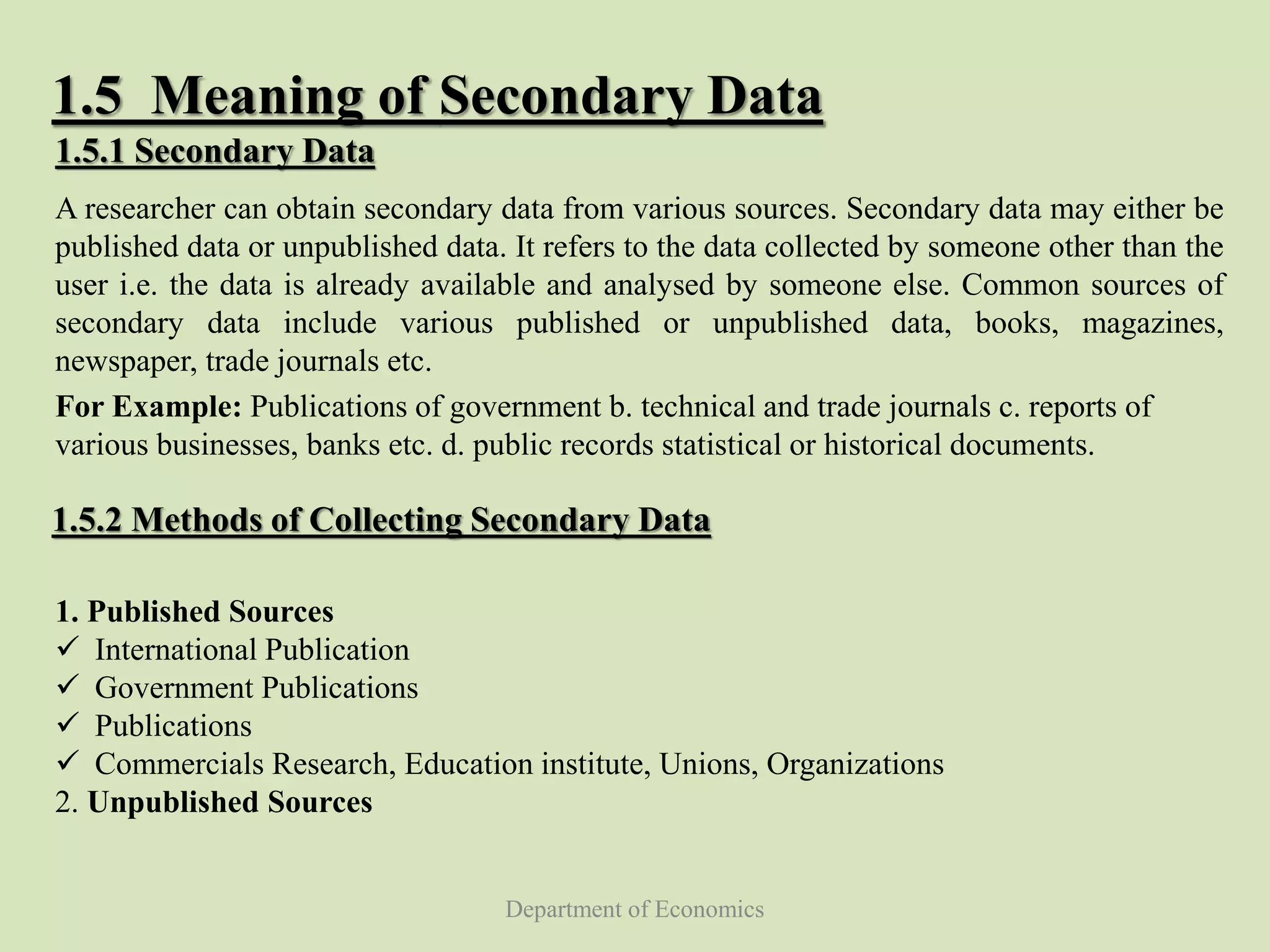
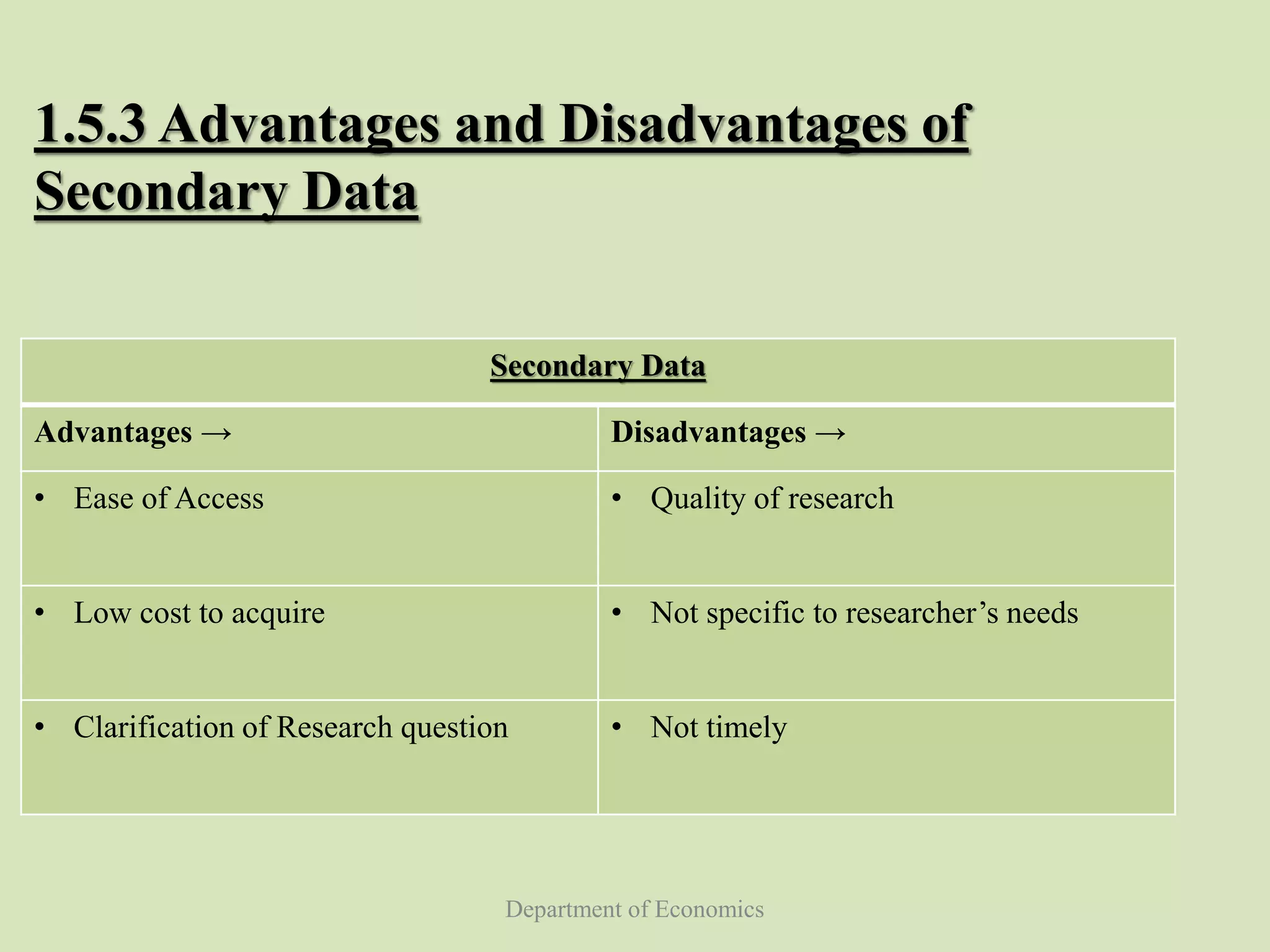
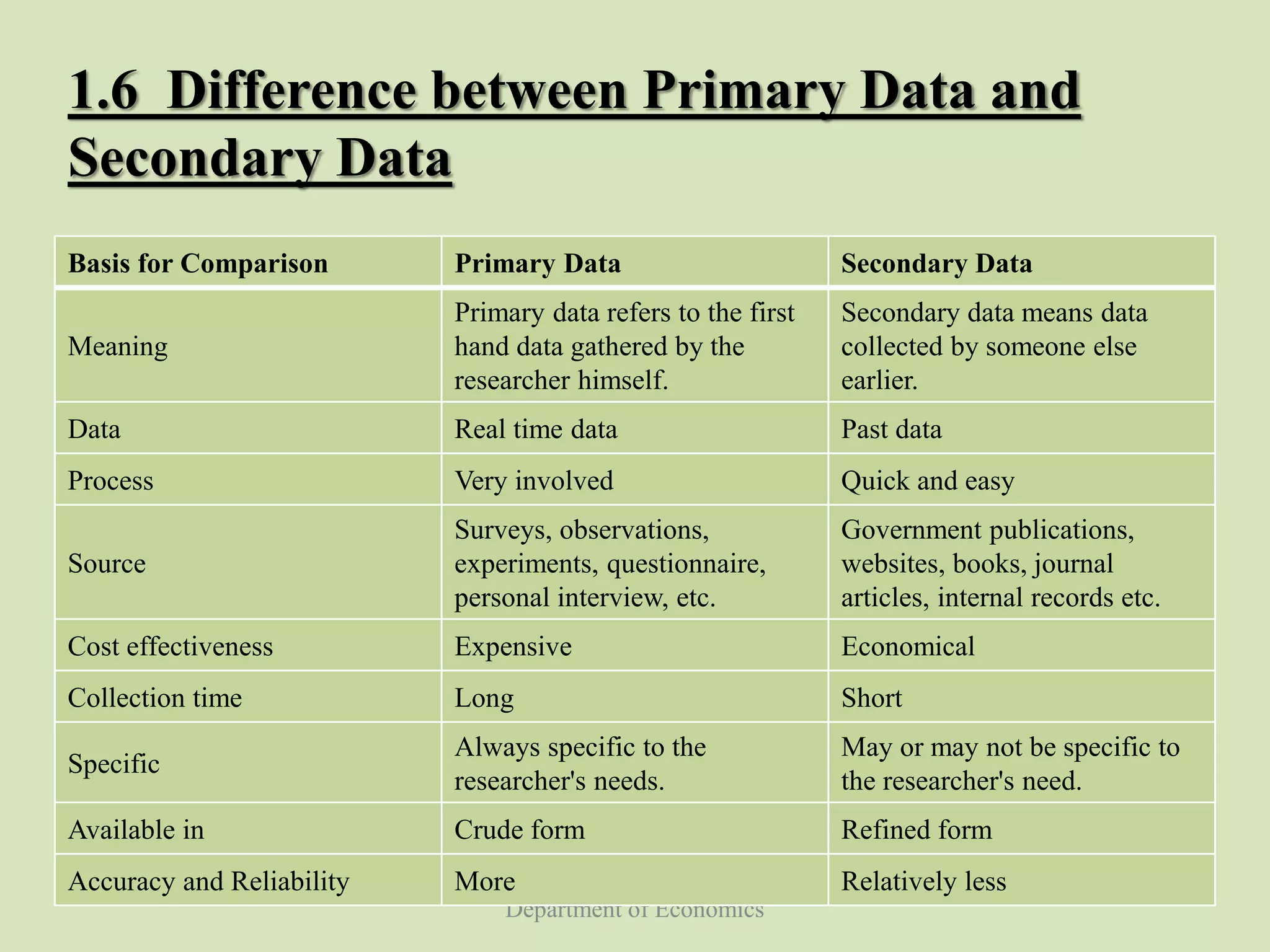
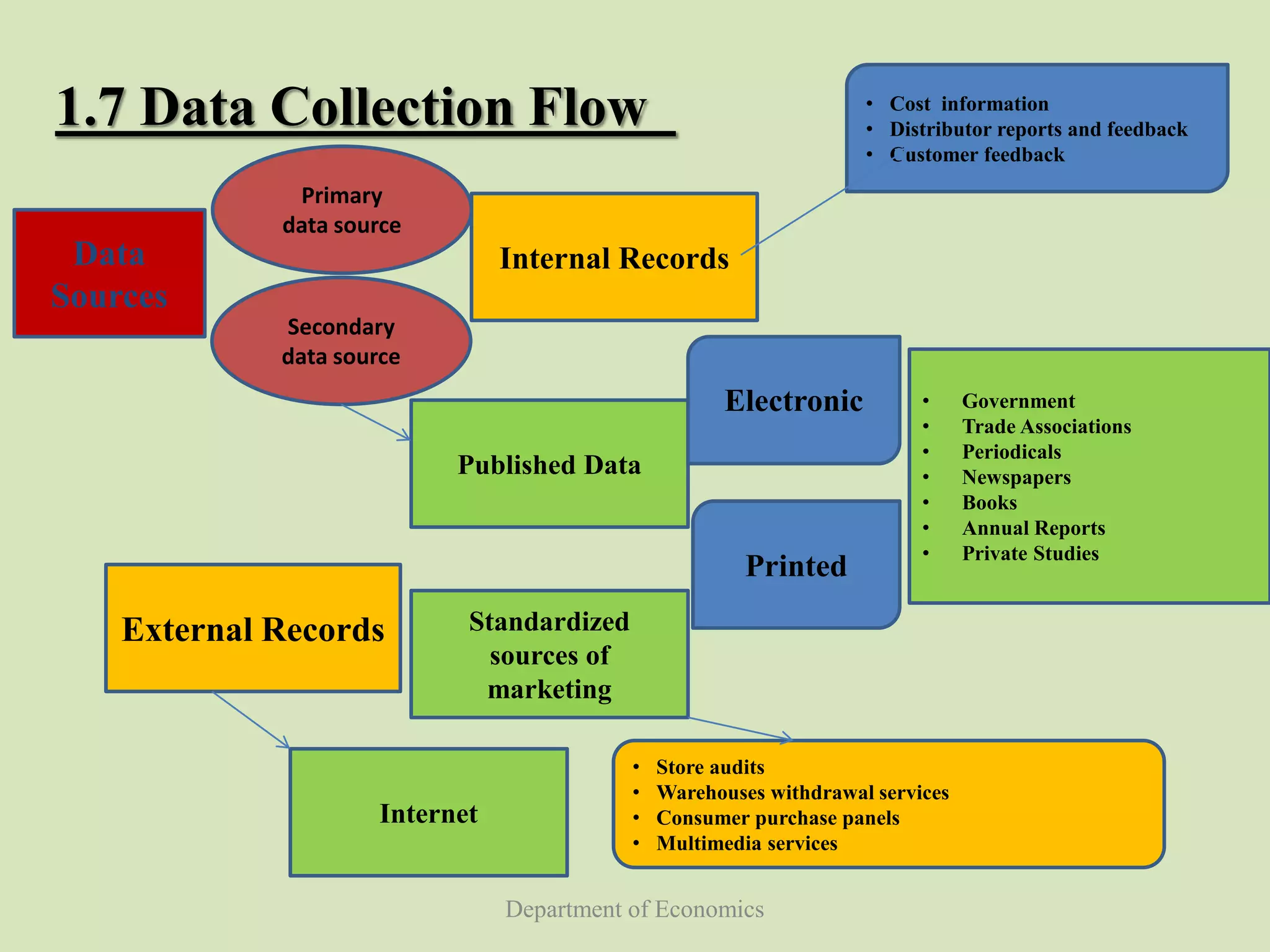
This document discusses data collection in economics. It defines data collection as the process of preparing and systematically gathering data from various sources. The objectives of the document are to understand the need for data collection, factors to consider, how to classify and collect data, and the differences between primary and secondary data. Primary data refers to raw data collected directly from first-hand sources like surveys. Secondary data is collected indirectly from past published sources like government publications. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of each approach and different methods for collecting primary data.