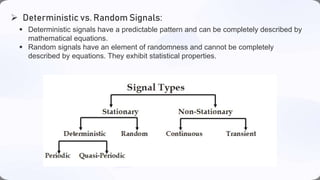
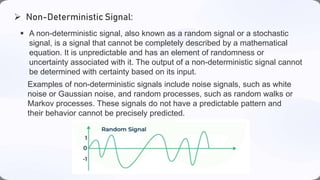
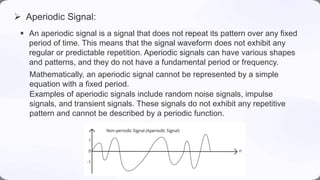
This document defines and provides examples of different types of signals. It discusses deterministic versus non-deterministic signals, periodic versus aperiodic signals, and provides examples like sine waves, noise, and impulse signals to illustrate each classification of signals.