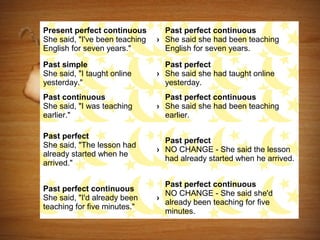
The document discusses the rules for changing direct speech into reported or indirect speech. It explains that verbs must change to past tense, pronouns and place/time references are adjusted, and that reporting verbs like "said" are used to indicate an statement was made indirectly. Indirect questions use "asked" and change word order. Indirect orders/requests use "told" or "asked" followed by an infinitive verb.