Embed presentation
Download to read offline




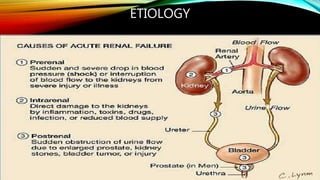
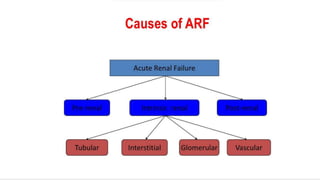
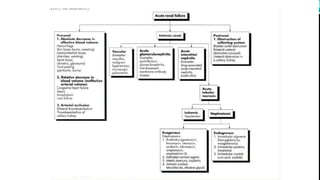
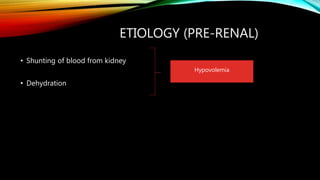
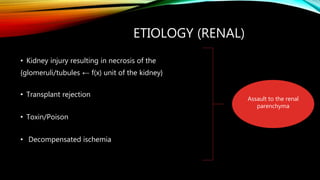
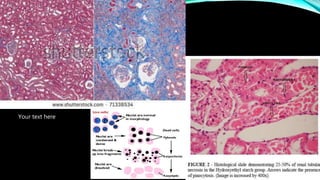
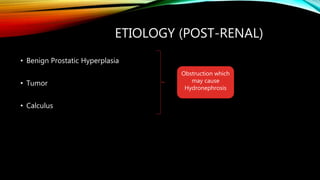
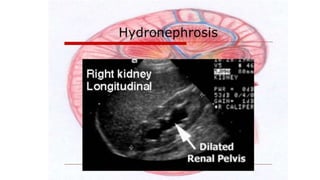

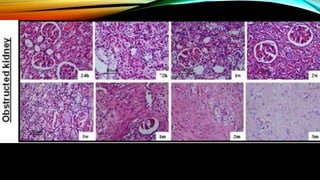
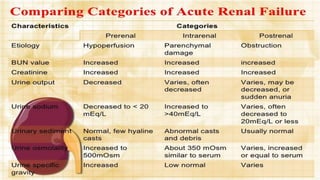

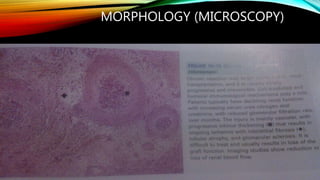


Renal failure is defined as the kidneys' inability to concentrate urine. It can be caused by pre-renal factors like decreased blood flow to the kidneys, renal factors such as direct kidney injury from toxins or ischemia, or post-renal factors involving obstruction of urine outflow. Risk factors include conditions that decrease blood volume or cause kidney damage. Diagnosis involves lab tests of kidney function. There are different types including acute or chronic. Effects can include complications if not treated and clinical signs are more prominent in chronic versus acute renal failure.


















