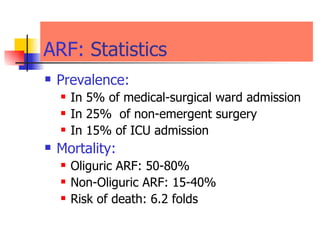
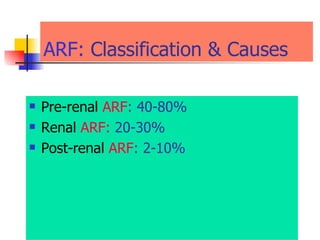
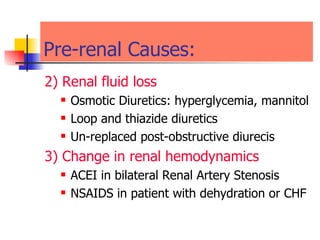
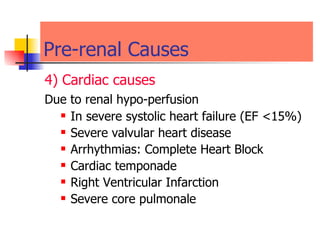
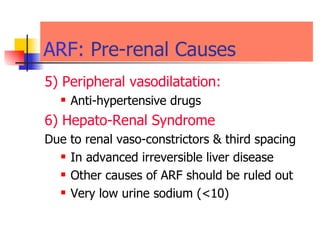
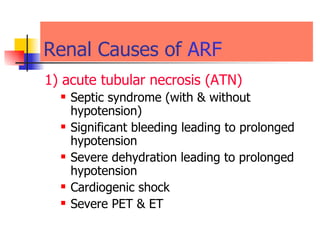
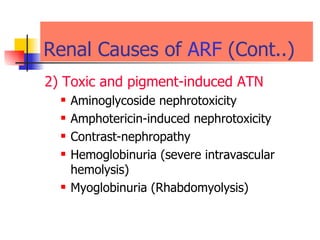
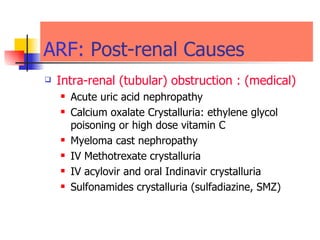
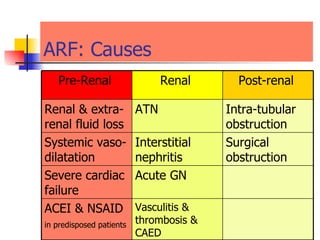
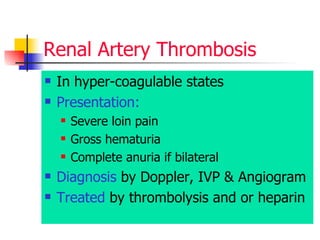
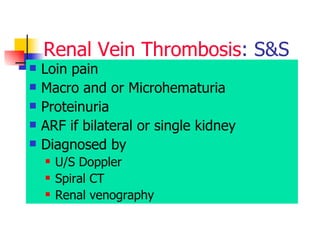
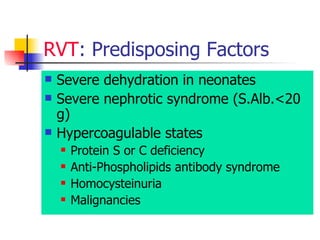
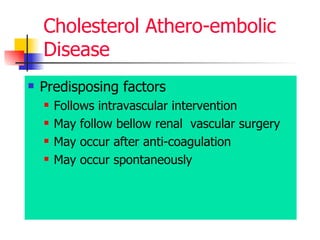
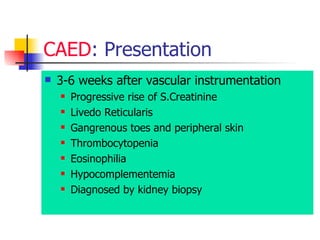
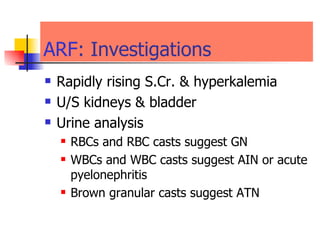
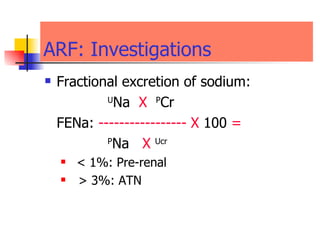
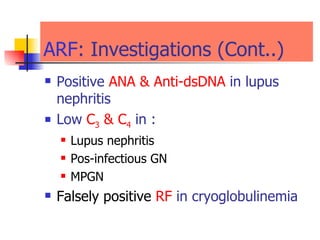
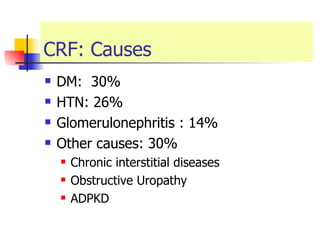
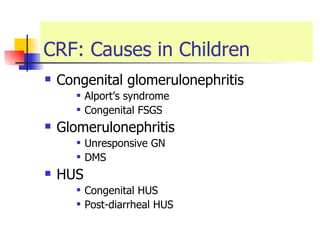
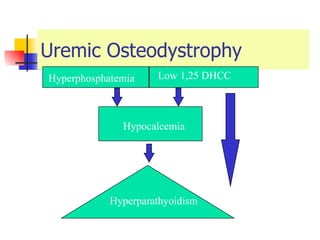
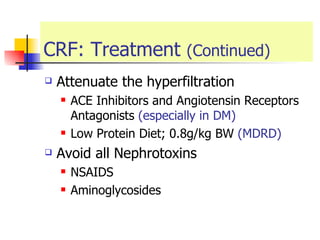
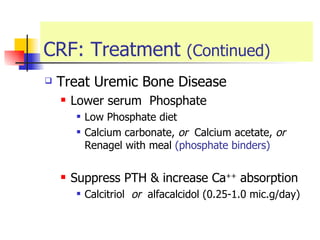
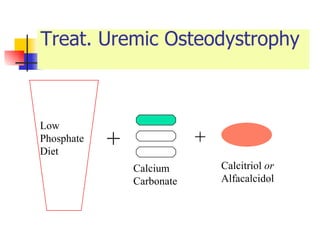
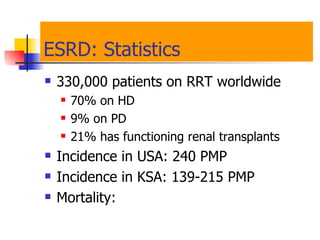
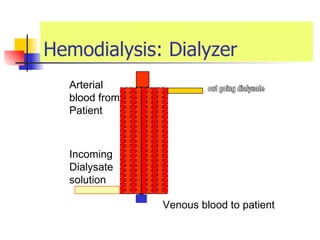
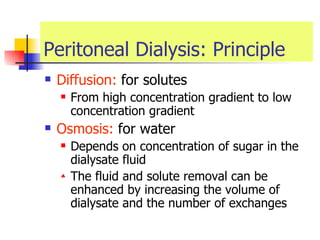
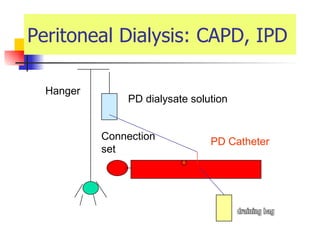
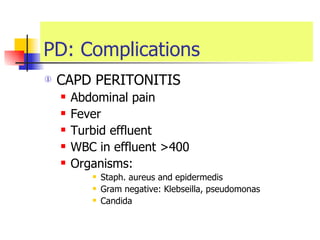
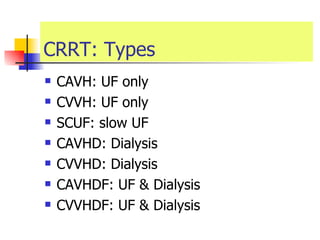
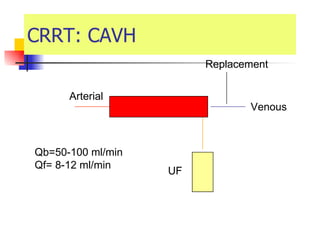
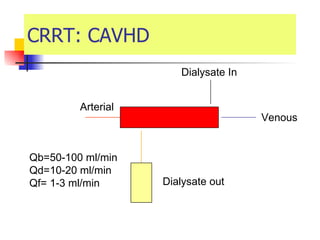
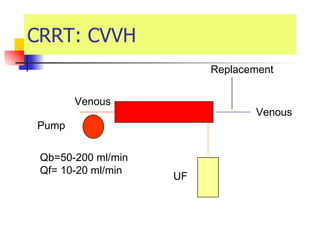
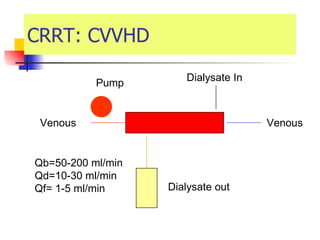
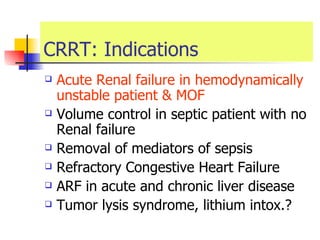
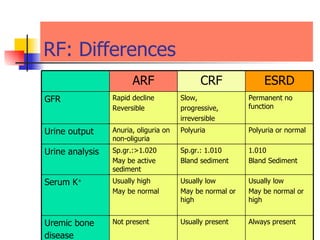
The document discusses renal failure including definitions of acute renal failure (ARF), chronic renal failure (CRF), and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). It covers classifications and common causes of renal failure. Key points include that ARF can be pre-renal, renal, or post-renal in origin and has many potential causes. CRF is a slow, progressive loss of kidney function that is irreversible and can be caused by diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, and other conditions. Monitoring of renal function includes tests of serum creatinine and clearance rates.