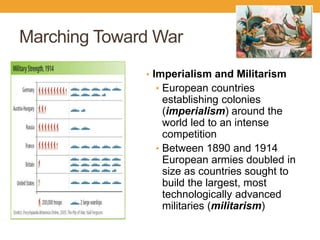
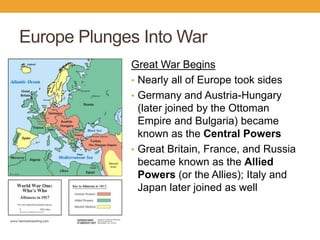
World War I began in 1914 after tensions between European powers led to a series of diplomatic crises and military alliances. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand triggered Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia, drawing in other countries through their alliance systems. Over four years of fighting resulted in stalemate as armies engaged in trench warfare with new military technologies. The US entry into the war in 1917 helped the Allies defeat Germany and its allies. The resulting 1919 Treaty of Versailles imposed punitive terms on Germany, sowing resentment and contributing to the causes of World War II.