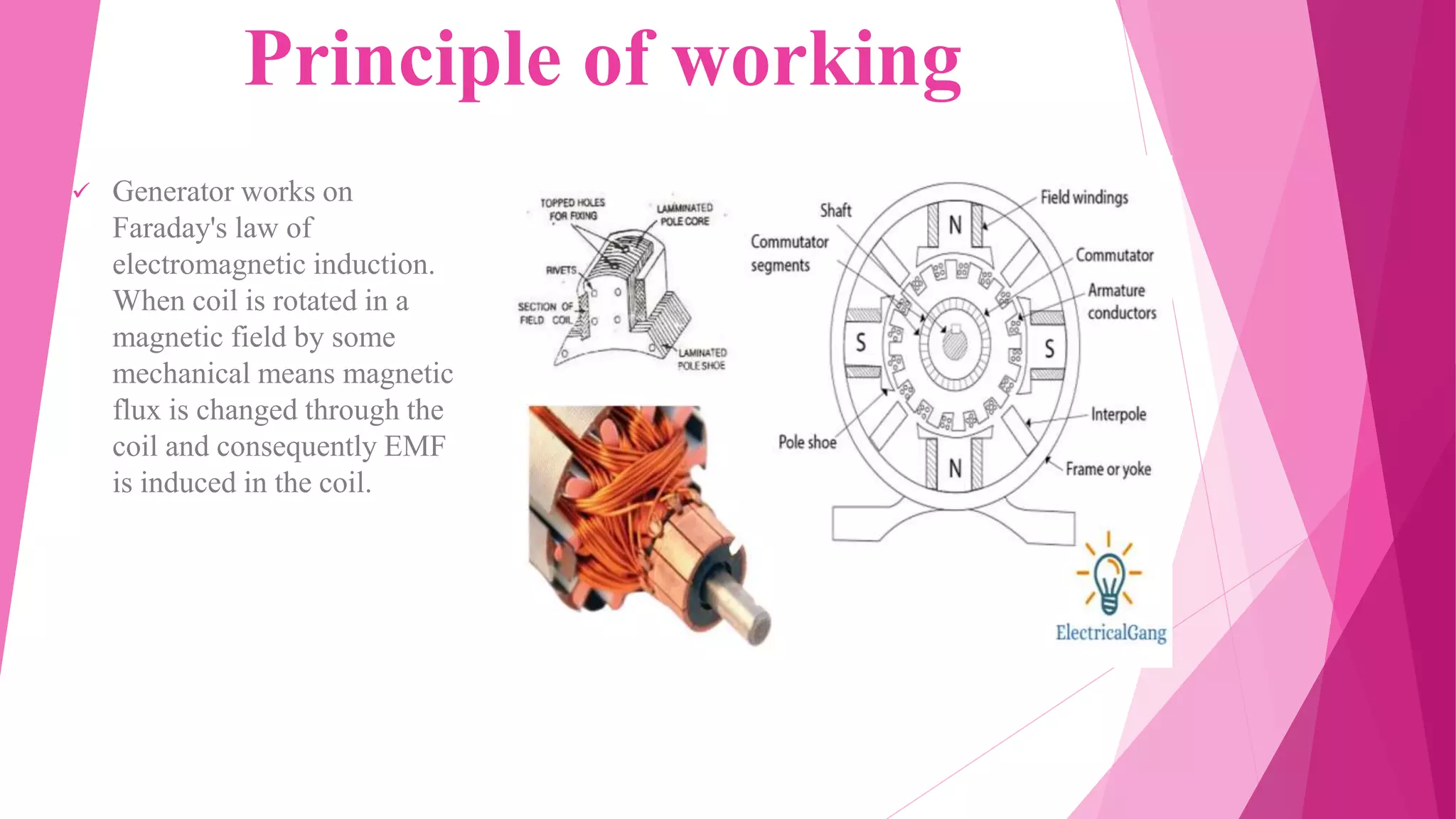
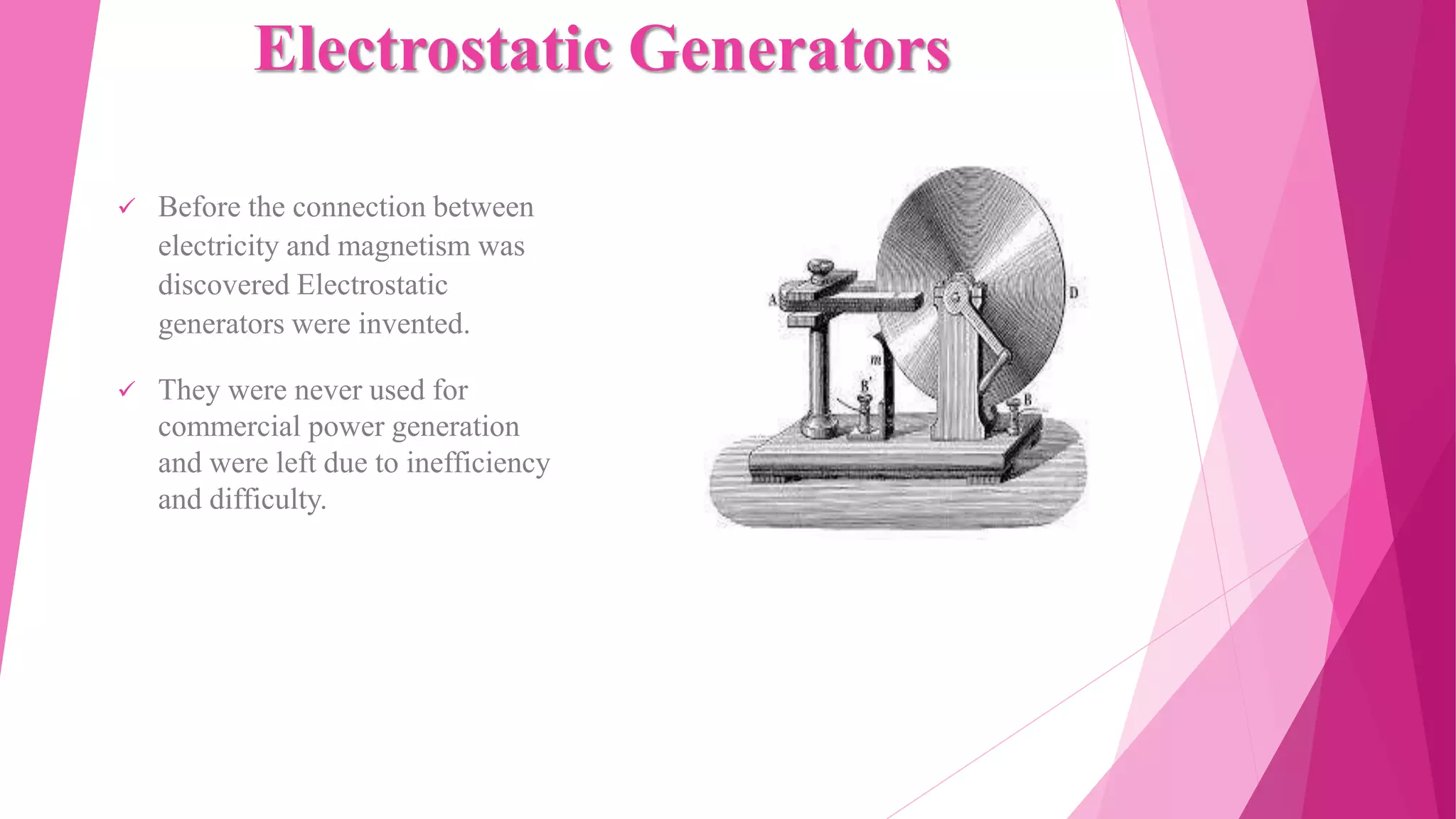
This document provides an overview of generators. It discusses the principle of how generators work by transforming mechanical energy into electrical energy using a coil and magnet. It then gives a brief history of generators from early electrostatic generators to modern alternators. It describes different types of generators such as AC/DC generators and engine, human-powered, turbine, and wind generators. It focuses on the main types of engine generators - standby, portable, and commercial generators - and their uses.