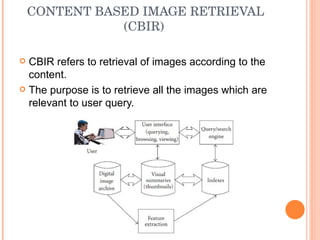
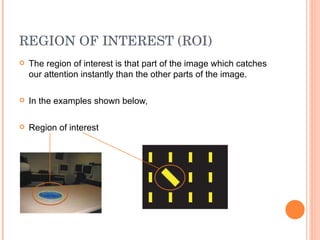
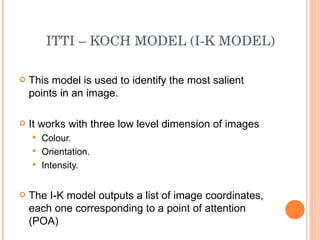
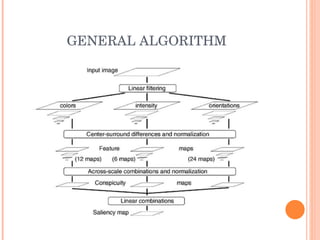
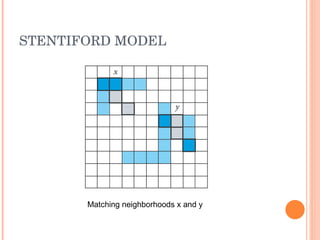
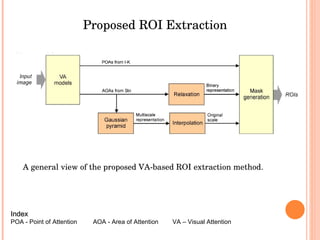
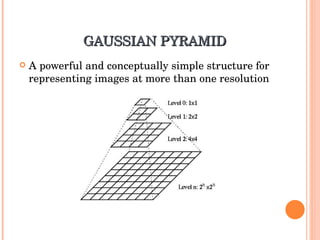
1. The document discusses different techniques for region of interest (ROI) extraction from images, including saliency maps, visual attention maps, the Itti-Koch model, and the Stentiford model.
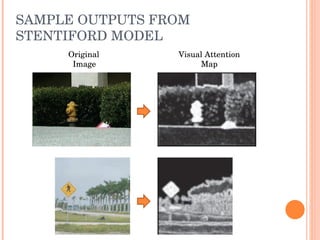
2. It provides examples of the output from these techniques, such as highlighting the most salient points or areas of an image.
3. While the models may identify different ROIs, combining their common ROIs can provide a better output for applications like thumbnail cropping or image indexing.