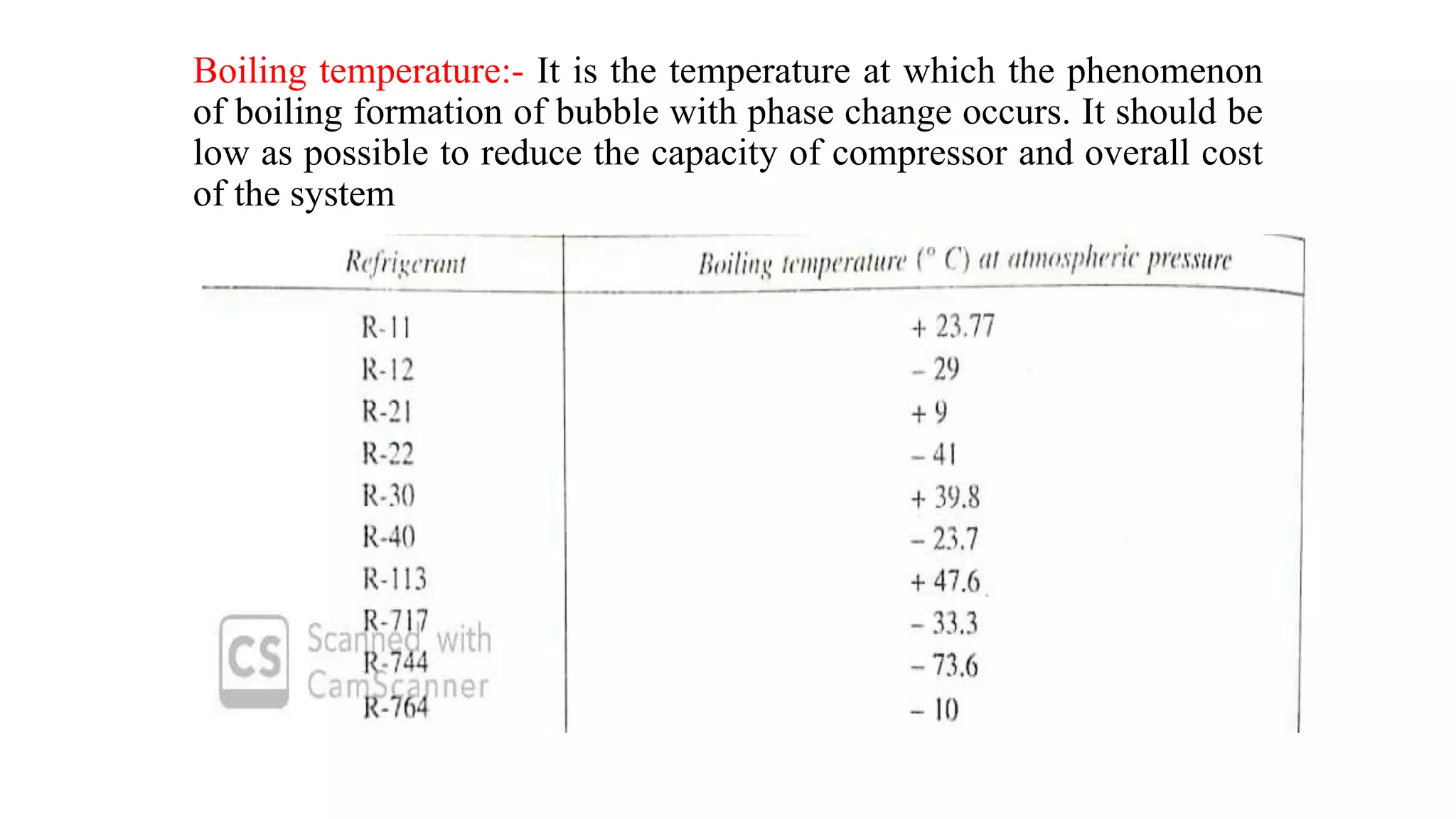
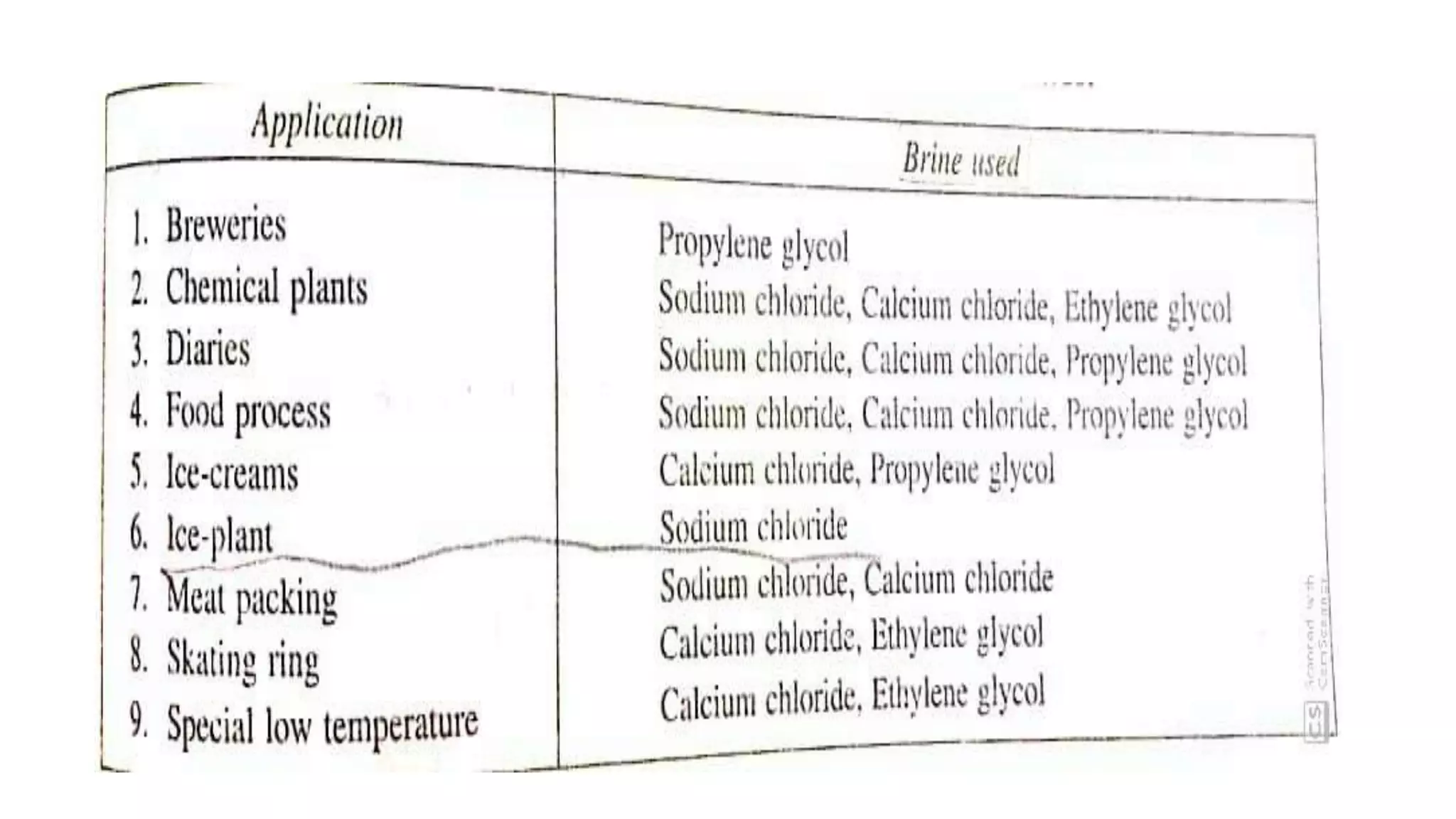
This document discusses refrigerants, including their classification, properties, environmental impacts, and alternatives. Refrigerants are heat carrying fluids that absorb heat from a low temperature system and release it to a high temperature system. Natural substances like ice were early refrigerants, followed by ether, ammonia, and sulfur dioxide in the 19th century. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) became popular but were later banned due to ozone depletion and global warming. Current alternatives include hydrocarbons, ammonia, carbon dioxide, and hydrofluorocarbons. An ideal refrigerant has desirable properties like high critical temperature, low boiling point, non-toxicity, stability, and being environmentally friendly.