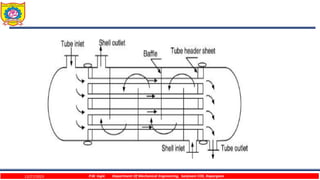
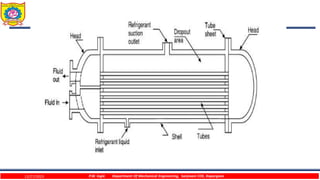
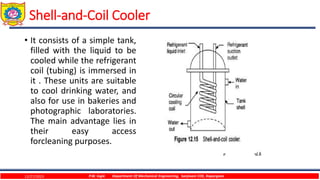
The document discusses different types of chillers used for liquid cooling. It describes direct expansion chillers where refrigerant evaporates inside tubes to cool liquid on the shell side. Flooded shell-and-tube chillers have liquid flowing through tubes immersed in refrigerant in the shell. Shell-and-coil chillers consist of a tank filled with liquid to be cooled, with a refrigerant coil immersed within it.