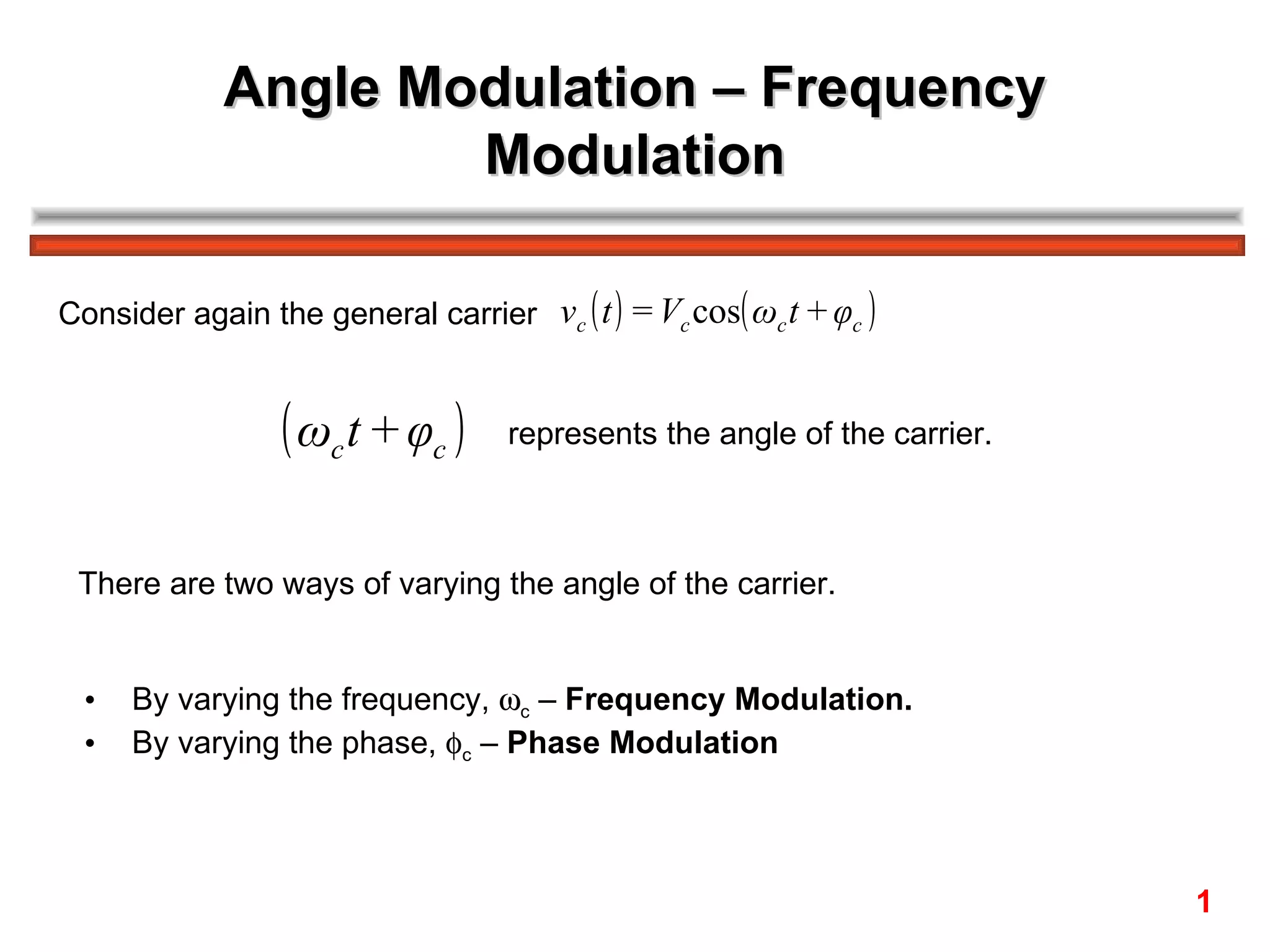
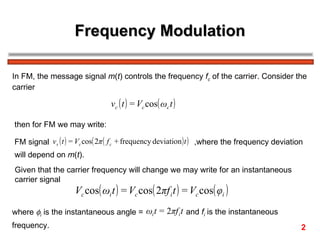
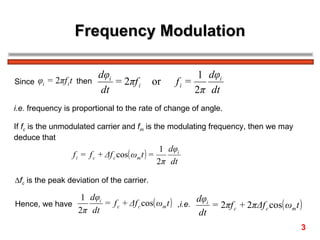
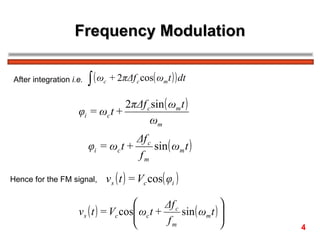
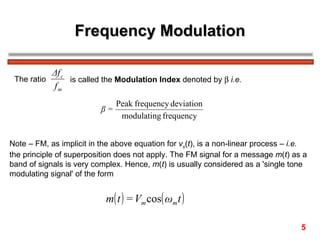
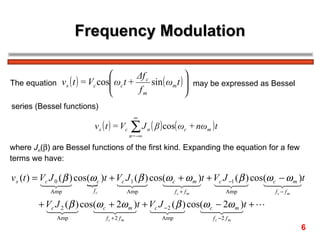
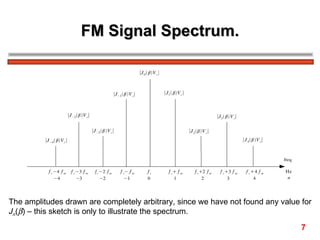
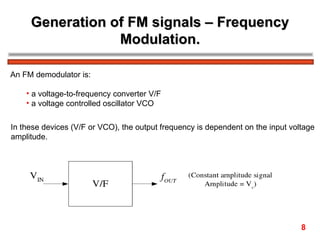
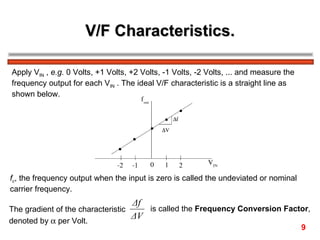
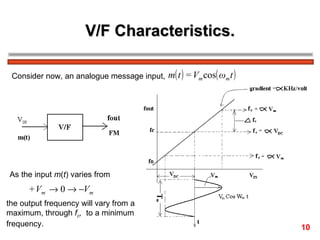
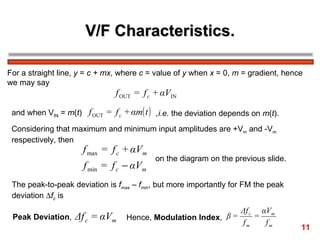
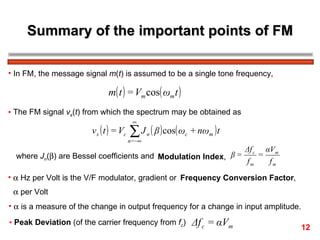
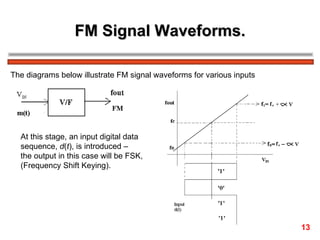
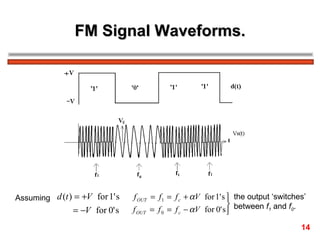
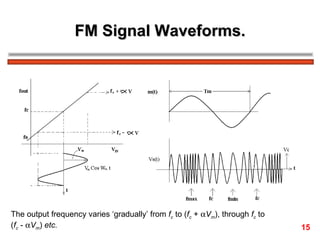
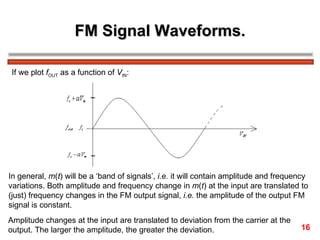
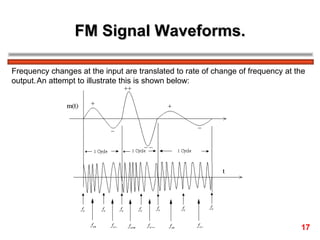
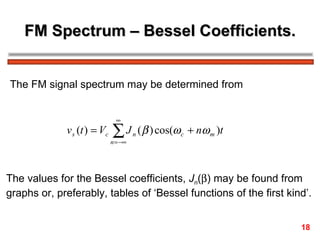
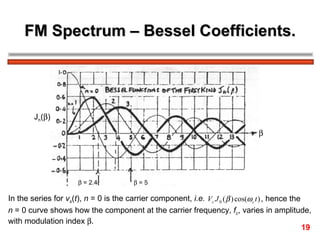
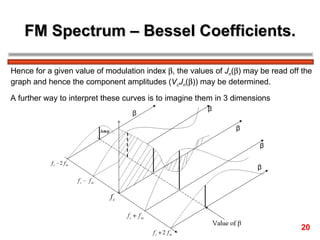
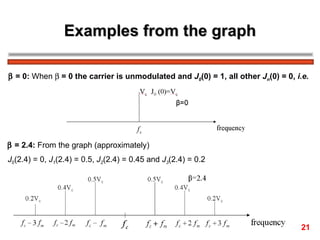
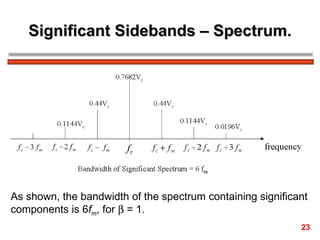
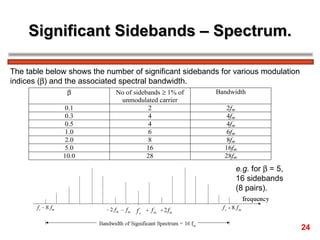
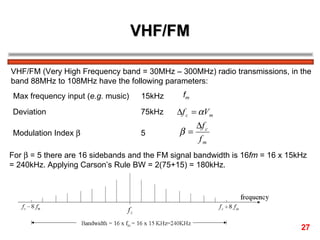
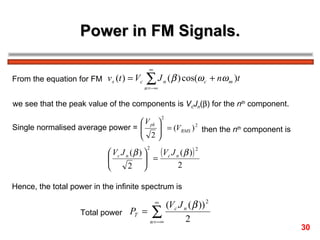
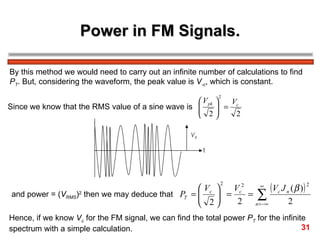
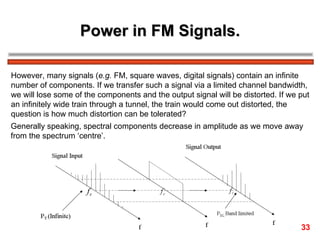
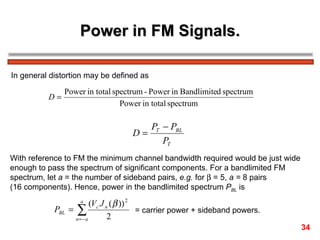
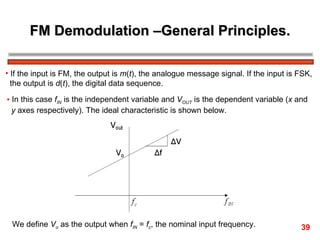
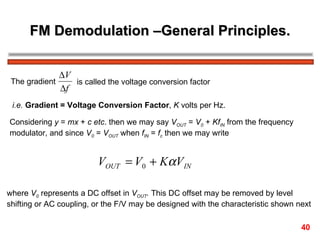
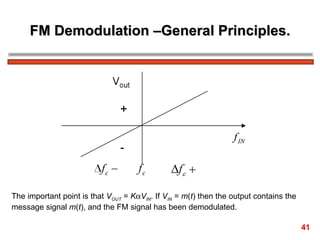
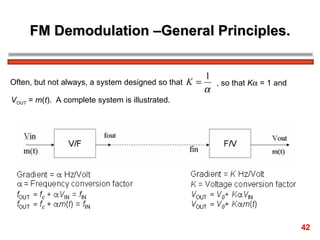
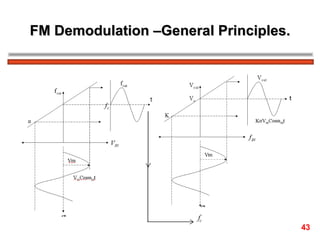
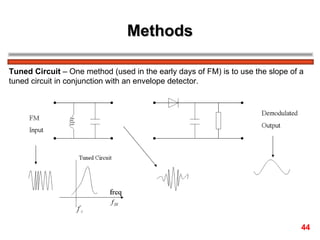
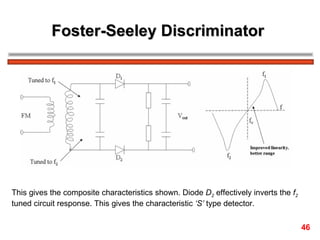
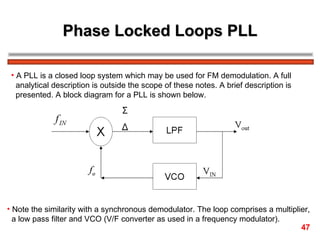
The document discusses frequency modulation (FM) in 3 sentences:
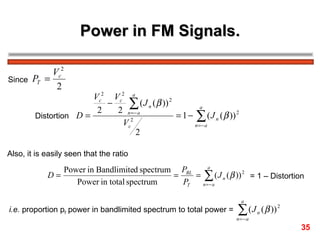
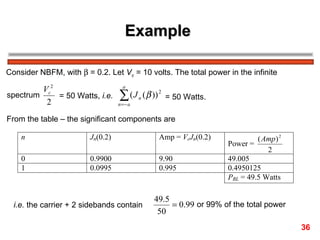
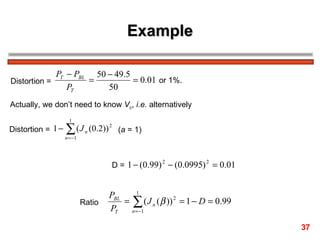
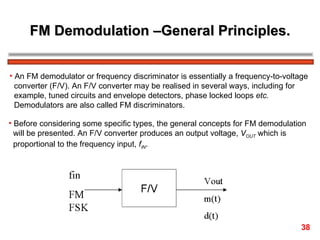
FM encodes information by varying the frequency of a carrier signal in proportion to an input message signal; the FM spectrum contains a carrier signal and an infinite number of sidebands whose amplitudes are determined by Bessel functions of the modulation index; narrowband FM uses low modulation indices producing a carrier and two dominant sidebands, while wideband FM uses higher indices creating more significant sidebands and a larger bandwidth.