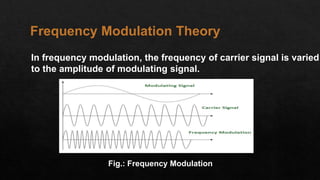
This document provides an overview of frequency modulation (FM). It defines FM as a modulation technique where the amplitude of the carrier signal remains constant while its frequency varies according to the modulating signal. The document discusses the need for modulation, classification of modulation techniques, FM theory, generation of FM signals in the lab using a function generator and FM modulator kit, experimental input/output waveshapes, advantages/disadvantages of FM, and applications of FM such as FM radio broadcasting, telemetry, radar, and music synthesis.