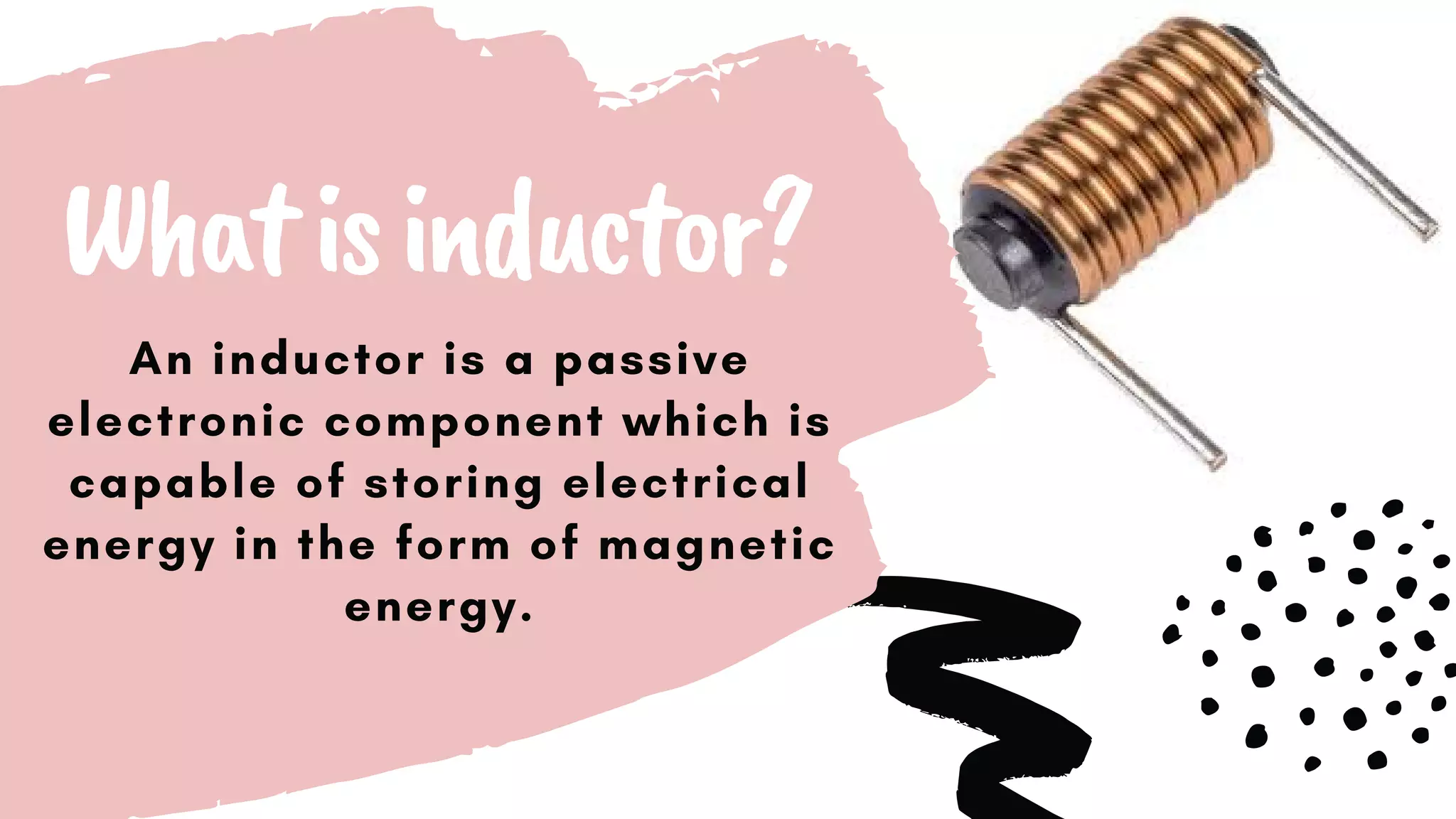
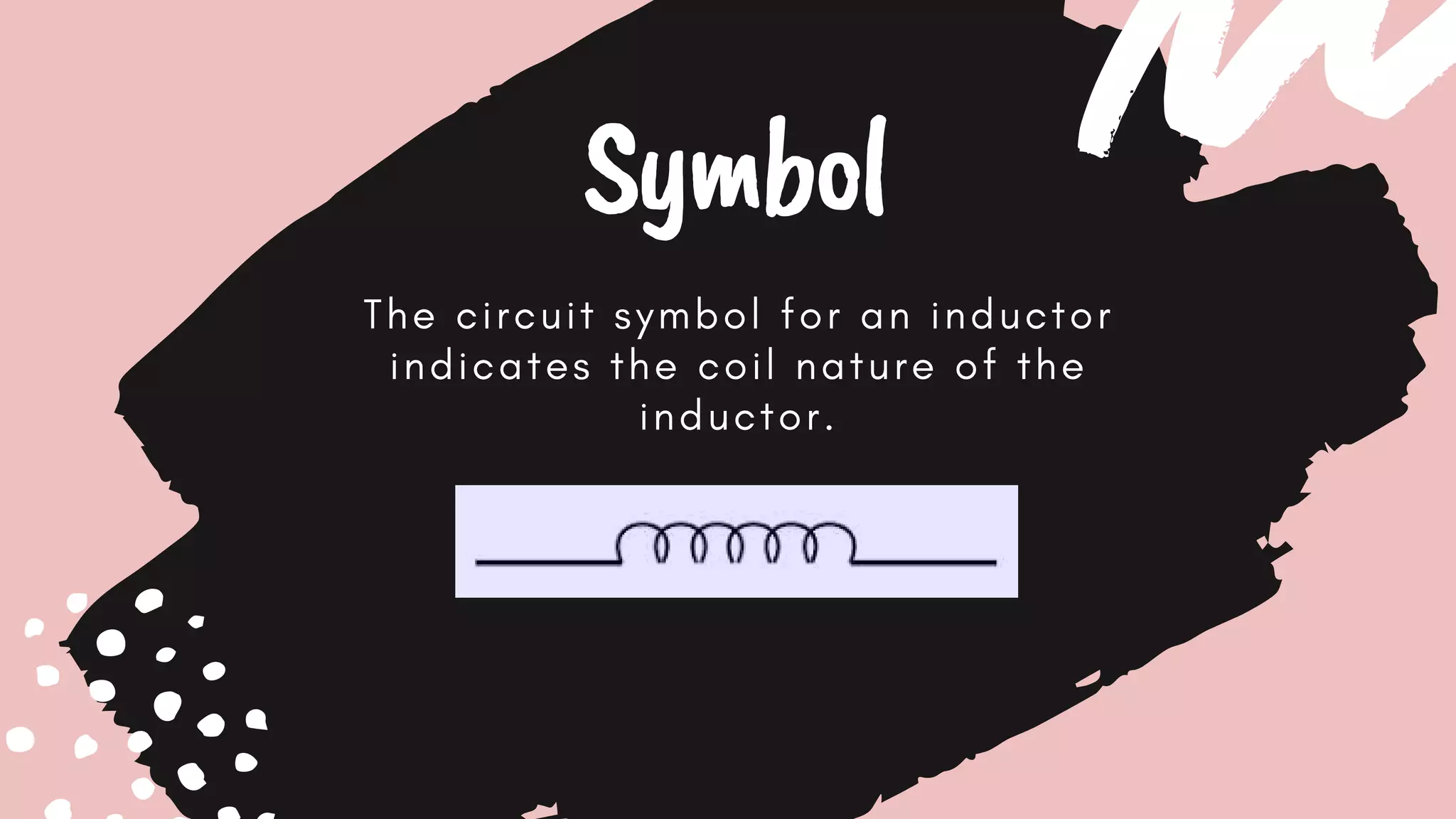
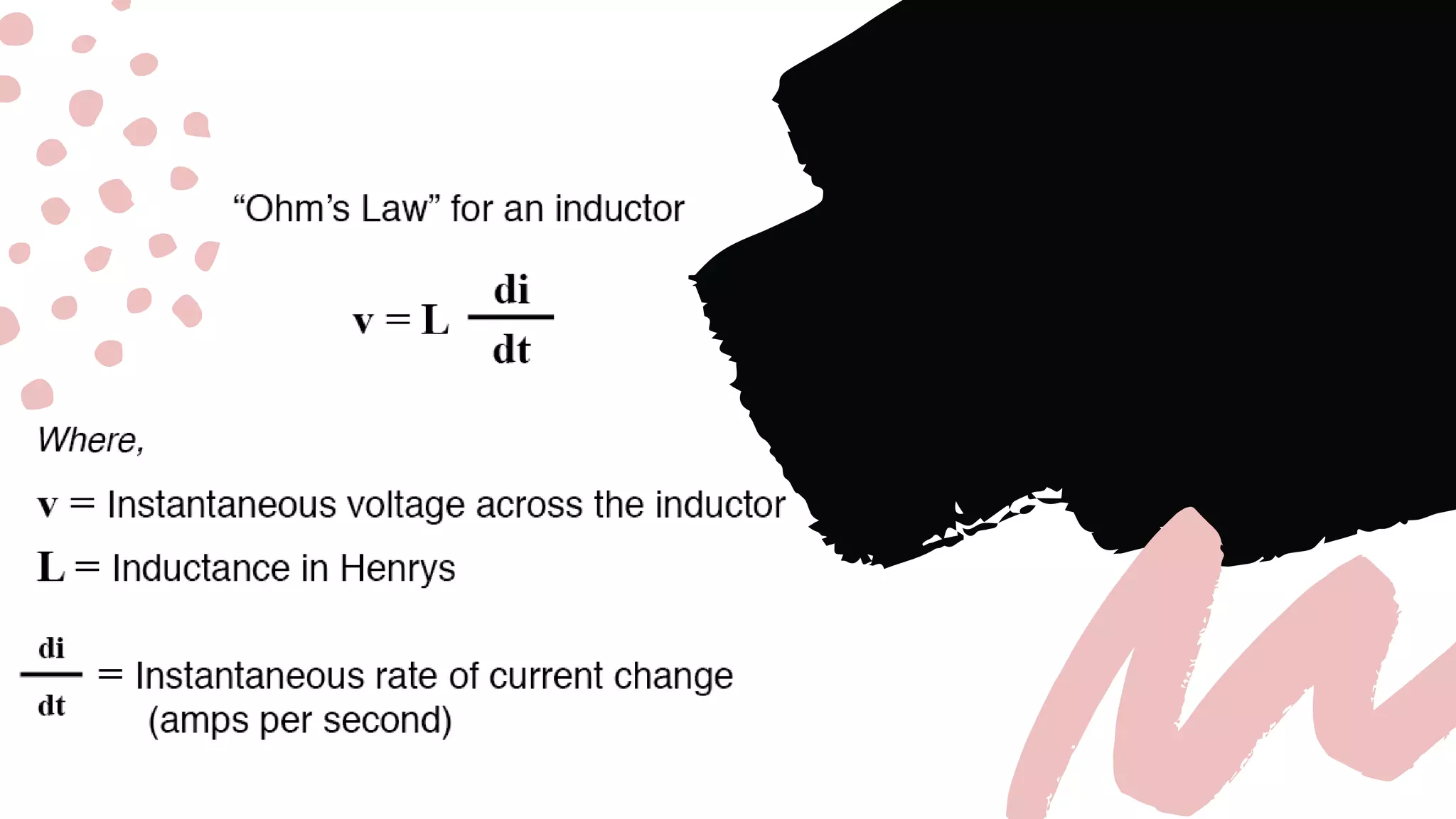
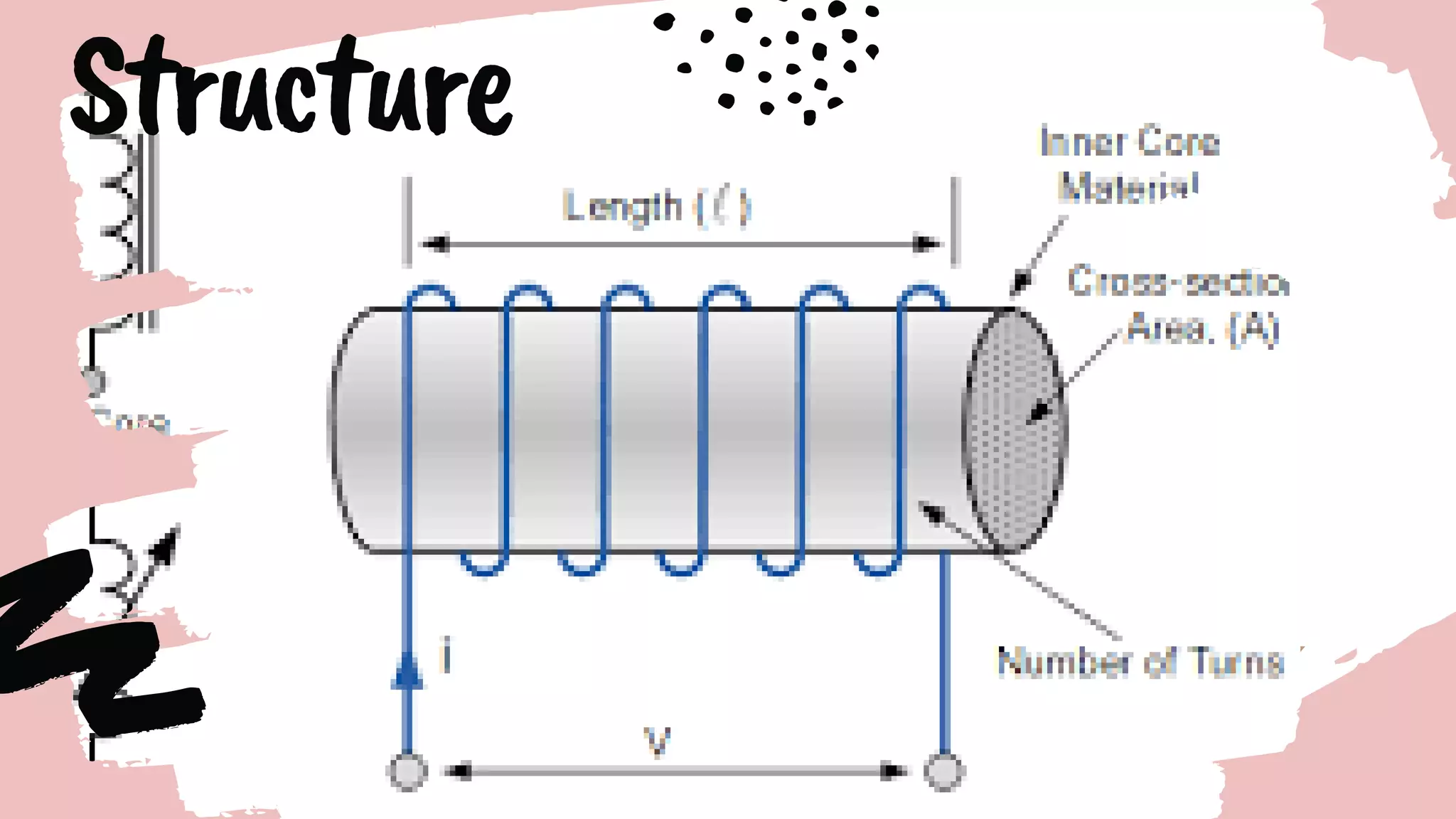
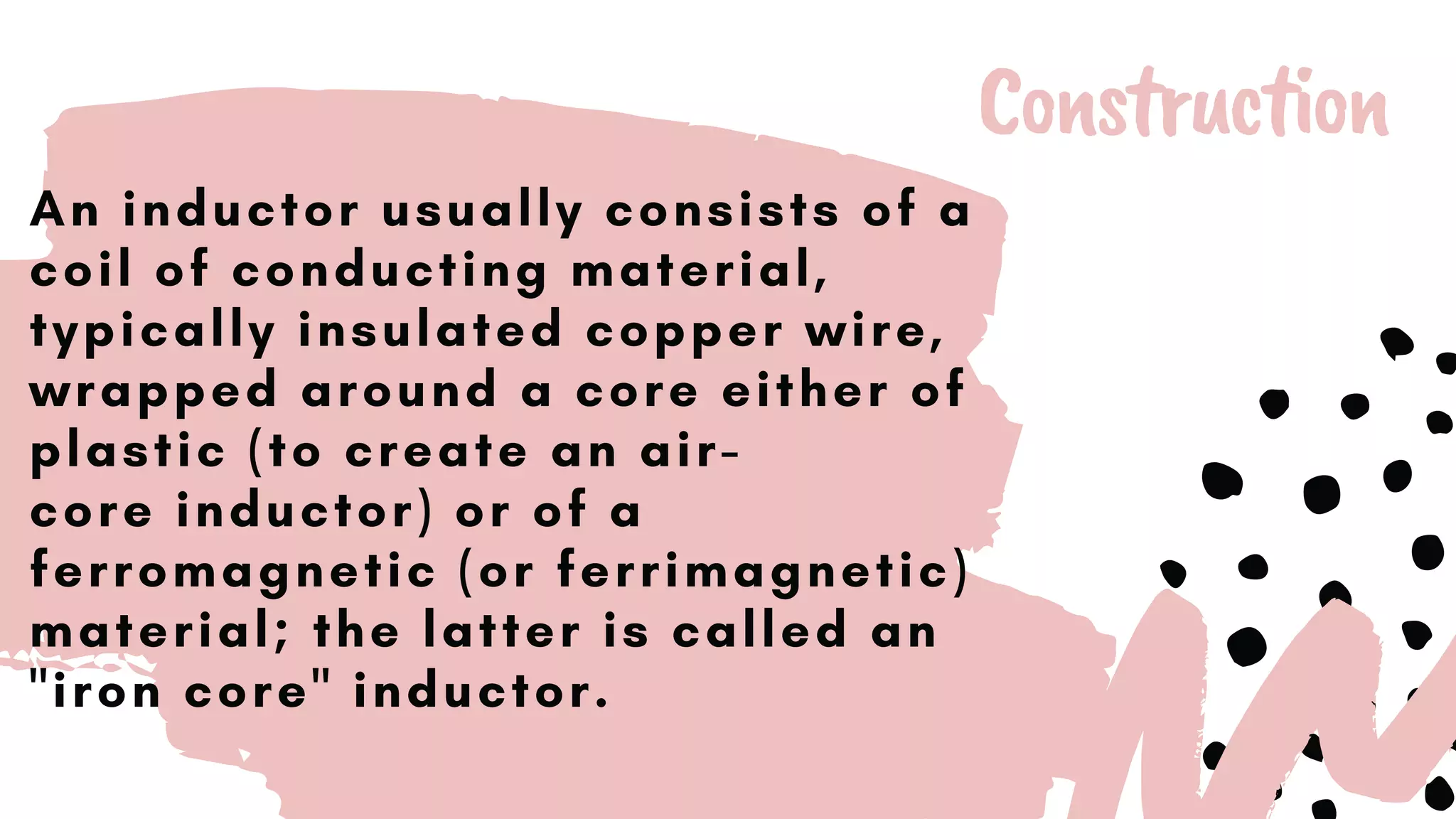
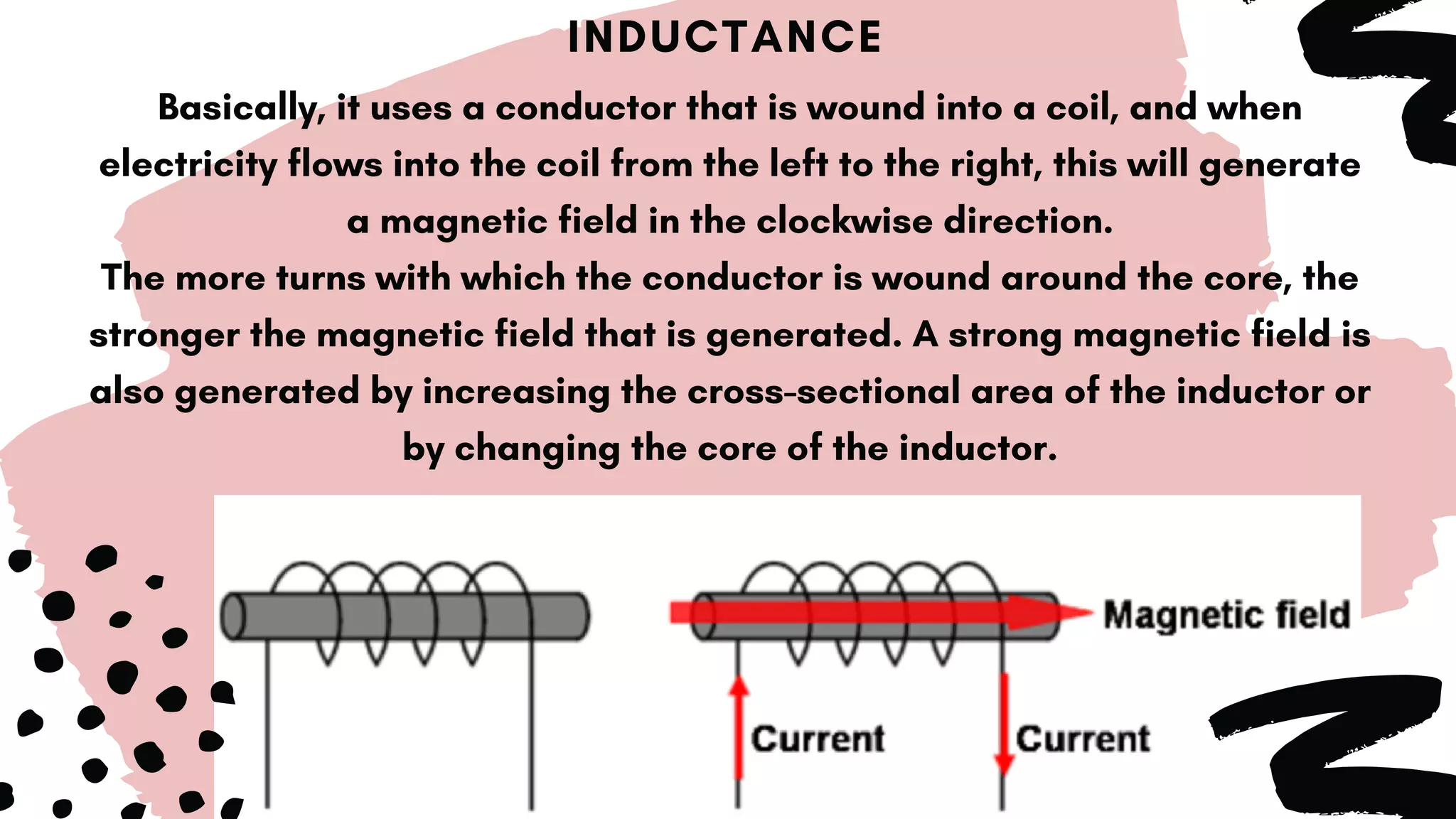
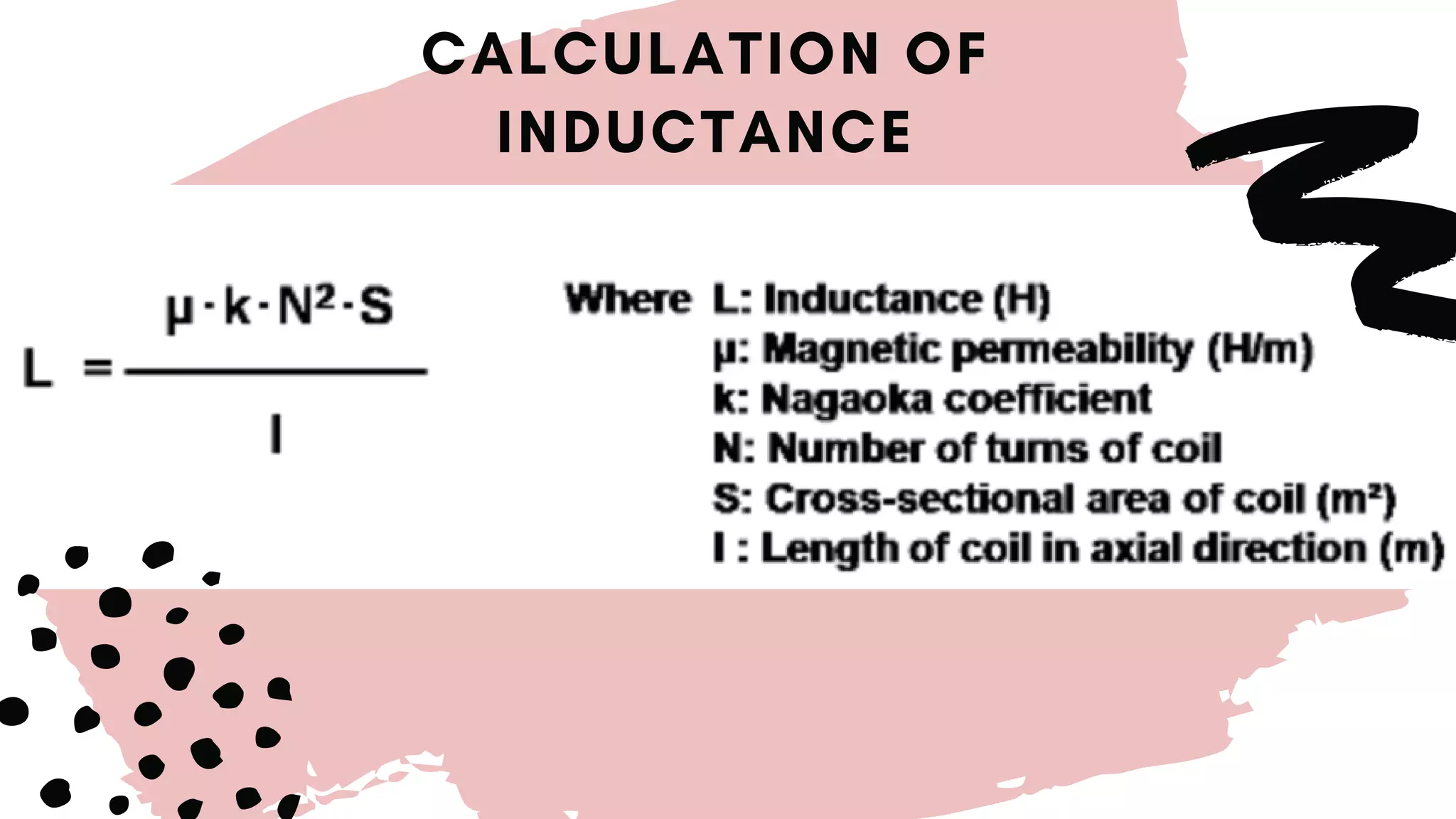
This document discusses inductors, which are passive electronic components that store electrical energy as magnetic energy. It defines an inductor as a coil of conducting material, typically copper wire, wrapped around a core. The more turns of the coil and the stronger the magnetic field generated. Inductors are used in applications such as filters, sensors, and transformers. They work by generating a magnetic field when electricity flows through the coil.