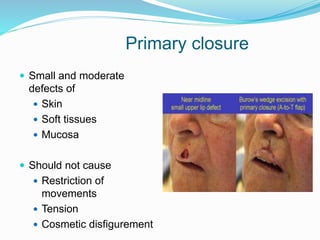
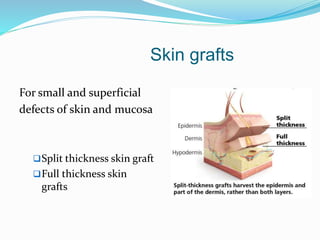
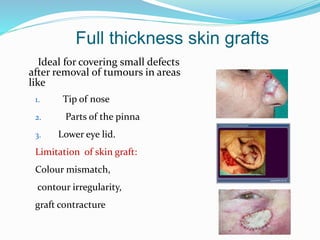
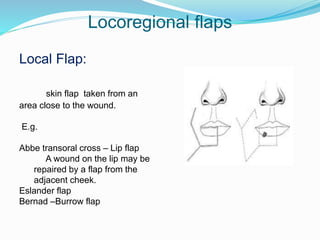
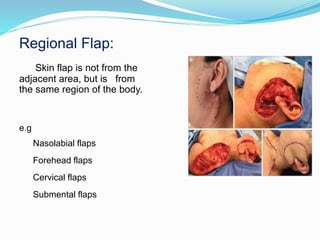
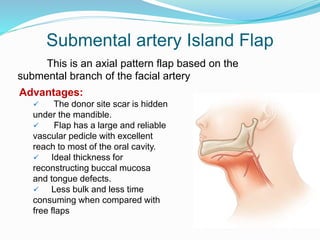
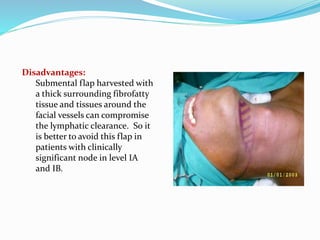
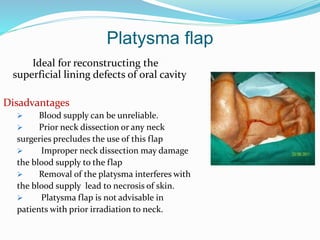
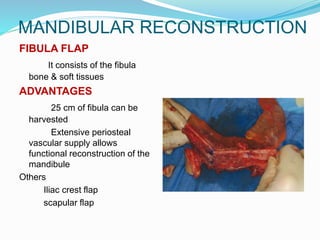
This document discusses various reconstructive surgery options for restoring form and function after defects in the head and neck region. It outlines a reconstructive ladder ranging from primary closure and skin grafts for small defects, to local and regional flaps, myocutaneous flaps, and free flaps for more complex reconstructions. Key flaps discussed include the pectoralis major flap, fibula flap, radial forearm flap, and anterolateral thigh flap. Patient factors, defect characteristics, and the goal of restoring oral competence, speech, and swallowing are considered in surgical planning. The conclusion emphasizes that reconstructive surgery is essential for improving head and neck cancer survivors' quality of life.