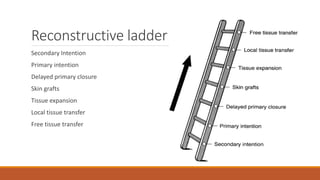
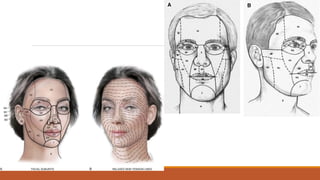
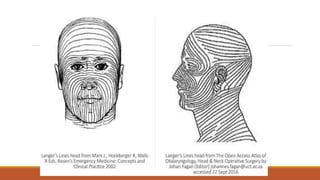
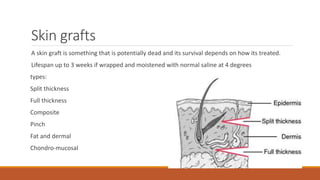
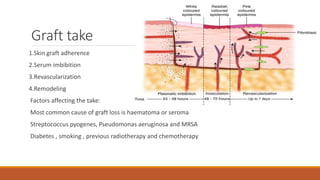
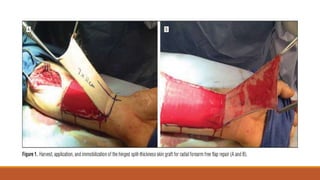
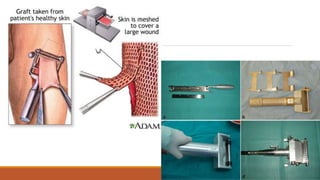
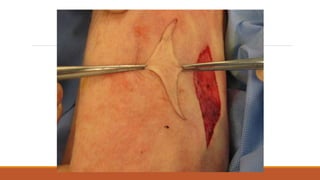
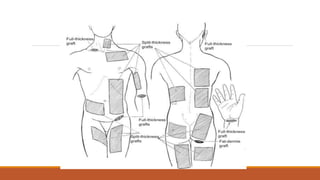
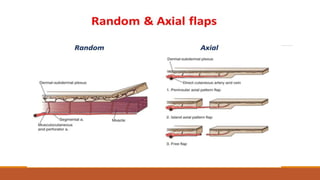
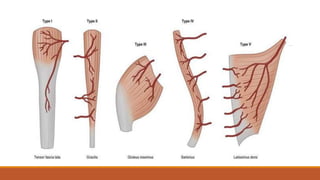
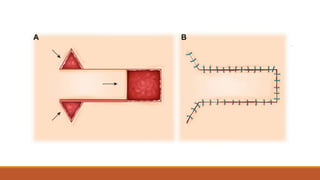
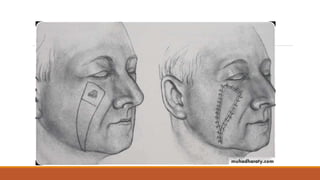
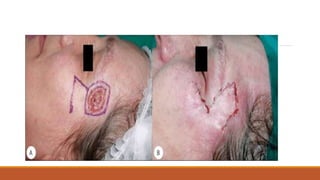
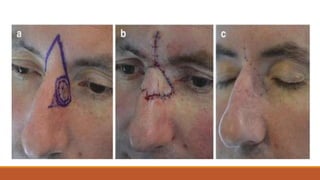
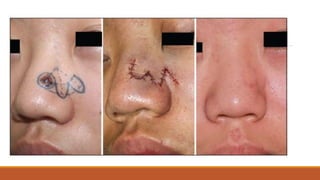
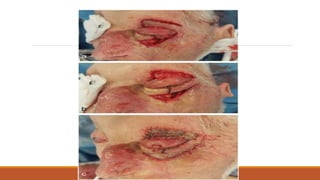
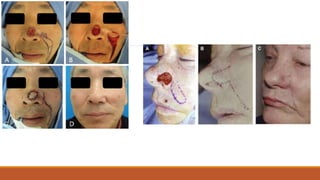
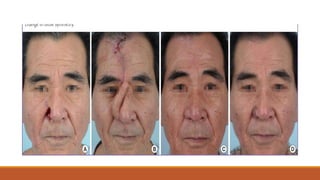
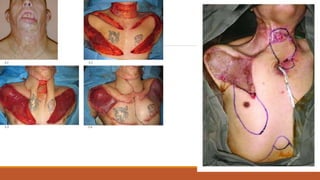
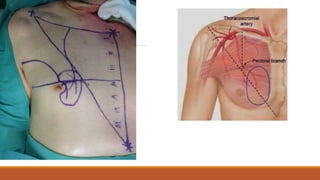
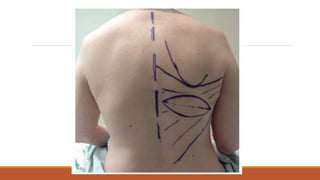
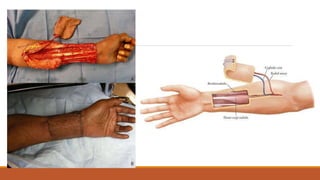
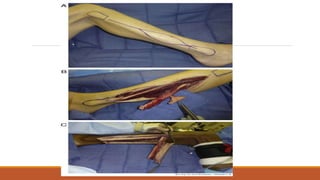
This document provides an overview of reconstruction techniques in head and neck surgery. It discusses Gillie's principles of reconstruction and the reconstructive ladder. It describes various techniques including skin grafts, local flaps such as nasolabial and forehead flaps, distant flaps such as deltopectoral and latissimus dorsi flaps, and free tissue transfers including radial forearm and fibula flaps. It discusses factors to consider for each technique such as blood supply, advantages, disadvantages and appropriate applications in head and neck reconstruction.