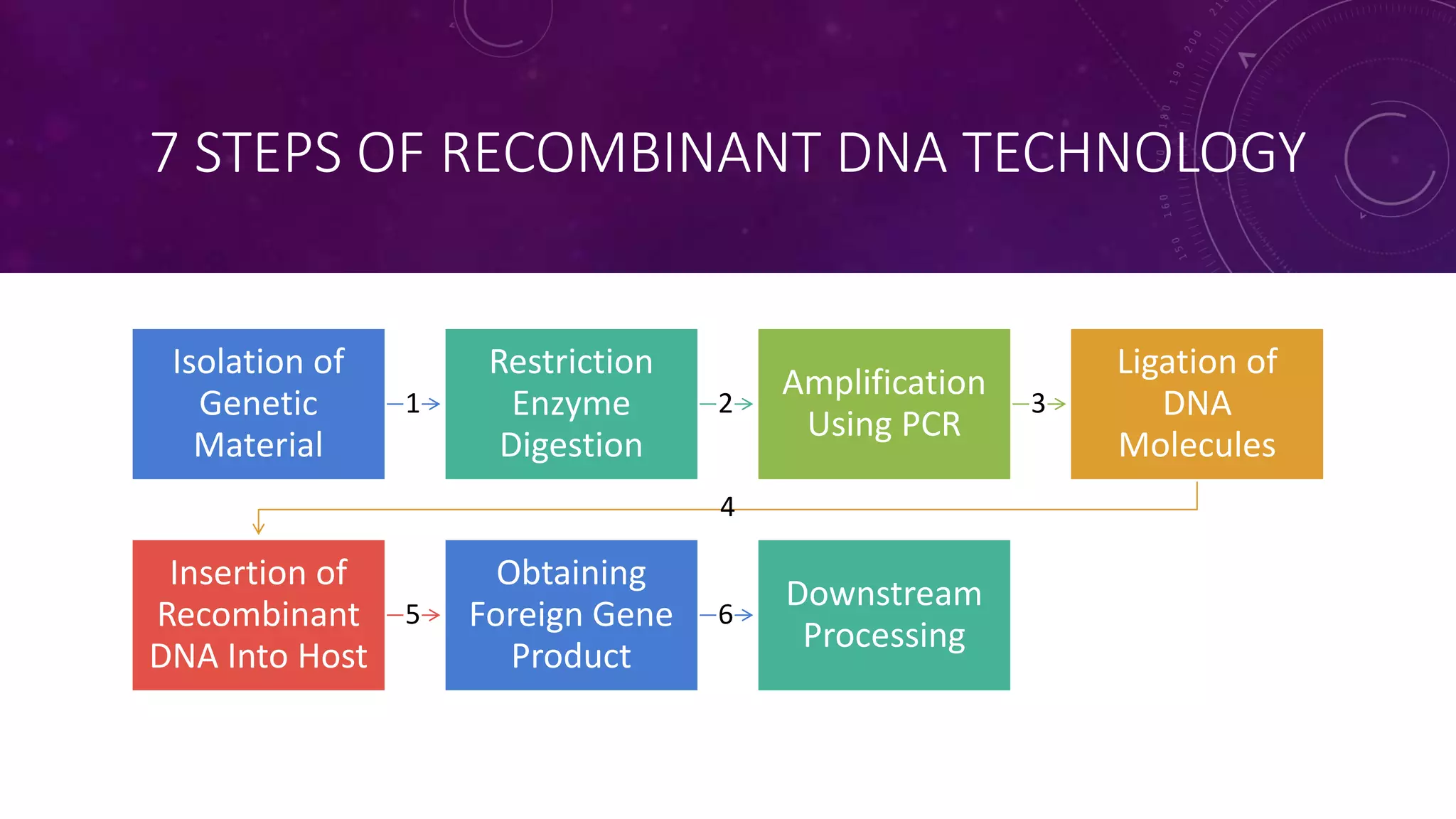
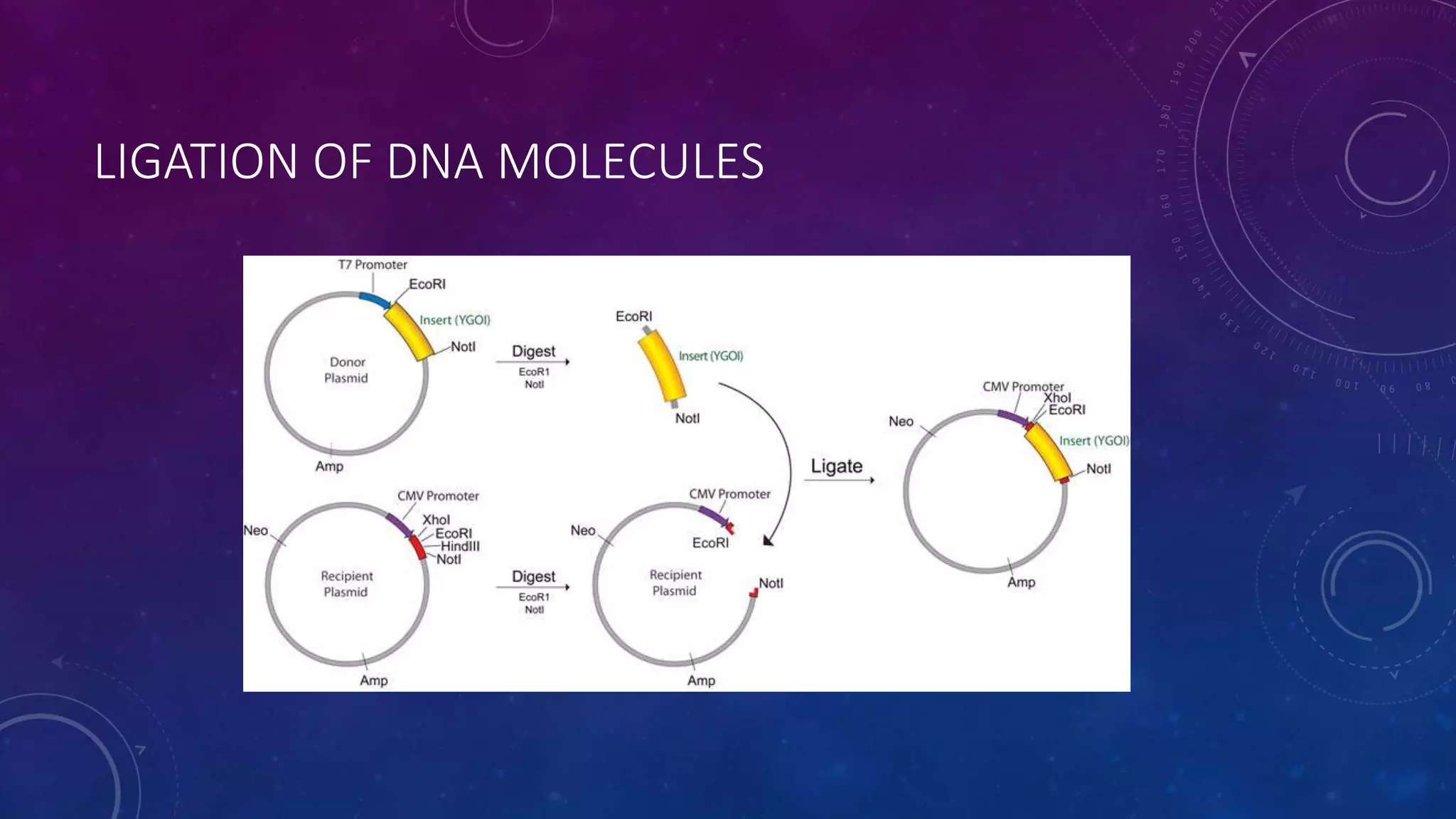
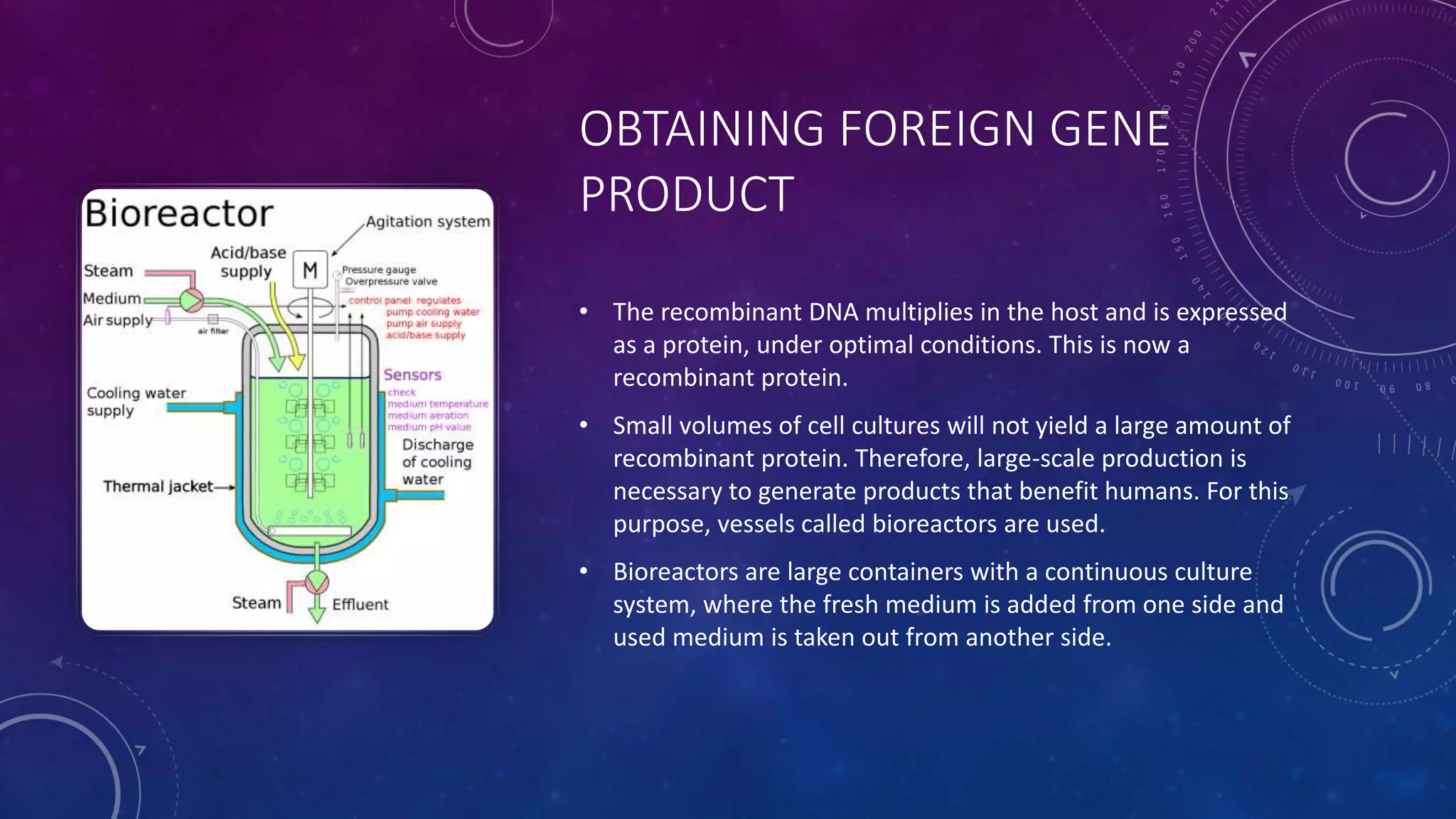
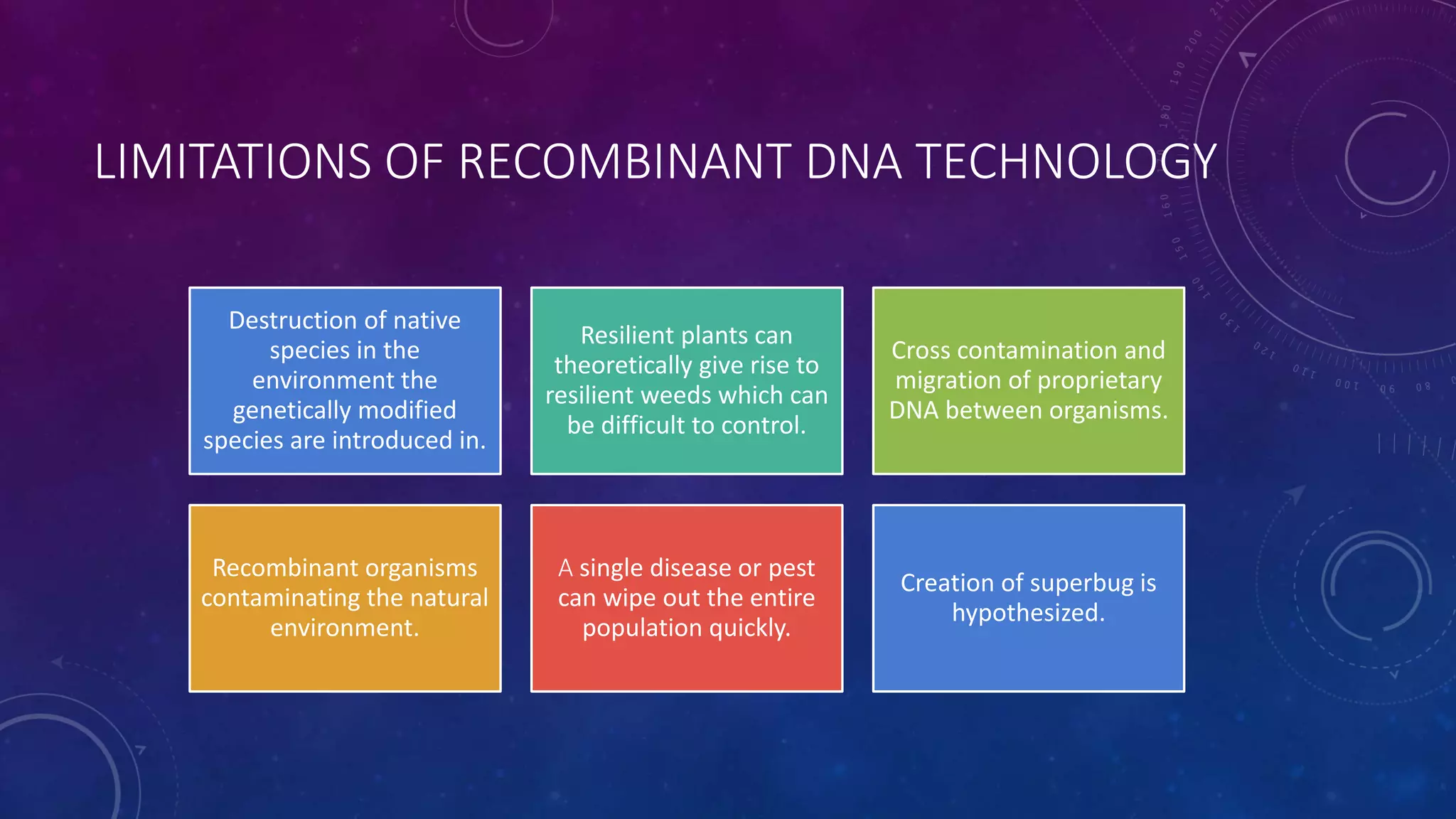
Recombinant DNA technology involves combining DNA molecules from two different sources into one molecule by cutting and joining DNA strands. It includes three main tools - restriction enzymes, vectors, and host organisms. Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sites, vectors carry recombinant DNA, and host organisms allow the expression of inserted genes. The process involves isolating DNA, cutting with restriction enzymes, joining DNA segments by ligation, inserting into a host, and amplifying the target gene product. It has many applications in research, medicine, and industry, but also poses limitations such as environmental impacts and creating disease-causing organisms.