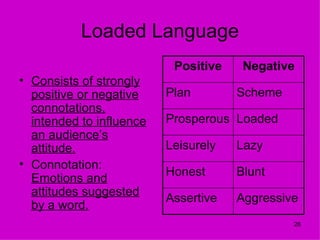
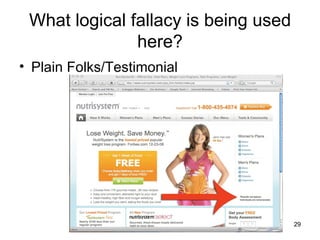
The document discusses common propaganda techniques such as logical fallacies, emotional appeals, and misleading language that are often used in advertising and political persuasion. It provides examples of logical fallacies like circular reasoning, overgeneralization, and false analogy. Additionally, it examines emotional appeals like fear, pity, and bandwagoning that aim to manipulate attitudes.