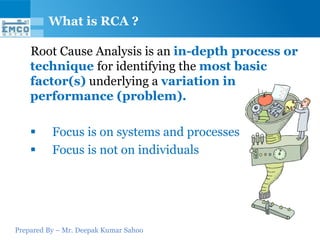
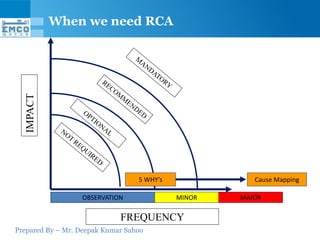
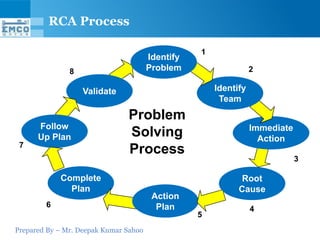
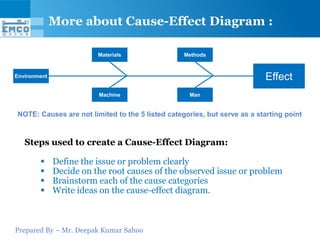
Here are some potential why-why analyses for the questions provided:
Why people turnover is high in EMCO?
- Employees are overworked
- Pay/benefits are not competitive
- No growth opportunities
- Poor management/culture
Why workload is more in QF?
- Inadequate staffing levels
- Processes not optimized
- Unclear responsibilities
- Too many changes/priorities
Why PPM in QF is not effective?
- Lack of commitment from leadership
- No accountability for completion
- Tasks not prioritized
- Resources/training insufficient
Why Rajnikant is too famous?
- Excellent acting skills
- Charismatic