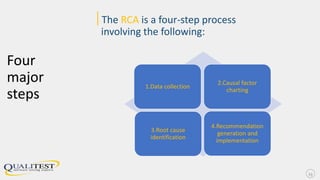
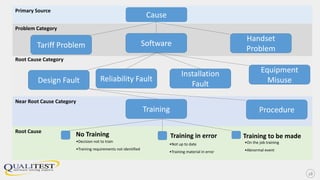
This document provides an overview of root cause analysis (RCA). RCA is a process used to investigate events that impact safety, quality, reliability and production. It involves collecting data, identifying causal factors, determining root causes, and generating recommendations. Root causes are underlying issues that management can control and for which effective recommendations can be made to prevent recurrence. The document outlines the four major steps of RCA and provides examples of using RCA to improve software processes, support agile development, and address issues with third party integrations.