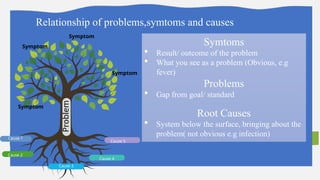
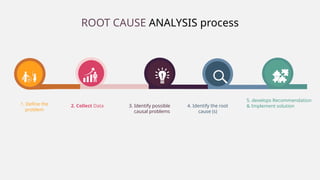
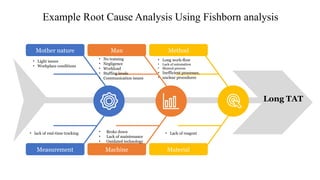
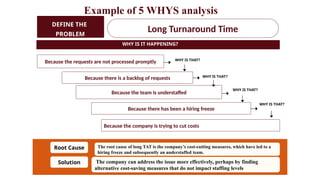
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic method to identify and address the underlying causes of problems, rather than just their symptoms, enabling effective long-term solutions. It involves defining the problem, collecting data, identifying causal factors, and implementing corrective actions, utilizing tools like the 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams. RCA helps organizations improve processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by transforming problems into opportunities for continuous improvement.