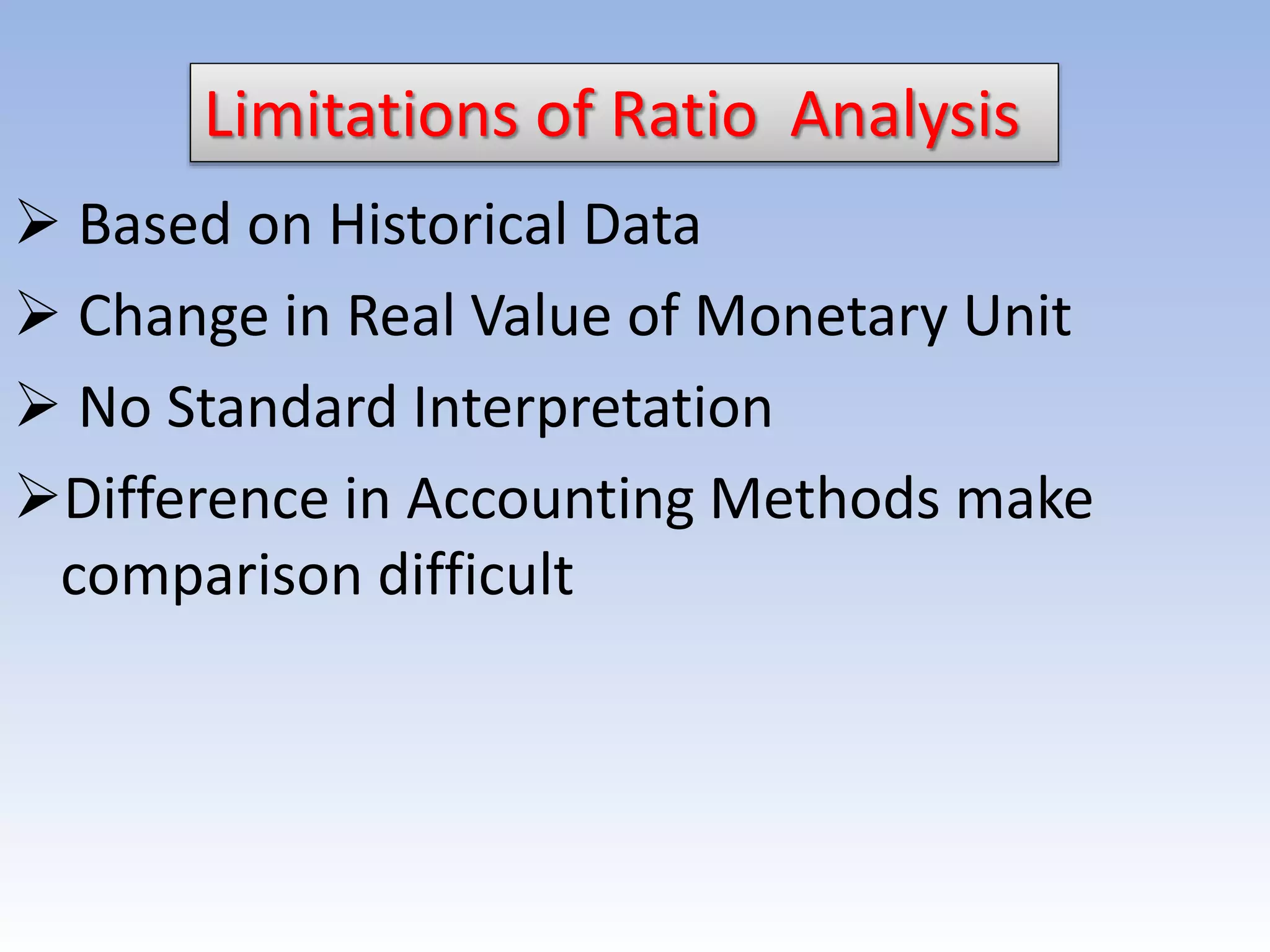
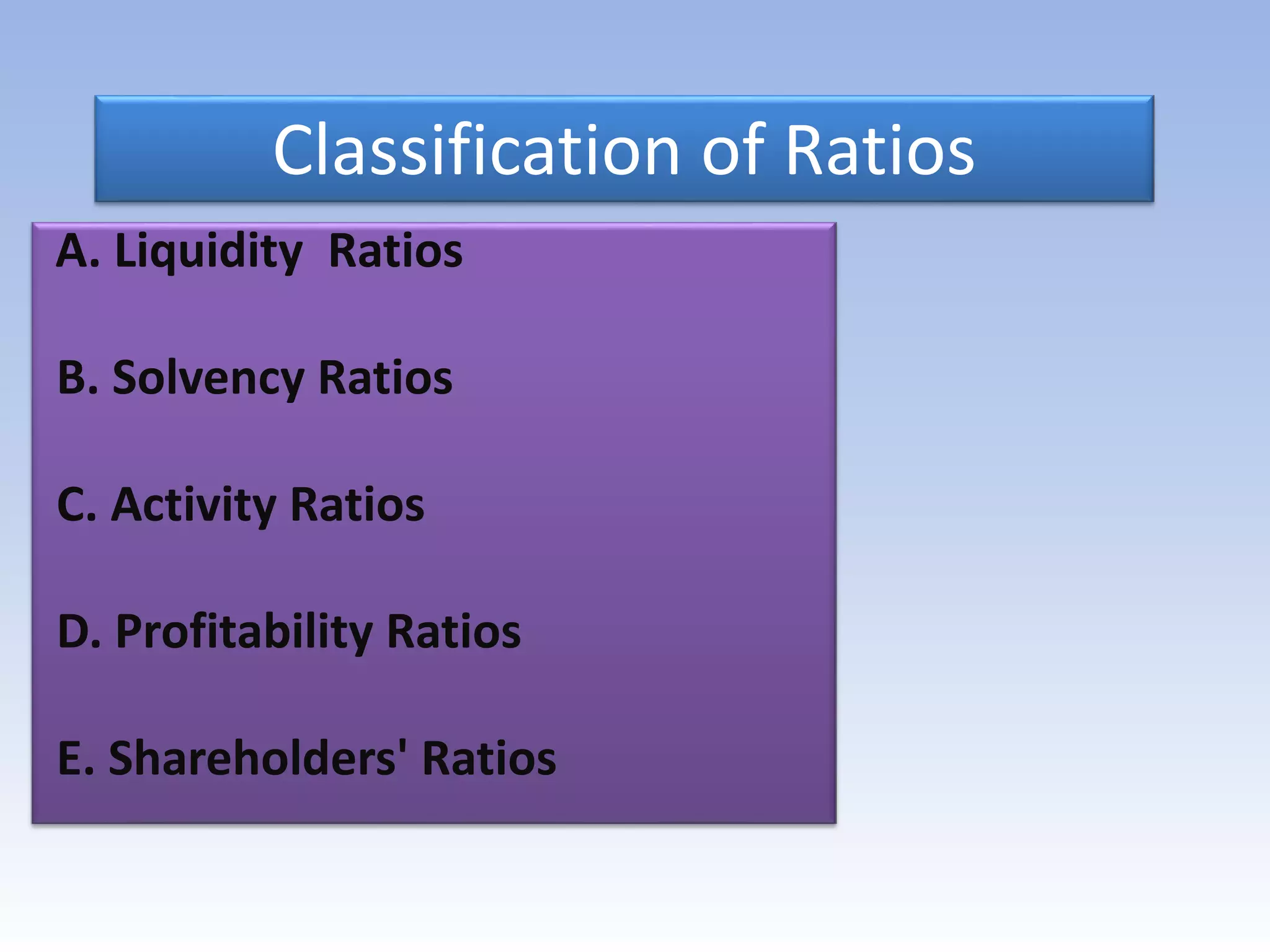
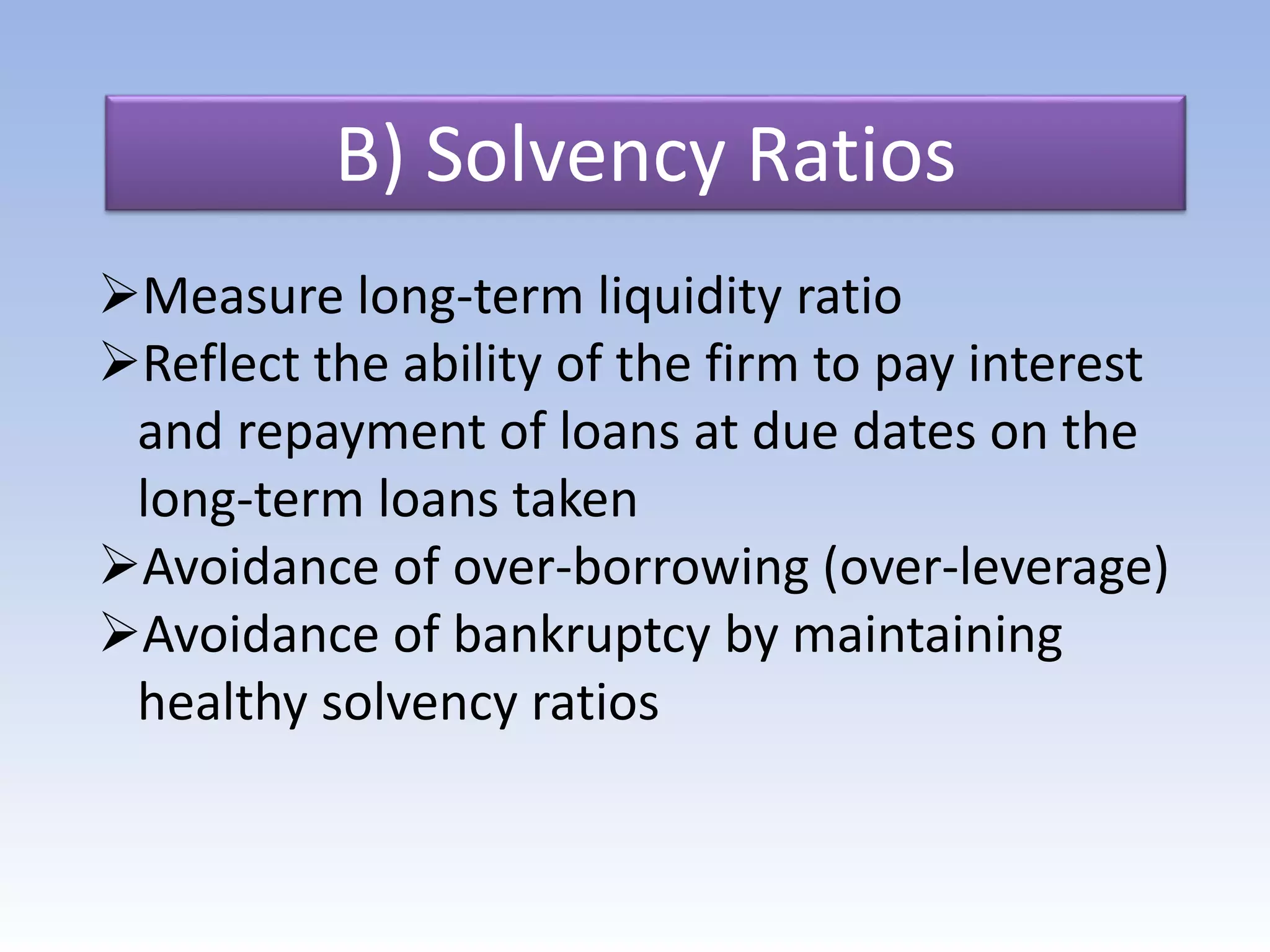
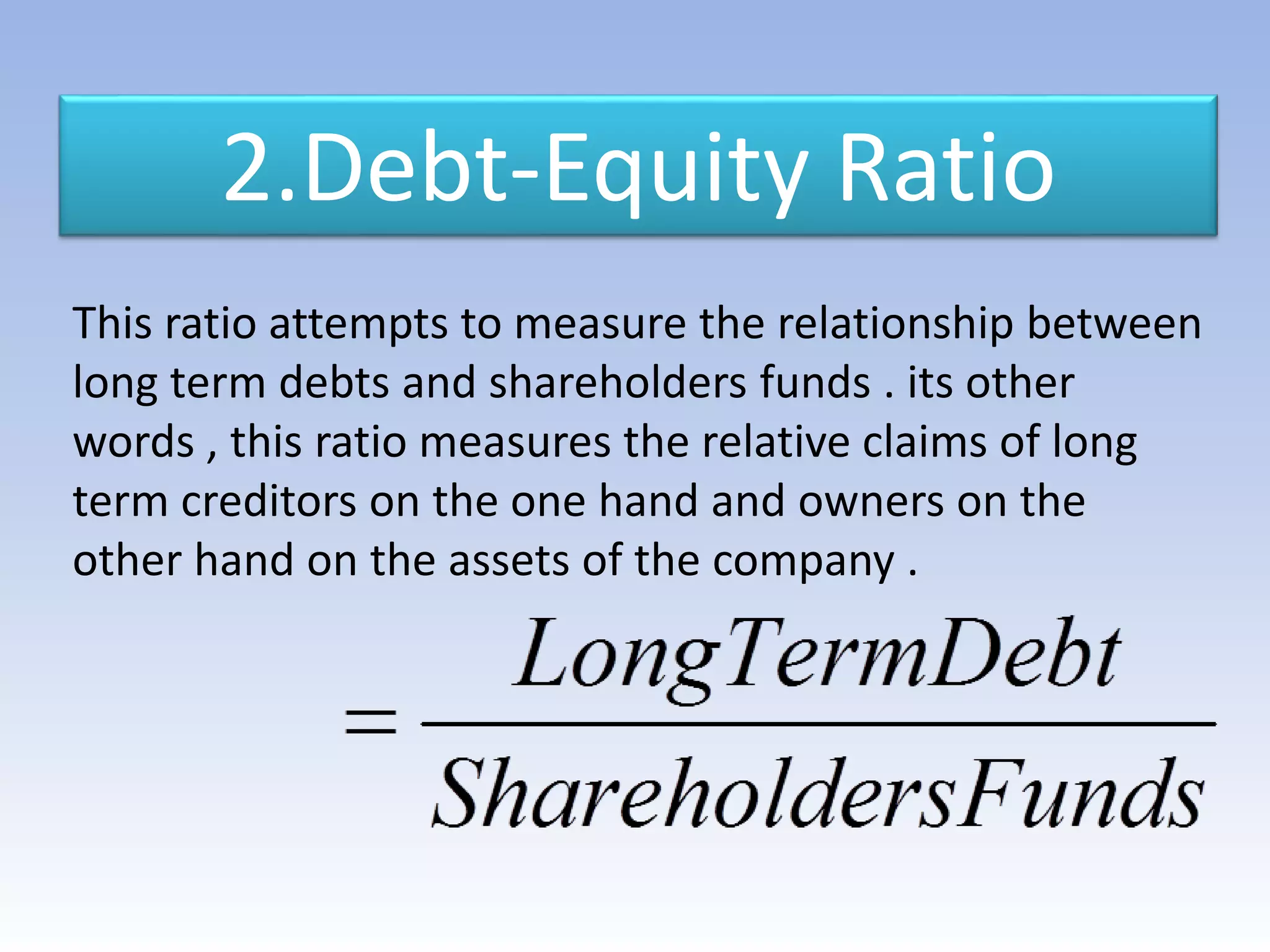
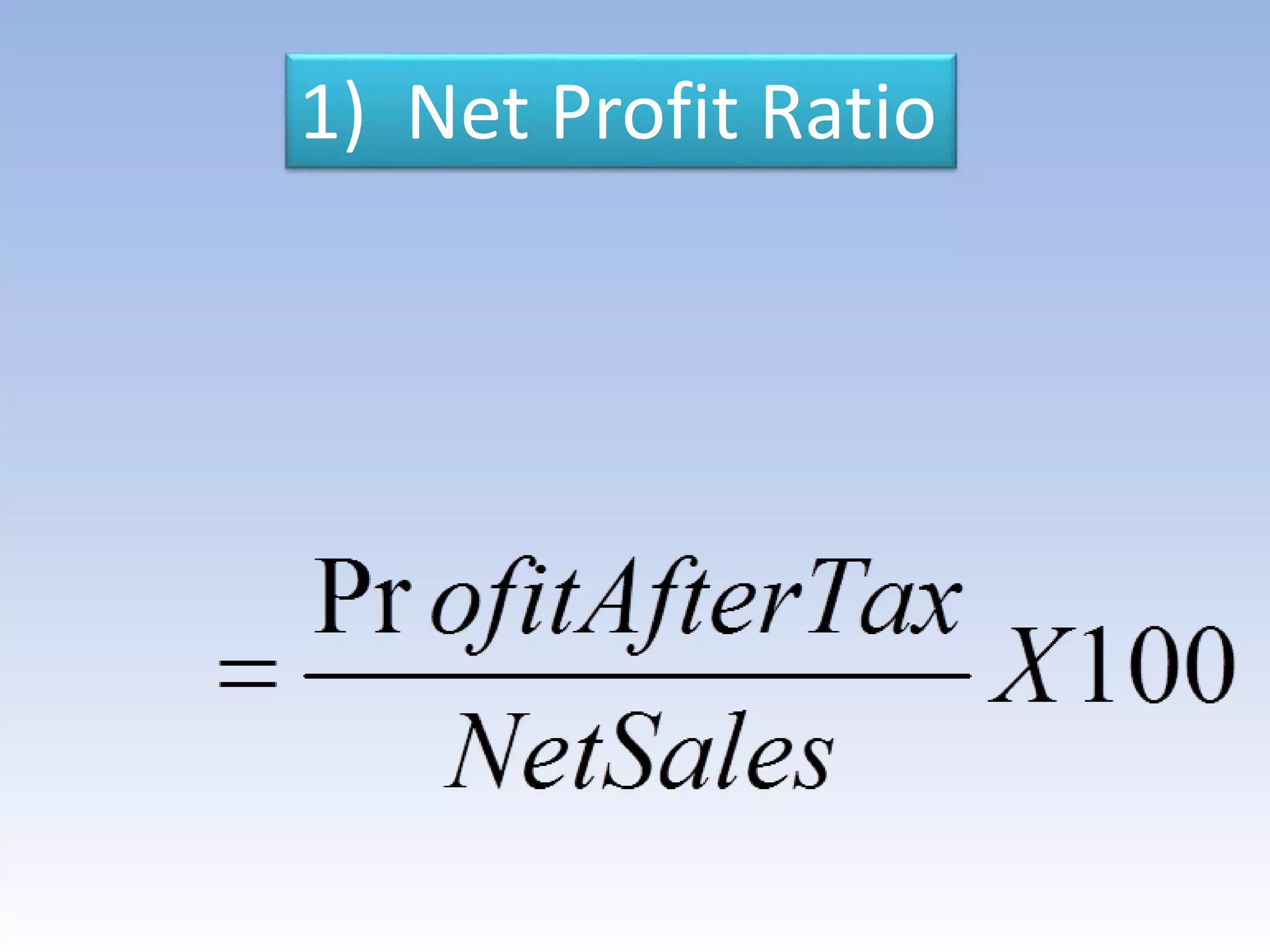
The document discusses ratio analysis as a method to evaluate an organization's financial strengths and weaknesses through quantitative relationships in its balance sheet and income statement. It outlines the purposes, advantages, and limitations of ratio analysis, and categorizes the various types of ratios into liquidity, solvency, activity, profitability, and shareholders' ratios, detailing their significance and calculation methods. Key ratios highlighted include current ratio, debt-equity ratio, inventory turnover ratio, and earnings per share, illustrating how they assess financial health and operational efficiency.