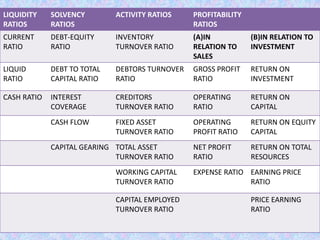
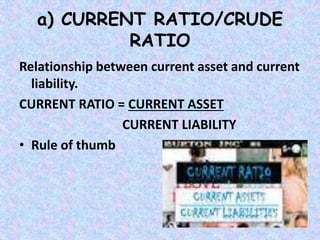
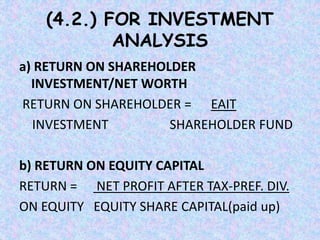
This document discusses various types of financial ratios used for ratio analysis. It defines ratio analysis as a technique used to analyze and interpret financial statements to help with decision making. It then covers different types of ratios including liquidity ratios, activity ratios, solvency ratios, profitability ratios, and market test/valuation ratios. Specific ratios discussed include current ratio, quick ratio, inventory turnover ratio, debt-equity ratio, return on equity, earnings per share, and others. The document provides formulas and explanations for calculating and interpreting these various financial ratios.