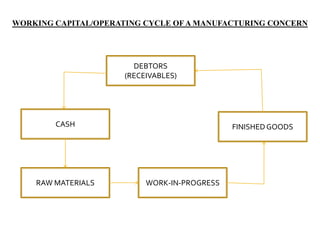
This document discusses factors that affect working capital requirements for businesses. It defines working capital and distinguishes between gross and net working capital. Some key factors that influence working capital needs include the nature of the business, size, production processes, seasonality, credit policies, and business growth rates. Manufacturing businesses tend to require more working capital due to longer production cycles. Faster inventory turnover and less generous credit terms also reduce working capital needs.