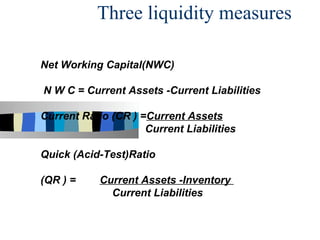
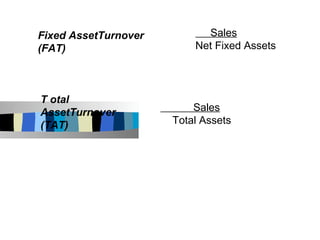
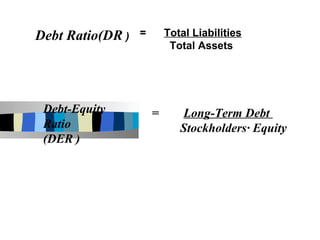
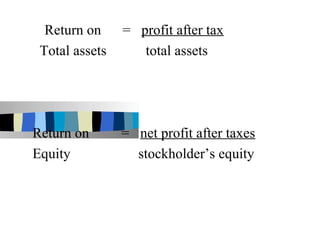
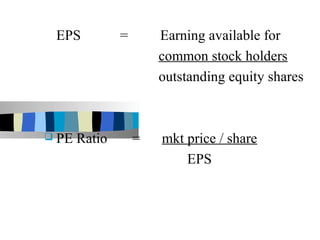
The document discusses ratio analysis and its importance in analyzing financial statements. Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios to assess a firm's performance and financial position. Ratios simplify accounting figures and are helpful for future forecasting and measuring profitability. The document then discusses limitations of ratios and different types of ratios including liquidity, activity, debt, and profitability ratios. It provides examples of specific ratios used to analyze different aspects of a company's financial health.