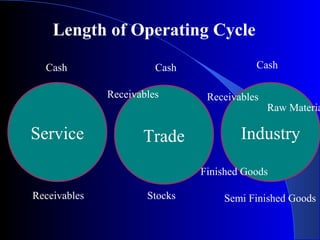
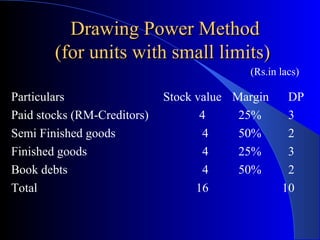
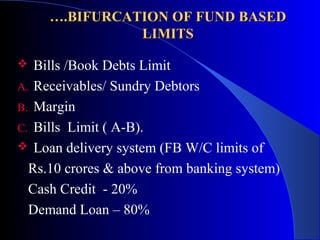
The document provides a comprehensive overview of working capital assessment, detailing its definition, sources, and calculation methods, including gross and net working capital. It discusses the components of current assets, the operating cycle, and various assessment methodologies, such as turnover and drawing power methods. Additionally, it highlights important ratios and exposure norms for different business categories related to working capital financing.