Embed presentation


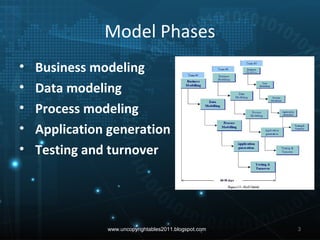






Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an incremental software development process used to build systems within 60-90 days. It involves business, data, and process modeling, application generation, and testing. RAD is based on agile methods like Scrum and extreme programming and enables quick reviews, constant integration, and flexibility. However, it requires a modularized approach and skilled developers, and is not suitable for small projects or all applications due to higher costs.







