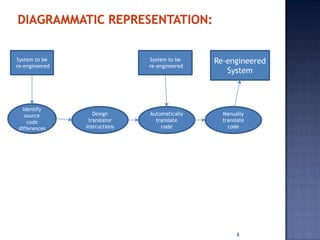
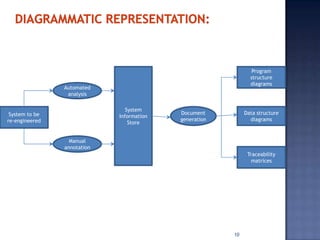
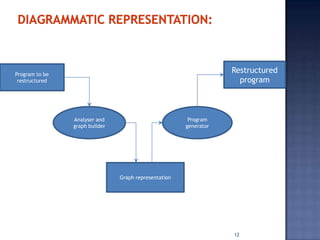
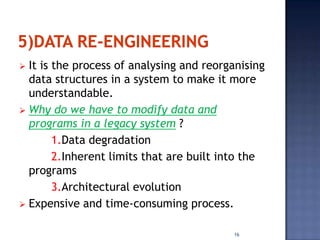
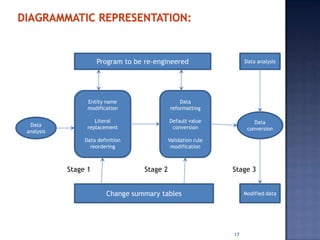
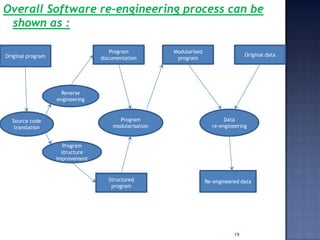
Software re-engineering is a process of examining and altering a software system to restructure it and improve maintainability. It involves sub-processes like reverse engineering, redocumentation, and data re-engineering. Software re-engineering is applicable when some subsystems require frequent maintenance and can be a cost-effective way to evolve legacy software systems. The key advantages are reduced risk compared to new development and lower costs than replacing the system entirely.