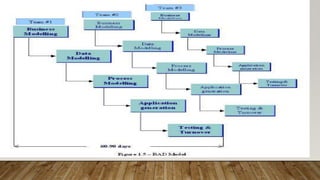
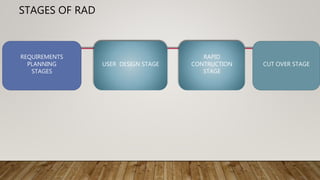
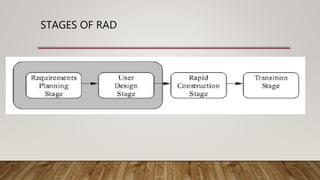
The Rapid Application Development (RAD) model is an incremental software development approach where components are developed in parallel like mini-projects. It focuses on quickly delivering a working prototype to users for early feedback. The RAD process involves requirements planning, user design, construction, and cutover stages. It is best for modularized systems that need to be created quickly within 2-3 months when high-skilled designers and adequate budget are available for modeling and code generation. Key benefits are reduced time-to-market and early user reviews, while high dependency on modeling skills is a disadvantage.