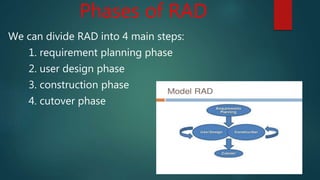
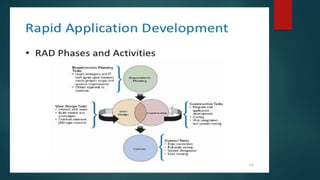
Rapid Application Development (RAD) is an iterative software development process that aims to develop software quickly. It was developed by IBM in the 1980s. RAD uses component-based development, with multiple teams working in parallel on discrete components. The RAD process has four phases: requirement planning, user design, construction, and cutover. In the requirement planning phase, user needs are discussed. The user design phase involves interactive modeling and prototyping. Construction focuses on programming and testing. Cutover implements the new system and trains users. RAD allows for faster delivery but requires skilled teams and commitment to its rapid cycles.