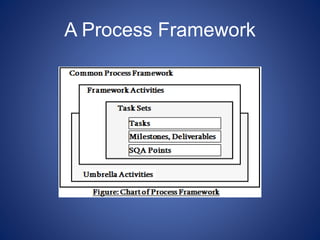
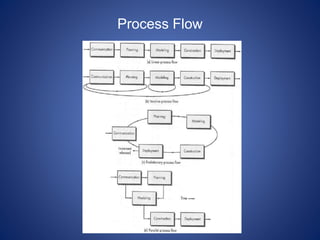
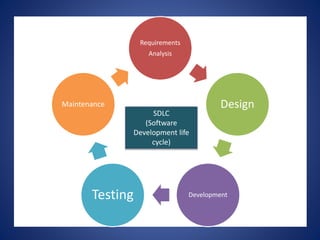
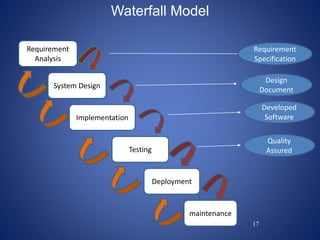
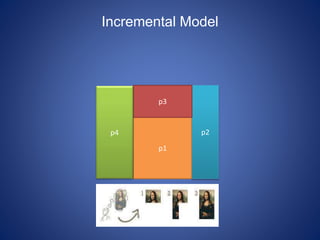
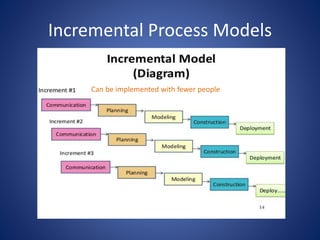
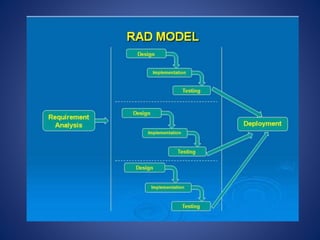
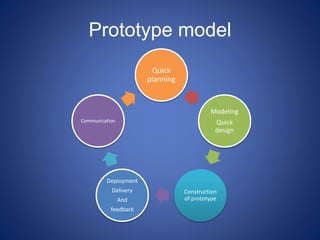
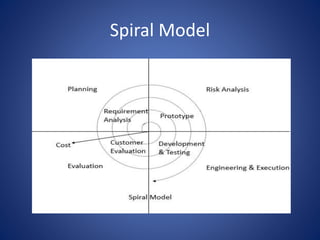
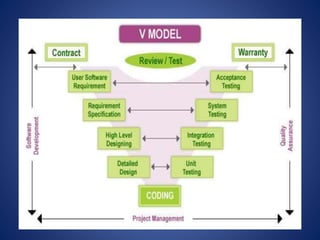
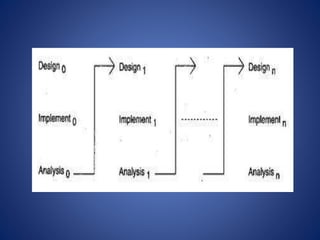
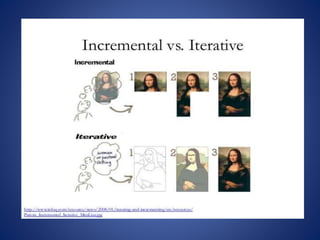
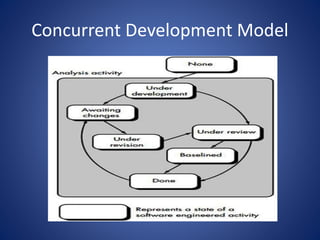
This document discusses software process models. It begins by defining a software process as a structured set of activities required to develop software, including specification, analysis, design, implementation, validation, and evolution. It then describes several prescriptive process models: the waterfall model executes phases sequentially; incremental and evolutionary models iterate phases; and concurrent models perform phases in parallel. The document evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of each model to determine the most appropriate approach based on project requirements and risks.