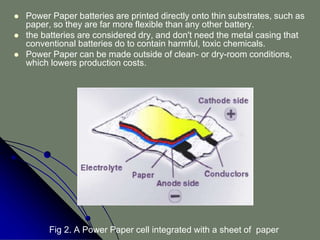
The document describes an ultra-thin, flexible organic radical battery called ORB that is made from cellulose and can power portable electronic devices. The battery is printed directly onto paper substrates using conductive inks, which allows it to be very thin, flexible, and inexpensive to produce. It generates 1.5 volts and can be recharged in about 30 seconds. Potential applications include powering smart cards, medical devices, wearable electronics, and more, since the batteries can be shaped as needed and integrated directly into products.