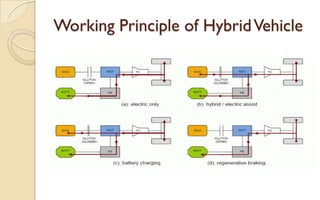
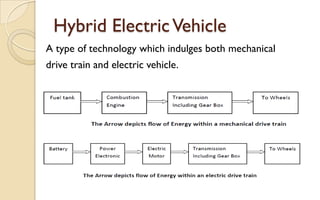
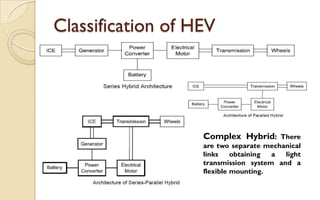
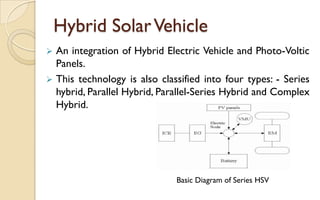
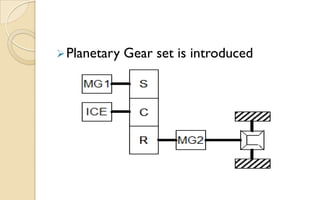
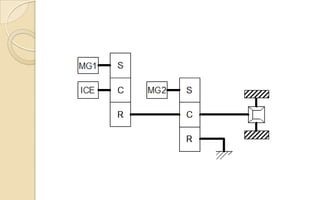
The document discusses the evolution and technology of hybrid vehicles, including the working principles and classifications such as hybrid electric vehicles, hybrid solar vehicles, and plug-in hybrids. It highlights the Toyota Prius as a case study, outlining its generations, benefits, challenges, and advancements in battery technology. The summary also addresses the advantages and drawbacks of hybrid vehicles compared to traditional internal combustion engine cars.