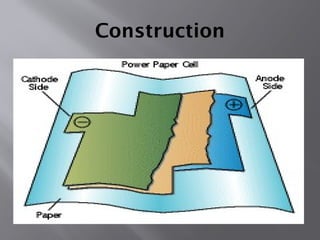
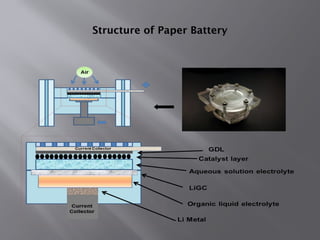
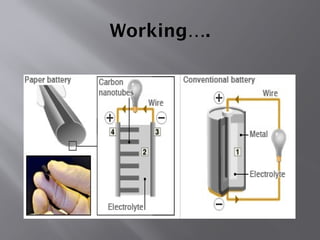
The document discusses paper batteries, which are flexible, ultra-thin energy storage devices made from cellulose and carbon nanotubes, combining the functions of a traditional battery and supercapacitor. It highlights their principles, applications in medical devices and electronics, advantages like being non-toxic and flexible, as well as limitations such as low strength and high production costs. The future scope suggests their potential use in portable power systems and biomedical applications.