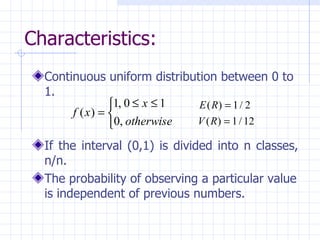
This document discusses random number generation and properties of pseudo-random numbers. It covers techniques for generating pseudo-random numbers like linear congruential methods and combined congruential methods. It also discusses hypothesis tests that can be used to test for uniformity and independence of random numbers, such as the frequency test, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, chi-square test, runs test, and autocorrelation test.







![Other Tests Good’s Serial Test [1953, 1967] Median-Spectrum Test [Cox and Lewis, 1966, Durbin, 1967] A Variance Heterogeneity Test [Cox and Lewis, 1966] Even with all these tests, it is still no guarantee that randomness is achieve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/randomnumbergeneration-110109215334-phpapp01/85/Random-number-generation-12-320.jpg)