Decision theory blockwood
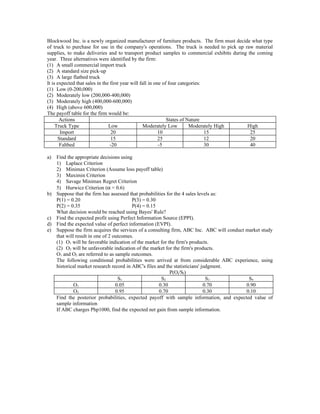
- 1. Blockwood Inc. is a newly organized manufacturer of furniture products. The firm must decide what type of truck to purchase for use in the company's operations. The truck is needed to pick up raw material supplies, to make deliveries and to transport product samples to commercial exhibits during the coming year. Three alternatives were identified by the firm: (1) A small commercial import truck (2) A standard size pick-up (3) A large flatbed truck It is expected that sales in the first year will fall in one of four categories: (1) Low (0-200,000) (2) Moderately low (200,000-400,000) (3) Moderately high (400,000-600,000) (4) High (above 600,000) The payoff table for the firm would be: Actions States of Nature Truck Type Low Moderately Low Moderately High High Import 20 10 15 25 Standard 15 25 12 20 Faltbed -20 -5 30 40 a) Find the appropriate decisions using 1) Laplace Criterion 2) Minimax Criterion (Assume loss payoff table) 3) Maximin Criterion 4) Savage Minimax Regret Criterion 5) Hurwicz Criterion (α = 0.6) b) Suppose that the firm has assessed that probabilities for the 4 sales levels as: P(1) = 0.20 P(3) = 0.30 P(2) = 0.35 P(4) = 0.15 What decision would be reached using Bayes' Rule? c) Find the expected profit using Perfect Information Source (EPPI). d) Find the expected value of perfect information (EVPI). e) Suppose the firm acquires the services of a consulting firm, ABC Inc. ABC will conduct market study that will result in one of 2 outcomes. (1) O1 will be favorable indication of the market for the firm's products. (2) O2 will be unfavorable indication of the market for the firm's products. O1 and O2 are referred to as sample outcomes. The following conditional probabilities were arrived at from considerable ABC experience, using historical market research record in ABC's files and the statisticians' judgment. P(Oj/SI) S1 S2 S3 S4 O1 0.05 0.30 0.70 0.90 O2 0.95 0.70 0.30 0.10 Find the posterior probabilities, expected payoff with sample information, and expected value of sample information If ABC charges Php1000, find the expected net gain from sample information.
- 2. 1. Consider the following payoff (profit) matrix. E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 A1 15 10 0 -6 17 A2 3 14 8 9 2 A3 1 5 14 20 -3 A4 7 19 10 2 0 No probabilities are known for the occurrence of the nature of states. Compare the solutions obtained by each of the following criteria: a. Laplace b. Maximin c. Savage Minimax Regret d. Hurwicz (α = 0.7) 2. The daily demand for loaves of bread in a grocery store can assume one of the following values: 100, 120, or 130 loaves with probabilities 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5. The owner of the store is thus limiting her alternatives to stocking one of the indicated three levels. If the stocks are more than she can sell in the same day, she must dispose of the remaining loaves at a discount price of 55 cents/loaf. Assuming that she pays 60 cents per loaf and sells it for $1.05, find the optimum stock level by using a decision tree representation. 3. Consider problem no. 2, suppose that the owner wishes to consider her decision problem over a 2-day period. Her alternatives for the second day are determined as follows. If the demand in day 1 is equal to the amount stocked, she will continue to order the same quantity on the second day. Otherwise, if the demand exceeds the amount stocked, she will have the options to order higher levels of stock on the second day. Finally, if day 1's demand is less than the amount stocked, she will have the options to order any of the lower levels of stock for the second day. Express the problem as a decision tree and find the optimum using the cost data in problem no. 2. 4. Pizza King and Noble Greek are two competing restaurants. Each must determine simultaneously whether to undertake small, medium, or large advertising campaigns. Pizza King believes that it is equally likely that Noble Greek will undertake a small, medium or large advertising campaign. Given the actions chosen by each restaurant, Pizza King’s profits are as shown in the table below. Noble Greek Chooses Pizza King Chooses Small Medium Large Small $6000 $5000 $2000 Medium $5000 $6000 $1000 Large $9000 $6000 $0 Determine Pizza King’s choice for advertising campaign using the following criteria: a) Laplace b) Maximin c) Minimax (assume given data are in terms of costs) d) Savage Minimax Regret e) Hurwicz (assume: α = 0.6) f) Suppose that Pizza King has assessed that probabilities that Noble Greek will undertake the above mentioned levels of advertising campaigns: P(S) = 0.25 P(M) = 0.40 P(L) = 0.35 What decision would be reached using Bayes' Rule? g) Find the expected profit using Perfect Information Source (EPPI).
- 3. h) Find the expected value of perfect information (EVPI). i) Suppose Pizza King acquires the services of a consulting firm, ABC Inc. ABC will conduct market study that will result in one of 2 outcomes. (1) O1 will be favorable indication of the market for the firm's products. (2) O2 will be unfavorable indication of the market for the firm's products. O1 and O2 are referred to as sample outcomes. The following conditional probabilities were arrived at from considerable ABC experience, using historical market research record in ABC's files and the statisticians' judgment. P(Oj/SI) Market Study Outcome Small Medium Large O1 0.05 0.30 0.70 O2 0.95 0.70 0.30 Find the posterior probabilities, expected payoff with sample information, and expected value of sample information If ABC charges $1,000, find the expected net gain from sample information. 5. Suppose that Pizza King and Noble Greek stop advertising but must determine the price they will charge for each pizza sold. Pizza King believes that Noble Greek’s price is a random variable D having the following mass function: P(D = $6) = 0.25, P(D = $8) = 0.50, P(D = $10) = 0.25. If Pizza King charges a price p1 and Noble Greek charges a price p2, Pizza King will sell 100 + 25(p2 – p1) pizzas. It costs Pizza King $4 to make a pizza. Pizza King is considering charging $5, $6, $7, $8, or $9 for a pizza. Use each decision criterion to determine the price that Pizza King should charge.
- 4. Sequential Decision Making The city of Metropolis is planning to construct a street that will run through the city perpendicular to the main east-west street. The city planners have to make a choice between a modern, wide (4- lane) street that would cost Php2M or a lesser-quality narrower street that would cost Php1M. We shall denote these two alternatives as W1 and N1. After 4 years, depending on whether the traffic on the street turns out to be light or heavy (LI or H1), the city will have the option of widening the street. The probability of these traffic conditions are estimated by city planners and economists as P(L1) = 0.25 and P(H1) = 0.75. If W1 is selected, maintenance expenses during the first 4 years will be Php5,000 or Php75,000 depending on whether the traffic is light or heavy. If N1 is selected, these costs are expected to be Php30,000 and Php150,000, respectively. Suppose street W1 is built then at the end of 4 years, no further work is required. If heavy traffic is experienced, either a minor or major repair must be made at costs of Php150,000 and Php200,000, respectively. If street N1 is built then at the end of 4 years, if traffic has been light, either a minor or major repair must be made at costs of Php50,000 and Php100,000, respectively. If traffic has been heavy, major repair must be made at a cost of Php900,000. Traffic during the next 6 years will be classified as light or heavy (L2 or H2). The probabilities of these two events, conditional on the traffic condition in years 1-4, are given as follows: P(L2/L1) = 0.75 P(L2/H1) = 0.10 P(H2/L1) = 0.25 P(H2/H1) = 0.90 Maintenance costs over years 5-10 will depend on which street was built in year 1, what type of repair was made at the end of year 4, and the amount of traffic during years 5-10. Street Repair Traffic Maintenance (Php) Year 1 Years 5-10 Year 5-10 W1 None L2 200,000 H2 250,000 Minor L2 150,000 H2 175,000 Major L2 125,000 H2 100,000 N1 Minor L2 200,000 H2 250,000 Major L2 175,000 H2 150,000 a) Construct a decision tree for this problem. b) Determine the optimal sequential strategy for the city of Metropolis
