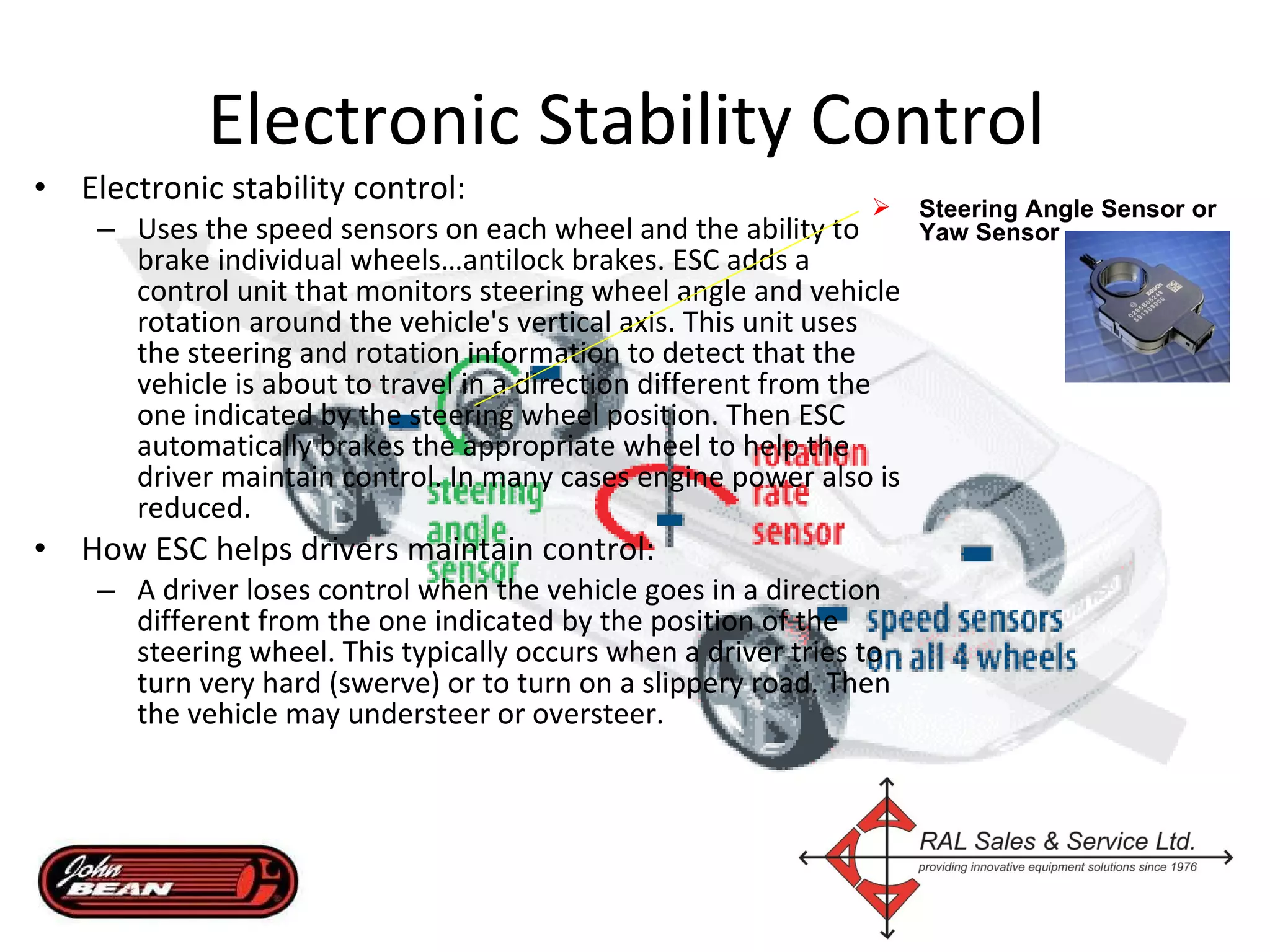
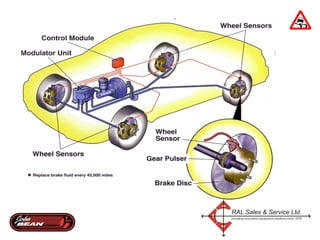
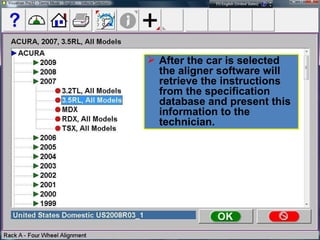
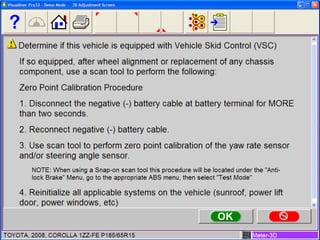
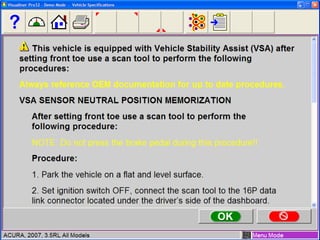
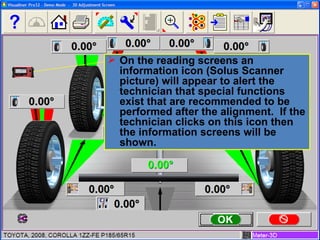
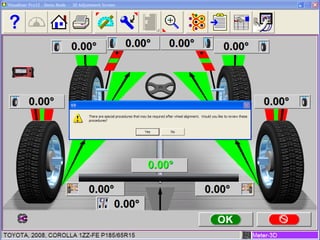
Electronic stability control uses sensors on each wheel and antilock brakes to monitor steering wheel angle and vehicle rotation. When it detects the vehicle may lose control, it automatically brakes wheels as needed and may reduce engine power to help the driver maintain stability, especially during hard turns or on slippery roads. Many vehicle manufacturers have their own names for electronic stability control systems, which will be required in all new vehicles by 2012. Using a scan tool during an alignment allows technicians to reset stability sensors and retrieve any trouble codes.