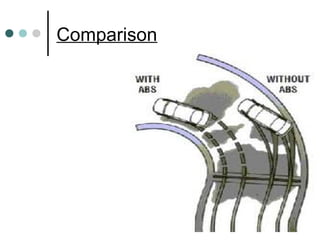
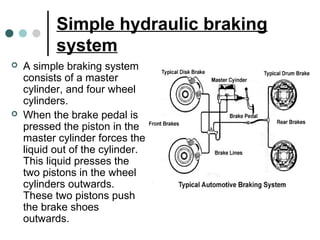
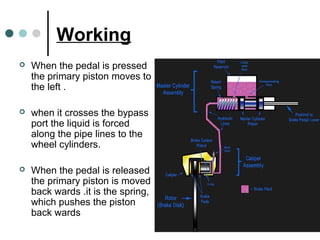
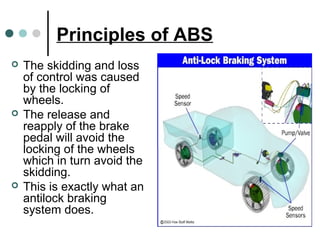
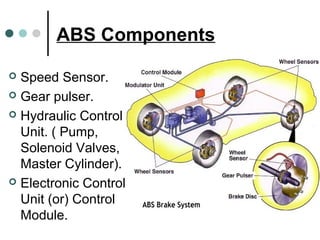
This document summarizes the key components and functioning of an antilock braking system (ABS). It describes how ABS uses electronic sensors and hydraulic controls to monitor wheel slip and modulate brake pressure to prevent locking during braking, improving vehicle stability and control. The key components of ABS are speed sensors, a gear pulser, hydraulic control unit, and electronic control unit. ABS cycling brake pressure up to 15 times per second to prevent wheel lockup and maintain steering ability during heavy braking.